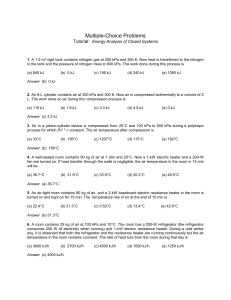
Multiple Choice Questions_1
... 6. A room contains 25 kg of air at 100 kPa and 10C. The room has a 250-W refrigerator (the refrigerator consumes 250 W of electricity when running) and 1-kW electric resistance heater. During a cold winter day, it is observed that both the refrigerator and the resistance heater are running continuo ...
... 6. A room contains 25 kg of air at 100 kPa and 10C. The room has a 250-W refrigerator (the refrigerator consumes 250 W of electricity when running) and 1-kW electric resistance heater. During a cold winter day, it is observed that both the refrigerator and the resistance heater are running continuo ...
P1_student_checklist 2016
... define specific heat capacity and understand that this measures the quantity of heat which a material can hold state and use the formula energy = mass x specific heat capacity x temperature change recognise that energy is being transferred when materials melt or boil although there is no change in t ...
... define specific heat capacity and understand that this measures the quantity of heat which a material can hold state and use the formula energy = mass x specific heat capacity x temperature change recognise that energy is being transferred when materials melt or boil although there is no change in t ...
smart power generation from waste heat by thermo electric generator
... energies are more attractive artificial to electricity generation, as it will also provide a pollution free and cost less. In this innovative project, we are using one device which is used to be created and introduced by human as a renewable energy that is thermo electric generator equipment to gene ...
... energies are more attractive artificial to electricity generation, as it will also provide a pollution free and cost less. In this innovative project, we are using one device which is used to be created and introduced by human as a renewable energy that is thermo electric generator equipment to gene ...
Slide 1
... g is heated to 125.0oC and then dropped into 375 g of water at 240.0oC. If the final temperature of the water is 34.2oC, what is the specific heat of the metal? When the metal enters the water, it begins to cool, losing heat to the water. At the same time, the temperature of the water rises. This pr ...
... g is heated to 125.0oC and then dropped into 375 g of water at 240.0oC. If the final temperature of the water is 34.2oC, what is the specific heat of the metal? When the metal enters the water, it begins to cool, losing heat to the water. At the same time, the temperature of the water rises. This pr ...
Section 16.3 ppt - Mrs. Graves Science
... In an internal combustion engine, the cooling system and exhaust transfer heat from the engine to the environment. Gasoline engines are more efficient than oldfashioned steam engines, but they still are not very efficient. About one third of the energy in a gasoline engine is converted to work. ...
... In an internal combustion engine, the cooling system and exhaust transfer heat from the engine to the environment. Gasoline engines are more efficient than oldfashioned steam engines, but they still are not very efficient. About one third of the energy in a gasoline engine is converted to work. ...
P3_U8doc - Port Fest Baltimore
... some of the torque delivered to the reduction gears by the engine is used to overcome friction in the drive train; thus the difference in BHP, SHP and DHP BHP-SHP = Line Losses numerically, HP = Torque (ft-lbs) x RPM ...
... some of the torque delivered to the reduction gears by the engine is used to overcome friction in the drive train; thus the difference in BHP, SHP and DHP BHP-SHP = Line Losses numerically, HP = Torque (ft-lbs) x RPM ...
study Heat tr and density SG 2013 14
... your answer to one place beyond the decimal (to the tenths place). Be sure your units are correct! Show formula and math work for credit. ...
... your answer to one place beyond the decimal (to the tenths place). Be sure your units are correct! Show formula and math work for credit. ...
Ch3_HeatTransfer_5
... film of fluid which remains stationary next to the barrier. This thin film of fluid is difficult to quantify, its characteristics depending upon complex conditions of turbulence and viscosity, but when dealing with thin high-conductance barriers it can sometimes be quite significant. ...
... film of fluid which remains stationary next to the barrier. This thin film of fluid is difficult to quantify, its characteristics depending upon complex conditions of turbulence and viscosity, but when dealing with thin high-conductance barriers it can sometimes be quite significant. ...
Heat Transfer
... insulating jacket since we assume the air space between it and the cup insulates it well, so that its temperature does not change significantly.) The final temperature of the system is 30.5°C. Calculate the specific heat of the alloy. ...
... insulating jacket since we assume the air space between it and the cup insulates it well, so that its temperature does not change significantly.) The final temperature of the system is 30.5°C. Calculate the specific heat of the alloy. ...
(C, ° F ) u = internal energy (J/kg, Btu
... Makes noise Affects comfort Affects indoor air quality ...
... Makes noise Affects comfort Affects indoor air quality ...
Heat - Ms. Bergman`s Classes at DCIS Montbello
... • In this investigation you are expected to – Answer all questions on your lab sheet – Complete both parts of the investigation – Contribute to your groups understanding of heat ...
... • In this investigation you are expected to – Answer all questions on your lab sheet – Complete both parts of the investigation – Contribute to your groups understanding of heat ...
electrically conductive grease 57000
... AOS CONDUCTIVE GREASE is a NON-SILICONE-based, chemically inert heat sink compound that is thermally stable and nonflammable. This advanced grease offers premium electrical and thermal conductivity. ...
... AOS CONDUCTIVE GREASE is a NON-SILICONE-based, chemically inert heat sink compound that is thermally stable and nonflammable. This advanced grease offers premium electrical and thermal conductivity. ...
Energy Worksheet - MICDS Intranet Menu
... A 5.0 kilogram block of ice at -10.0oC is placed in a container of warm water. The entire block of ice is warmed to 0.0oC, and 4.0 kilograms of ice remains unmelted. At this point, how many joules were transferred from the warm water completely? q = mct = 5000gr x 2.09 J/gr oC x (-10oC - 0oC) = - 10 ...
