Severe combined immune deficiency syndrome
... 8. Infections that do not resolve with antibiotic treatment for two or more months 9. Failure to gain weight or grow normally 10. Infections that require intravenous antibiotic treatment 11. Deep-seated infections, such as pneumonia that affects an entire lung or an abscess in the liver 12. Persiste ...
... 8. Infections that do not resolve with antibiotic treatment for two or more months 9. Failure to gain weight or grow normally 10. Infections that require intravenous antibiotic treatment 11. Deep-seated infections, such as pneumonia that affects an entire lung or an abscess in the liver 12. Persiste ...
prrs_3_pathogenesis
... The target cells in which PRRSV replicates are subsets of macrophages that have specific glycoprotein receptors for the virus. These include pulmonary alveolar and interstitial macrophages and macrophages in lymphoid tissues. In order for replication to take place maturity and/or activation are requ ...
... The target cells in which PRRSV replicates are subsets of macrophages that have specific glycoprotein receptors for the virus. These include pulmonary alveolar and interstitial macrophages and macrophages in lymphoid tissues. In order for replication to take place maturity and/or activation are requ ...
File
... Vaccination is the injection of a weakened or mild form of a pathogen to cause immunity. Active immunity results from vaccines or natural exposure to an antigen. Passive immunity forms when antibodies are introduced into the body. It lasts only until the immune system destroys the foreign antibodies ...
... Vaccination is the injection of a weakened or mild form of a pathogen to cause immunity. Active immunity results from vaccines or natural exposure to an antigen. Passive immunity forms when antibodies are introduced into the body. It lasts only until the immune system destroys the foreign antibodies ...
Introduction to the MRC Centre for Inflammation Research video
... My team is focussed on infectious diseases caused by viruses and bacteria. We are interested in how the cells in our bodies respond to infection and the molecules they produce at the earlier stages. In particular we are interested in molecules called antimicrobial peptides which can kill infectious ...
... My team is focussed on infectious diseases caused by viruses and bacteria. We are interested in how the cells in our bodies respond to infection and the molecules they produce at the earlier stages. In particular we are interested in molecules called antimicrobial peptides which can kill infectious ...
Science alone cannot win the battle against infectious diseases
... for research into drugs for infectious diseases are still feeble compared with those for the chronic diseases of affluence. Nevertheless, funds have risen from historic lows, and methods for combating drug resistance and preventing the spread of infection are being debated at the highest levels. It ...
... for research into drugs for infectious diseases are still feeble compared with those for the chronic diseases of affluence. Nevertheless, funds have risen from historic lows, and methods for combating drug resistance and preventing the spread of infection are being debated at the highest levels. It ...
Pathogens unit review
... b. How do bacteria become antibiotic resistant (at the microbe and at the human level)? ...
... b. How do bacteria become antibiotic resistant (at the microbe and at the human level)? ...
May 13, 2015
... myeloma. The data being presented relates to the phenotypic and functional evaluation of the engineered T cells administered to patients and the data may suggest that the engineered autologous T cells administered can expand and persist in patients without exhibiting signs of T cell exhaustion. Yoav ...
... myeloma. The data being presented relates to the phenotypic and functional evaluation of the engineered T cells administered to patients and the data may suggest that the engineered autologous T cells administered can expand and persist in patients without exhibiting signs of T cell exhaustion. Yoav ...
Autoimmunity 3rd yr
... These are not seen by the developing immune system – will not induce selftolerance. Exposure of T cells to these normally sequestered/tissue-specific self-antigens in the periphery results in their activation ...
... These are not seen by the developing immune system – will not induce selftolerance. Exposure of T cells to these normally sequestered/tissue-specific self-antigens in the periphery results in their activation ...
Infectious Diseases and Disease Processes
... Disease may be defined as abnormality of the structure or function of a part, organ, or system. Disease may be of known or unknown causes and may show marked variation in severity and effects on an individual ...
... Disease may be defined as abnormality of the structure or function of a part, organ, or system. Disease may be of known or unknown causes and may show marked variation in severity and effects on an individual ...
prevention of infectious diseases, emerging food-, water
... Despite the spectacular progress of modern medicine, infectious diseases remain a global threat for public health. Poverty-related and neglected diseases are of high relevance to the present call due to their high burden in the LAC region. Emerging food, water and vector-borne diseases still have hi ...
... Despite the spectacular progress of modern medicine, infectious diseases remain a global threat for public health. Poverty-related and neglected diseases are of high relevance to the present call due to their high burden in the LAC region. Emerging food, water and vector-borne diseases still have hi ...
