lab1
... Catalyst are the substance that accelerate chemical reaction Organic catalyst (enzyme) 2 Mg,2 Cl-) Inorganic catalyst(Zn, Enzymes are proteins that catalyze (i.e., increase the rates of) chemical reactions Nearly all known enzymes are proteins in nature with the exception of certain RNA molecu ...
... Catalyst are the substance that accelerate chemical reaction Organic catalyst (enzyme) 2 Mg,2 Cl-) Inorganic catalyst(Zn, Enzymes are proteins that catalyze (i.e., increase the rates of) chemical reactions Nearly all known enzymes are proteins in nature with the exception of certain RNA molecu ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... The main goal of PSP is to model the free energy of the given amino acid chain and then to find minimum energy conformations. Experiment and theory show folding proceeds fairly directly to the native structure which is energetically very stable. The challenges in finding out the native (3D) structur ...
... The main goal of PSP is to model the free energy of the given amino acid chain and then to find minimum energy conformations. Experiment and theory show folding proceeds fairly directly to the native structure which is energetically very stable. The challenges in finding out the native (3D) structur ...
nature of polyethyleneimine-glucose oxidase interactions
... Based on the best docked energies: -5.8 and -4.5 kcal/mol, two sites were differentiated on the protein body, which show the best affinity to PEI (Table 1). In the first case, the ligand is bound to amino acids inside of the protein area (LIG1, Figure 5), while in the second case the binding takes p ...
... Based on the best docked energies: -5.8 and -4.5 kcal/mol, two sites were differentiated on the protein body, which show the best affinity to PEI (Table 1). In the first case, the ligand is bound to amino acids inside of the protein area (LIG1, Figure 5), while in the second case the binding takes p ...
What is Bioinformatics? is the application of computational techniques
... Textbook is written for senior/graduate level so problems at the end of the chapters are very hard We’ll split the text approximately in halve between: Chapters: 1- 6 will be covered in Computing for Bioinformatics I Chapter 1: Introduction Chapter 2: Algorithms and Complexity - some of this is writ ...
... Textbook is written for senior/graduate level so problems at the end of the chapters are very hard We’ll split the text approximately in halve between: Chapters: 1- 6 will be covered in Computing for Bioinformatics I Chapter 1: Introduction Chapter 2: Algorithms and Complexity - some of this is writ ...
Oxygen Radicals and Related Species
... because O2 has two unpaired electrons in the ground state, which makes it a triplet molecule (Figure 1A). In contrast, most organic molecules possess all electrons paired, being singlet in the ground state. To react with them, O2 has to receive a pair of electrons, but this requires spin inversion, ...
... because O2 has two unpaired electrons in the ground state, which makes it a triplet molecule (Figure 1A). In contrast, most organic molecules possess all electrons paired, being singlet in the ground state. To react with them, O2 has to receive a pair of electrons, but this requires spin inversion, ...
AP Biology Summer Assignment Chapter 3 Quiz 2016-17
... 19. Which statement regarding allosteric regulation is true? a. Allosteric regulation involves noncovalent binding but not covalent binding of regulator molecules to an enzyme. b. Shape changes in proteins cannot be transmitted across long distances, which means that allosteric sites must overlap wi ...
... 19. Which statement regarding allosteric regulation is true? a. Allosteric regulation involves noncovalent binding but not covalent binding of regulator molecules to an enzyme. b. Shape changes in proteins cannot be transmitted across long distances, which means that allosteric sites must overlap wi ...
Enzymes: Introduction
... coenzymes, derived from vitamins) for their catalytic activities. – Different cofactors are useful for different kinds of chemical reactions, including transfers of specific kinds of groups or transfers of electrons. • Kinetics: the study of reaction rates. Rates depend on rate constants. – Rate con ...
... coenzymes, derived from vitamins) for their catalytic activities. – Different cofactors are useful for different kinds of chemical reactions, including transfers of specific kinds of groups or transfers of electrons. • Kinetics: the study of reaction rates. Rates depend on rate constants. – Rate con ...