... A 5.0 kilogram block of ice at -10.0oC is placed in a container of warm water. The entire block of ice is warmed to 0.0oC, and 4.0 kilograms of ice remains unmelted. At this point, how many joules were transferred from the warm water completely? q = mct = 5000gr x 2.09 J/gr oC x (-10oC - 0oC) = - 10 ...
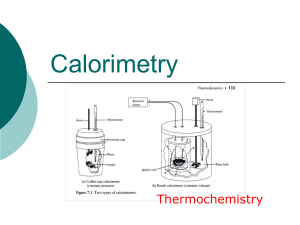
Thermochemistry - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... one another (insulation), then filled with a specific quantity of water and covered with another cup as a cover. A chemical reaction or phase change takes place inside and a thermometer is placed within to measure any change in temperature that occurs to the system. ...
... one another (insulation), then filled with a specific quantity of water and covered with another cup as a cover. A chemical reaction or phase change takes place inside and a thermometer is placed within to measure any change in temperature that occurs to the system. ...
Specific heat
... properties of a thermodynamic system such as temperature, specific heat, and pressure are related to the molecular level of matter, including kinetic or potential energy of atoms ...
... properties of a thermodynamic system such as temperature, specific heat, and pressure are related to the molecular level of matter, including kinetic or potential energy of atoms ...
Radiant Barrier Training 7-2013 - Fi-Foil
... materials and reradiated to the mass insulation and ceiling below. Attic air temperatures climb to superheated levels…typically 140 degrees Fahrenheit in the summer. Radiant heat transfers into air conditioning ducts increasing energy costs. Attic structure and contents saturate and continue to tran ...
... materials and reradiated to the mass insulation and ceiling below. Attic air temperatures climb to superheated levels…typically 140 degrees Fahrenheit in the summer. Radiant heat transfers into air conditioning ducts increasing energy costs. Attic structure and contents saturate and continue to tran ...
Heat
... There are a few problems that deal with heat: – Heat as enthalpy – Specific heat – Heat of fusion – Heat of vaporization ...
... There are a few problems that deal with heat: – Heat as enthalpy – Specific heat – Heat of fusion – Heat of vaporization ...
Physics 1a Revision Higher - School
... Electricity can be generated from several different resources such as wind, water, fossil fuels, light, biomass and nuclear. Some are renewable (can be used again) and other are non renewable. Fossil fuels are fuels which were made from plants and animals that lived millions of years ago. Examples o ...
... Electricity can be generated from several different resources such as wind, water, fossil fuels, light, biomass and nuclear. Some are renewable (can be used again) and other are non renewable. Fossil fuels are fuels which were made from plants and animals that lived millions of years ago. Examples o ...
Lesson
... 5. Go to your lab station and gently stir the water. Wait a few minutes for both the water and metal to reach a common temperature and record it. a. Why do we stir the cup? _________________________________ b. Why do we cover the cup?________________________________ 6. Repeat for the other metal. I ...
... 5. Go to your lab station and gently stir the water. Wait a few minutes for both the water and metal to reach a common temperature and record it. a. Why do we stir the cup? _________________________________ b. Why do we cover the cup?________________________________ 6. Repeat for the other metal. I ...
1 - Southwest High School
... 2.) A 5 g sample of metal with a specific heat of 350 c / g oC is heated and the temperature changes by 10 oC. How much heat does the material gain? In this question, what is the unknown variable? __________ In this question, what is the value for m ? __________ In this question, what is the value f ...
... 2.) A 5 g sample of metal with a specific heat of 350 c / g oC is heated and the temperature changes by 10 oC. How much heat does the material gain? In this question, what is the unknown variable? __________ In this question, what is the value for m ? __________ In this question, what is the value f ...
Cogeneration

Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time. Trigeneration or combined cooling, heat and power (CCHP) refers to the simultaneous generation of electricity and useful heating and cooling from the combustion of a fuel or a solar heat collector. Cogeneration is a thermodynamically efficient use of fuel. In separate production of electricity, some energy must be discarded as waste heat, but in cogeneration this thermal energy is put to use. All thermal power plants emit heat during electricity generation, which can be released into the natural environment through cooling towers, flue gas, or by other means. In contrast, CHP captures some or all of the by-product for heating, either very close to the plant, or—especially in Scandinavia and Eastern Europe—as hot water for district heating with temperatures ranging from approximately 80 to 130 °C. This is also called combined heat and power district heating (CHPDH). Small CHP plants are an example of decentralized energy. By-product heat at moderate temperatures (100–180 °C, 212–356 °F) can also be used in absorption refrigerators for cooling.The supply of high-temperature heat first drives a gas or steam turbine-powered generator and the resulting low-temperature waste heat is then used for water or space heating as described in cogeneration. At smaller scales (typically below 1 MW) a gas engine or diesel engine may be used. Trigeneration differs from cogeneration in that the waste heat is used for both heating and cooling, typically in an absorption refrigerator. CCHP systems can attain higher overall efficiencies than cogeneration or traditional power plants. In the United States, the application of trigeneration in buildings is called building cooling, heating and power (BCHP). Heating and cooling output may operate concurrently or alternately depending on need and system construction.Cogeneration was practiced in some of the earliest installations of electrical generation. Before central stations distributed power, industries generating their own power used exhaust steam for process heating. Large office and apartment buildings, hotels and stores commonly generated their own power and used waste steam for building heat. Due to the high cost of early purchased power, these CHP operations continued for many years after utility electricity became available.