Case Study Template 1
... The data suggest a coupling of SecA nucleotide occupancy to the opening of the SecY proteinchannel, with perturbations within SecY feeding back to SecA to regulate nucleotide exchange. The observations are supported using a FRET pair across the SecY lateral gate, and stopped-flow analyses of the rat ...
... The data suggest a coupling of SecA nucleotide occupancy to the opening of the SecY proteinchannel, with perturbations within SecY feeding back to SecA to regulate nucleotide exchange. The observations are supported using a FRET pair across the SecY lateral gate, and stopped-flow analyses of the rat ...
Enzymes How Do Enzymes Work?
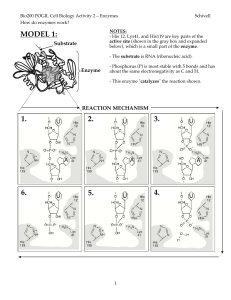
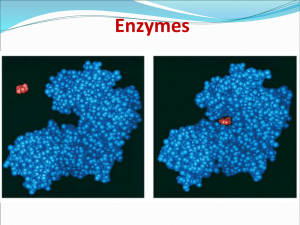
... Enzymes bind the substrate (reactants) in the active site. This is a cleft that is lined with an array of polar, non-polar, and charged amino acids arranged in such a way as to interact favorably, and selectively, with the substrate. ...
... Enzymes bind the substrate (reactants) in the active site. This is a cleft that is lined with an array of polar, non-polar, and charged amino acids arranged in such a way as to interact favorably, and selectively, with the substrate. ...
Practice Exam 3
... Which enzyme catalyzes a reaction in which NADH is produced? _____________________ Which enzyme converts G3P into 1,3 BPG? __________________________ Name two enzyme reactions from glycolysis that operate at G ≈ 0 _______________________ 8. Three reactions in glycolysis operate far from equilibrium ...
... Which enzyme catalyzes a reaction in which NADH is produced? _____________________ Which enzyme converts G3P into 1,3 BPG? __________________________ Name two enzyme reactions from glycolysis that operate at G ≈ 0 _______________________ 8. Three reactions in glycolysis operate far from equilibrium ...
Practice Exam 3 Answers
... Which enzyme catalyzes a reaction in which NADH is produced? _____________________ Which enzyme converts G3P into 1,3 BPG? __________________________ Name two enzyme reactions from glycolysis that operate at G ≈ 0 _______________________ 8. Three reactions in glycolysis operate far from equilibrium ...
... Which enzyme catalyzes a reaction in which NADH is produced? _____________________ Which enzyme converts G3P into 1,3 BPG? __________________________ Name two enzyme reactions from glycolysis that operate at G ≈ 0 _______________________ 8. Three reactions in glycolysis operate far from equilibrium ...
Computer modeling: Hyperchem tutorial
... 3. L-click the cursor on the workspace. A carbon atom will appear. (Make sure drawing tool is selected. R-click on the atom if you want to delete it) 4. Repeat (2) and choose oxygen instead of carbon. Move the cursor to the carbon centre and drag the mouse from the carbon centre to an empty workspac ...
... 3. L-click the cursor on the workspace. A carbon atom will appear. (Make sure drawing tool is selected. R-click on the atom if you want to delete it) 4. Repeat (2) and choose oxygen instead of carbon. Move the cursor to the carbon centre and drag the mouse from the carbon centre to an empty workspac ...
Rxn Types
... Single Displacement Reactions Not all single displacement reactions that can be written actually happen. The metal or non-metal must be more active than the ion it is replacing. It will depend upon the element’s Activity as ...
... Single Displacement Reactions Not all single displacement reactions that can be written actually happen. The metal or non-metal must be more active than the ion it is replacing. It will depend upon the element’s Activity as ...
Time
... -calculate rate of reactions using: r = Δc/Δt - explain the factors which effect reaction rates; predicting rate of reactions - concentration vs time graphs – instantaneous rate of reaction - use activation energy diagrams and kinetic energy diagrams to show effect of temperature and catalysts on re ...