Word Document
... 2. Explain the cause of spectral lines and why they are different for each element. 1. What Period 2 element has exactly three p orbital electrons in its shell? ...
... 2. Explain the cause of spectral lines and why they are different for each element. 1. What Period 2 element has exactly three p orbital electrons in its shell? ...
Enzymes are NOT reactants!
... NOTE: Enzymes are NOT reactants! The reaction should still occur without itit just speeds it up. LOCK and KEY Model Each enzyme generally catalyzes one reaction, therefore enzymes are specific to a certain substrate the same way a key is specific to a lock. This is because the protein (the enzyme) h ...
... NOTE: Enzymes are NOT reactants! The reaction should still occur without itit just speeds it up. LOCK and KEY Model Each enzyme generally catalyzes one reaction, therefore enzymes are specific to a certain substrate the same way a key is specific to a lock. This is because the protein (the enzyme) h ...
Chapter 3
... ions, held together with six carboxylate groups of the chiral ligands and a bridging oxo oxygen, form a trinuclear subunit. These trinuclear units are interconnected through coordinative bonds between the zinc ions and pyridyl groups of 1, thereby generating two-dimensional (2D) infinite layers. (Fi ...
... ions, held together with six carboxylate groups of the chiral ligands and a bridging oxo oxygen, form a trinuclear subunit. These trinuclear units are interconnected through coordinative bonds between the zinc ions and pyridyl groups of 1, thereby generating two-dimensional (2D) infinite layers. (Fi ...
Structure of Tryptophan
... systems have been divesed. Of particular relevance among these are biochemical systems theory (BST) and metabolic control analysis (MCA). Within the framework of BST, optimization methods were developed for biochemical processes represented as S-systems, where S indicates the fact that these equati ...
... systems have been divesed. Of particular relevance among these are biochemical systems theory (BST) and metabolic control analysis (MCA). Within the framework of BST, optimization methods were developed for biochemical processes represented as S-systems, where S indicates the fact that these equati ...
Fig. 3
... issue, numerical modelling has been introduced in physiopathology and therapeutic research because of the decreasing innovation efficiency in therapeutics and the growing difficulties for physicians to make optimal treatment decision for a given patient through combining the many available modestly ef ...
... issue, numerical modelling has been introduced in physiopathology and therapeutic research because of the decreasing innovation efficiency in therapeutics and the growing difficulties for physicians to make optimal treatment decision for a given patient through combining the many available modestly ef ...
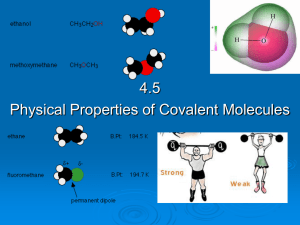
4.5 Physical properties of molecular covalent
... Covalent molecules are not charged because they are overall neutral and therefore do not conduct electricity. • Some covalent molecules can react with water and produce free ions which can carry an electrical current. • E.g. ammonia, NH3 NH3 (l) + H2O (l) ↔ NH4+ (aq) + OH- (aq) ...
... Covalent molecules are not charged because they are overall neutral and therefore do not conduct electricity. • Some covalent molecules can react with water and produce free ions which can carry an electrical current. • E.g. ammonia, NH3 NH3 (l) + H2O (l) ↔ NH4+ (aq) + OH- (aq) ...
Respiration of Glucose: The first stage of glucose metabolism is: is
... Respiration of Glucose: The first stage of glucose metabolism is: All steps are reversible except step #s ...
... Respiration of Glucose: The first stage of glucose metabolism is: All steps are reversible except step #s ...
IJCA 40A(6) 652-655
... of v(C=N) and ring breathing modes due to the ring nitrogen in the complex under study at 1601 and 1086 em·', respectively, (as compared to that of the free ligand at 1590 and 994 em·', respectively) is indicative of the coordination of this ligand through the ring nitrogen atom. DADPS complex The p ...
... of v(C=N) and ring breathing modes due to the ring nitrogen in the complex under study at 1601 and 1086 em·', respectively, (as compared to that of the free ligand at 1590 and 994 em·', respectively) is indicative of the coordination of this ligand through the ring nitrogen atom. DADPS complex The p ...
