Thermal concepts - Uplift North Hills Prep
... the links between the macroscopic measurements essential to many scientific models with the microscopic properties that underlie these models. Nature of science: Evidence through experimentation: Scientists from the 17th and 18th centuries were working without the knowledge of atomic structure and s ...
... the links between the macroscopic measurements essential to many scientific models with the microscopic properties that underlie these models. Nature of science: Evidence through experimentation: Scientists from the 17th and 18th centuries were working without the knowledge of atomic structure and s ...
Energy PP
... Thermal Energy – the total amount of internal energy for all the atoms of a substance Temperature – the average moving energy of the atoms of a substance Heat – the thermal energy that is transferred between objects that have different temperatures (high concentration to low concentration) ...
... Thermal Energy – the total amount of internal energy for all the atoms of a substance Temperature – the average moving energy of the atoms of a substance Heat – the thermal energy that is transferred between objects that have different temperatures (high concentration to low concentration) ...
Thermodynamics Exam 1 Info/Problems
... Crosse winter day, it will probably become much colder than 0 C. Ice may be able to exist at temperatures above that, but certainly not at atmospheric pressure (and probably not much warmer, in any event). 25. The air in the middle of the two panes acts as an insulator, adding to your overall “R” v ...
... Crosse winter day, it will probably become much colder than 0 C. Ice may be able to exist at temperatures above that, but certainly not at atmospheric pressure (and probably not much warmer, in any event). 25. The air in the middle of the two panes acts as an insulator, adding to your overall “R” v ...
- Uponorpro.com
... the strategies used in forcedair systems are not necessarily applicable for radiant systems. The way in which energy is evaluated and managed is on a more finite level with radiant systems. The temperature in one room will not impact the temperature in the next room. This is why it is easier and les ...
... the strategies used in forcedair systems are not necessarily applicable for radiant systems. The way in which energy is evaluated and managed is on a more finite level with radiant systems. The temperature in one room will not impact the temperature in the next room. This is why it is easier and les ...
Heat and Thermodynamics
... loss through the wall of a house, the rate of conduction heat transfer is: ...
... loss through the wall of a house, the rate of conduction heat transfer is: ...
Unit 1, Lecture 3 - Massey University
... transfer of energy by heat in thermal processes and the transfer of energy by work in mechanical processes Although Q and W each are dependent on the path, Q + W is independent of the path. Neither can be determined solely by the end points of a thermodynamic process The concept of energy was genera ...
... transfer of energy by heat in thermal processes and the transfer of energy by work in mechanical processes Although Q and W each are dependent on the path, Q + W is independent of the path. Neither can be determined solely by the end points of a thermodynamic process The concept of energy was genera ...
• Heating foods • Moist-heat method • Dry
... in moist-heat methods, because water can be heated only to its boiling point of 100oC, or slightly higher under pressure, whereas ovens can reach up to 260oC • Examples of dry-heat method include baking, roasting, broiling, grilling, barbequing, rotisserie cooking, stir frying, shallow frying, and d ...
... in moist-heat methods, because water can be heated only to its boiling point of 100oC, or slightly higher under pressure, whereas ovens can reach up to 260oC • Examples of dry-heat method include baking, roasting, broiling, grilling, barbequing, rotisserie cooking, stir frying, shallow frying, and d ...
heat
... system is allowed to reach a final intermediate temperature. Heat lost by hot object = Heat gained by cold water Cs material (mass)material (Tfinal-Tinitial)material = Cs water (mass)water (Tfinal-Tinitial)water ...
... system is allowed to reach a final intermediate temperature. Heat lost by hot object = Heat gained by cold water Cs material (mass)material (Tfinal-Tinitial)material = Cs water (mass)water (Tfinal-Tinitial)water ...
Lesson 3 - School Web Link
... Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly completes each sentence. Some terms may be used more than once or not at all. ...
... Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly completes each sentence. Some terms may be used more than once or not at all. ...
Temperature, Heat, and Expansion
... increase. If a total mass of 11.5 kg falls 1.3 m and all of the mechanical energy is converted to internal energy, by how much will the internal energy of the water increase? (Assume no energy is transferred as heat out of the vessel to the surroundings or from the surroundings to the vessel’s inter ...