... -calculate rate of reactions using: r = Δc/Δt - explain the factors which effect reaction rates; predicting rate of reactions - concentration vs time graphs – instantaneous rate of reaction - use activation energy diagrams and kinetic energy diagrams to show effect of temperature and catalysts on re ...
Review Questions for Advanced Biochemistry Course
... B. Succinate dehydrogenase is embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane C. Neither the single- or 2-electron forms of FAD dissociate from the enzyme D. Complex II transfers its electrons directly to cytochrome c ...
... B. Succinate dehydrogenase is embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane C. Neither the single- or 2-electron forms of FAD dissociate from the enzyme D. Complex II transfers its electrons directly to cytochrome c ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
Class3 POGIL Enzyme Mechanics Worksheet
... b. Which mutant helps to answer this question? ________ 14. When the transfer of a proton between the enzyme and substrate is prevented, is the reaction rate changed slightly or dramatically? __________ 15. Even if an R-group (that is part of the active site) does not normally accept or donate proto ...
... b. Which mutant helps to answer this question? ________ 14. When the transfer of a proton between the enzyme and substrate is prevented, is the reaction rate changed slightly or dramatically? __________ 15. Even if an R-group (that is part of the active site) does not normally accept or donate proto ...
Chapter 7 7 The Behavior of Proteins: Enzymes Mechanisms and
... also so se serves es as a positive (stimulatory) modulator, or activator; e.g., the binding g of aspartate p ((its substrate)) to ATCase. ((tends to be positive regulator) • hetero heterotropic tropic p effects: allosteric interactions that occur when different substances are bound to the protein; e ...
... also so se serves es as a positive (stimulatory) modulator, or activator; e.g., the binding g of aspartate p ((its substrate)) to ATCase. ((tends to be positive regulator) • hetero heterotropic tropic p effects: allosteric interactions that occur when different substances are bound to the protein; e ...
Systems Biology Solutions to Microarray Nightmare
... (B) Microarray experimental results can further restrict the models’ biological solutions. Step 2: All the possible solutions are compared and grouped in a 2D representation according to their common mechanistic patterns. By this clustering, it is possible to identify groups of similar outcomes. Alt ...
... (B) Microarray experimental results can further restrict the models’ biological solutions. Step 2: All the possible solutions are compared and grouped in a 2D representation according to their common mechanistic patterns. By this clustering, it is possible to identify groups of similar outcomes. Alt ...
Protein Family Classification with Neural Networks
... Our LSTM implementation achieved near perfect accuracy on the training set, so we attempted to decrease the hidden state size as a way to generalize the model further. During training we saw that the gap between training and validation was higher, so we attempted to decrease the dropout probability ...
... Our LSTM implementation achieved near perfect accuracy on the training set, so we attempted to decrease the hidden state size as a way to generalize the model further. During training we saw that the gap between training and validation was higher, so we attempted to decrease the dropout probability ...
Chapter 4 Quantities of Reactants and Products 4.1 Chemical
... The symbols “------->” or “=”, mean “forms”, “yields”, or “produces.” The reactants are the starting substances and the products are the substances formed. The following abbreviations indicate the phases of the reacting participants. gas =(___); liquid = (___); solid = (___); aqueous = (____) Combus ...
... The symbols “------->” or “=”, mean “forms”, “yields”, or “produces.” The reactants are the starting substances and the products are the substances formed. The following abbreviations indicate the phases of the reacting participants. gas =(___); liquid = (___); solid = (___); aqueous = (____) Combus ...
Allosteric Enzymes
... which results from noncovalent interaction among subunits. Hb and ATCase are examples of allosteric proteins where they exhibits cooperative effect • Positive cooperative refers to the fact that binding of low level of substrate facilitate the action of the protein at higher level of substrate ...
... which results from noncovalent interaction among subunits. Hb and ATCase are examples of allosteric proteins where they exhibits cooperative effect • Positive cooperative refers to the fact that binding of low level of substrate facilitate the action of the protein at higher level of substrate ...
A Survey of Recent Work on Evolutionary Approaches to the Protein
... mutation operators, but an inversion operator was added to establish genetic \linkage" between pairs of bits. This GA was recently used in the de novo design of a small peptide chain [16]. 2.4 Docking Docking problem solutions predict how two organic molecules will energetically and physically bind ...