Enzymes POGIL 2014
... three different enzyme mutants. For each, one aspect of the active site's structure is slightly changed. The mutant enzymes are mixed with RNA in solution. The reaction rates are shown underneath each image. ...
... three different enzyme mutants. For each, one aspect of the active site's structure is slightly changed. The mutant enzymes are mixed with RNA in solution. The reaction rates are shown underneath each image. ...
The Origin and Evolution of Early Life
... From a chemical point of view, cells are roughly speaking aggregates of organic molecules large and small, mixed with water molecules and inorganic ions in a partially fluid state. Present day cells are thought to have derived from more primitive ones that had a roughly similar chemical composition. ...
... From a chemical point of view, cells are roughly speaking aggregates of organic molecules large and small, mixed with water molecules and inorganic ions in a partially fluid state. Present day cells are thought to have derived from more primitive ones that had a roughly similar chemical composition. ...
Reciprocal Linkage between Self-organizing Processes is Sufficient
... itself, replicates itself, and is capable of evolving.” However, many authors demand more explicit definitions that fill in details of these component processes with additional specifications. For example, Moreno (1998) defines a living organism as “a type of dissipative chemical structure which bui ...
... itself, replicates itself, and is capable of evolving.” However, many authors demand more explicit definitions that fill in details of these component processes with additional specifications. For example, Moreno (1998) defines a living organism as “a type of dissipative chemical structure which bui ...
KEY_Reaction Types WS
... Balance the Molecular Equation: In the “molecular” equation, nothing is broken up into ions. Salt formulas are written so that the cation charges exactly balance out the anion charges so that the salt is neutral. Then the equation is balanced for atoms. Balance the Total Ionic Equation: The first st ...
... Balance the Molecular Equation: In the “molecular” equation, nothing is broken up into ions. Salt formulas are written so that the cation charges exactly balance out the anion charges so that the salt is neutral. Then the equation is balanced for atoms. Balance the Total Ionic Equation: The first st ...
The Physiological Roles of Enzymes
... A. Enzymes use a variety of strategies to catalyze reactions, and individual enzymes often use more than one strategy. B. Substrate binding by an enzyme helps catalyze the reaction by bringing the reactants into proximity with the optimal orientation for reaction. C. Amino acid side chains within ac ...
... A. Enzymes use a variety of strategies to catalyze reactions, and individual enzymes often use more than one strategy. B. Substrate binding by an enzyme helps catalyze the reaction by bringing the reactants into proximity with the optimal orientation for reaction. C. Amino acid side chains within ac ...
Gluconeogenesis
... humans. In mammals, some tissues depend almost completely on glucose for their metabolic energy. The human brain alone requires 120 g of glucose each day, more than half of which is stored as glycogen in muscle and liver. ...
... humans. In mammals, some tissues depend almost completely on glucose for their metabolic energy. The human brain alone requires 120 g of glucose each day, more than half of which is stored as glycogen in muscle and liver. ...
Balancing RedOx reactions handout
... in the reduction half reaction equals the total number of electrons in the oxidation half 9. Add the two half reactions together and cancel those things (usually electrons, H2O, and H+) that are common to both sides. 10. Check the equation to be sure that the equation is balanced by atoms and by cha ...
... in the reduction half reaction equals the total number of electrons in the oxidation half 9. Add the two half reactions together and cancel those things (usually electrons, H2O, and H+) that are common to both sides. 10. Check the equation to be sure that the equation is balanced by atoms and by cha ...
! !! ! n nn N P =
... A. Energy can never be created or destroyed but it can be changed from one form to another. B. Two bodies in thermal contact are at thermal equilibrium with each other if the two bodies are at the same absolute temperature. C. Any process carried out in several steps, the overall ∆H is equal to the ...
... A. Energy can never be created or destroyed but it can be changed from one form to another. B. Two bodies in thermal contact are at thermal equilibrium with each other if the two bodies are at the same absolute temperature. C. Any process carried out in several steps, the overall ∆H is equal to the ...