... increase. If a total mass of 11.5 kg falls 1.3 m and all of the mechanical energy is converted to internal energy, by how much will the internal energy of the water increase? (Assume no energy is transferred as heat out of the vessel to the surroundings or from the surroundings to the vessel’s inter ...
Kémiai technológia I
... 11. Mixing of liquid as a problem of the flow around immersed object. Differential equation of force for impellers. Power consumption of stirrer. (MSH pp. 244-) 12. Definition of heat and temperature. Units of heat and temperature. Definition of specific heat and heat capacity and latent heat. Heat ...
... 11. Mixing of liquid as a problem of the flow around immersed object. Differential equation of force for impellers. Power consumption of stirrer. (MSH pp. 244-) 12. Definition of heat and temperature. Units of heat and temperature. Definition of specific heat and heat capacity and latent heat. Heat ...
Chapter 6 Thermal Energy
... If no heat flows across the boundary and there is no outside work done, then the system is a closed system. The thermal energy of a closed system doesn’t change. Because energy cannot be created or destroyed, the total energy stays constant in a closed system. ...
... If no heat flows across the boundary and there is no outside work done, then the system is a closed system. The thermal energy of a closed system doesn’t change. Because energy cannot be created or destroyed, the total energy stays constant in a closed system. ...
Science Unit 5 Powerpoint 2 Energy
... For example, suppose you place an ice cube in a glass of water. Because the water is warmer than the ice, heat flows from the water to the ice until the two reach the same temperature. Heat does not flow from the ice to the water. ...
... For example, suppose you place an ice cube in a glass of water. Because the water is warmer than the ice, heat flows from the water to the ice until the two reach the same temperature. Heat does not flow from the ice to the water. ...
Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection and Latent Heat In addition
... The exchanges of energy by radiation, conduction, convection and latent heat can be quite complex, but in the end they all balance ...
... The exchanges of energy by radiation, conduction, convection and latent heat can be quite complex, but in the end they all balance ...
Lecture 32 - PhysicsGivesYouWings
... – For monatomic ideal gas: – For cold diatomic ideal gas: – For hot diatomic ideal gas: M. Afshar ...
... – For monatomic ideal gas: – For cold diatomic ideal gas: – For hot diatomic ideal gas: M. Afshar ...
Document
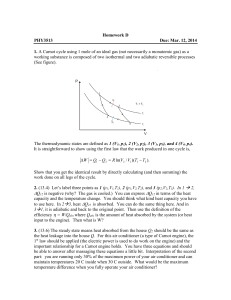
... Show that you get the identical result by directly calculating (and then summing) the work done on all legs of the cycle. 2. (13.4) Let’s label three points as 1 (p1,V1,T1), 2 (p1,V2,T2), and 3 (p2,V2,T3). In 1 2, ∆Q12 is negative (why? The gas is cooled.) You can express ∆Q12 in terms of the heat ...
... Show that you get the identical result by directly calculating (and then summing) the work done on all legs of the cycle. 2. (13.4) Let’s label three points as 1 (p1,V1,T1), 2 (p1,V2,T2), and 3 (p2,V2,T3). In 1 2, ∆Q12 is negative (why? The gas is cooled.) You can express ∆Q12 in terms of the heat ...
Phase Changes
... 5. How much heat is absorbed by 550g block of ice to raise the temperature from -15 to 0C? 6. How much heat energy must be absorbed to raise the temperature of a 200 gram block of ice from -10 to 0C and then completely melt it to a liquid at the same temperature? 7. How much energy would be required ...
... 5. How much heat is absorbed by 550g block of ice to raise the temperature from -15 to 0C? 6. How much heat energy must be absorbed to raise the temperature of a 200 gram block of ice from -10 to 0C and then completely melt it to a liquid at the same temperature? 7. How much energy would be required ...







![科目名 Course Title Thermal Engineering [熱工学E] 講義題目 Subtitle](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022970293_1-8d5861074e83e836baec8d9b5d560a01-300x300.png)