... mutation operators, but an inversion operator was added to establish genetic \linkage" between pairs of bits. This GA was recently used in the de novo design of a small peptide chain [16]. 2.4 Docking Docking problem solutions predict how two organic molecules will energetically and physically bind ...
CSCI 2951G: Guide to the proteins Code
... specifies the equilibrium angle. The sixth parameter specifies the degree of the cosine function that contributes to the energy (check out the equation for energy from the first lecture). • VDW contains parameters for all the “nonbonded” interactions, which includes the Lennard-Jones potential and elec ...
... specifies the equilibrium angle. The sixth parameter specifies the degree of the cosine function that contributes to the energy (check out the equation for energy from the first lecture). • VDW contains parameters for all the “nonbonded” interactions, which includes the Lennard-Jones potential and elec ...
Enzyme Class
... which functions as a biological catalyst, speeding up reaction rate by lowering activation energy without being affected by the reaction it catalyse ...
... which functions as a biological catalyst, speeding up reaction rate by lowering activation energy without being affected by the reaction it catalyse ...
Polarizable molecules in the vibrational spectroscopy of water
... fluctuating charge and inducible dipole POL5–TZ (6) model. Both the three-site and four-site FQ models confine the charges to the molecular plane and do not allow for an out-of-plane polarization. The DC and POL5–TZ models, however, do allow the molecule to polarize out of the plane. All of the pote ...
... fluctuating charge and inducible dipole POL5–TZ (6) model. Both the three-site and four-site FQ models confine the charges to the molecular plane and do not allow for an out-of-plane polarization. The DC and POL5–TZ models, however, do allow the molecule to polarize out of the plane. All of the pote ...
Use of Amino Acid-Nucleotide Base Pair Potentials in Screening
... the protein-DNA structure is still difficult through the biochemistry experiment directly. Until January 5, 2013, there are over 87,000 structures deposited in the PDB (Protein Data Bank) [3], where the number of protein-NA structure is just almost 4,000. Hence, computational techniques such as prot ...
... the protein-DNA structure is still difficult through the biochemistry experiment directly. Until January 5, 2013, there are over 87,000 structures deposited in the PDB (Protein Data Bank) [3], where the number of protein-NA structure is just almost 4,000. Hence, computational techniques such as prot ...
Enzymes - CSUN Moodle
... • Kinetic mechanism: the order of binding of substrates and release of products • When two or more reactants are involved, enzyme kinetics allows to distinguish between different kinetic mechanisms – Sequential mechanism – Ping-Pong mechanism ...
... • Kinetic mechanism: the order of binding of substrates and release of products • When two or more reactants are involved, enzyme kinetics allows to distinguish between different kinetic mechanisms – Sequential mechanism – Ping-Pong mechanism ...
PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
... The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and the citric acid cycle enzymes exist in the matrix of the mitochondrion in eukaryotes Pyruvate in generated by glycolysis in the cytosol and needs to be moved into the mitochondria MITOCHONDRIAL STRUCTURE ...
... The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and the citric acid cycle enzymes exist in the matrix of the mitochondrion in eukaryotes Pyruvate in generated by glycolysis in the cytosol and needs to be moved into the mitochondria MITOCHONDRIAL STRUCTURE ...
Tutorial 3 (Ans Scheme) ERT 317, Sem 1 2015/2016
... The enzyme phosphoglycerokinase transfers a P from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to a molecule of ADP to form ATP. This happens for each molecule of 1,3bisphosphoglycerate. The process yields two 3-phosphoglycerate molecules and two ATP molecules. 2 molecules of 1,3-bisphoshoglycerate (C3H4O4P2) + phospho ...
... The enzyme phosphoglycerokinase transfers a P from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to a molecule of ADP to form ATP. This happens for each molecule of 1,3bisphosphoglycerate. The process yields two 3-phosphoglycerate molecules and two ATP molecules. 2 molecules of 1,3-bisphoshoglycerate (C3H4O4P2) + phospho ...