Sex affects health - University of San Francisco (USF)
... Interleukin-1-receptor-II (reduces the inflammatory response), is present in higher concentration in men than women ...
... Interleukin-1-receptor-II (reduces the inflammatory response), is present in higher concentration in men than women ...
06-Understanding Stress and Disease
... • Human Immunodeficiency Virus • Destroys the T-cells in the immune system ...
... • Human Immunodeficiency Virus • Destroys the T-cells in the immune system ...
Bacteria vs. Viruses
... Responses 1. The second time you are infected by a pathogen (foreign invader), your immune system works faster to fight it. WHY? ...
... Responses 1. The second time you are infected by a pathogen (foreign invader), your immune system works faster to fight it. WHY? ...
Immunology Worksheet Allergy
... A Read and fill the gaps. The principal role of the immune system _____(1) to defend the body against possible infections by discriminating between self and non-self. The immune system has evolved over millions of years to respond and destroy any organisms _____(2) have gained entry into the body. T ...
... A Read and fill the gaps. The principal role of the immune system _____(1) to defend the body against possible infections by discriminating between self and non-self. The immune system has evolved over millions of years to respond and destroy any organisms _____(2) have gained entry into the body. T ...
Ocular Autoimmune Disease: An Introduction
... (inflammation). In most instances, this collaboration between ophthalmologist and chemotherapist works very well, and our experience in helping ophthalmologists to establish such collaborations and to effectively treat patients with autoimmune diseases affecting the eye has been gratifyingly success ...
... (inflammation). In most instances, this collaboration between ophthalmologist and chemotherapist works very well, and our experience in helping ophthalmologists to establish such collaborations and to effectively treat patients with autoimmune diseases affecting the eye has been gratifyingly success ...
Chapter One Concept Checks
... 3. Highly specific molecules that act as antibodies. They combine with antigens to neutralize them. ____________ 4. Lymphocytes that operate within the humoral part of the system and circulate in the blood and bodily fluids. ____________ 5. These are created so that when a specific antigen is encoun ...
... 3. Highly specific molecules that act as antibodies. They combine with antigens to neutralize them. ____________ 4. Lymphocytes that operate within the humoral part of the system and circulate in the blood and bodily fluids. ____________ 5. These are created so that when a specific antigen is encoun ...
Jeannie Taylor Microbiology Due: 11/15/2013 Assignment #7
... blood cells that expressed a protein called CD71+. These cells suppress the immune response by making an enzyme called arginase. Way and his colleagues then gave the baby mice antibodies that caused the immune system to destroy the CD71+ cells and remove them form the animals’ blood. These mice were ...
... blood cells that expressed a protein called CD71+. These cells suppress the immune response by making an enzyme called arginase. Way and his colleagues then gave the baby mice antibodies that caused the immune system to destroy the CD71+ cells and remove them form the animals’ blood. These mice were ...
Bio07_TR__U10_CH40.QXD
... functions. Types of pathogens include viruses, bacteria, protists, worms, and fungi. Infectious diseases can be transmitted in several ways. Many are spread from one person to another through coughing, sneezing, or physical contact. Some are spread through contaminated water or food. Others are spre ...
... functions. Types of pathogens include viruses, bacteria, protists, worms, and fungi. Infectious diseases can be transmitted in several ways. Many are spread from one person to another through coughing, sneezing, or physical contact. Some are spread through contaminated water or food. Others are spre ...
File - The Building Blocks For Learning
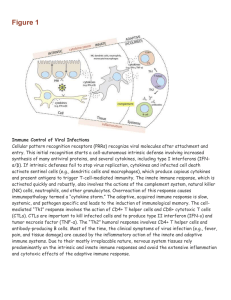
... Cellular pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) recognize viral molecules after attachment and entry. This initial recognition starts a cell-autonomous intrinsic defense involving increased synthesis of many antiviral proteins, and several cytokines, including type I interferons (IFNα/β). If intrinsic ...
... Cellular pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) recognize viral molecules after attachment and entry. This initial recognition starts a cell-autonomous intrinsic defense involving increased synthesis of many antiviral proteins, and several cytokines, including type I interferons (IFNα/β). If intrinsic ...
06-Understanding Stress and Disease
... • HIV destroys immune system - AIDS vulnerable to bacterial, viral, and other diseases ...
... • HIV destroys immune system - AIDS vulnerable to bacterial, viral, and other diseases ...
The Immune System
... Infectious Disease • Diseases caused by pathogens that can be transmitted from one individual to another are called infectious diseases. • Methods of transmittal include: ▫ coughing ▫ Sneezing ▫ Contaminated food or water ...
... Infectious Disease • Diseases caused by pathogens that can be transmitted from one individual to another are called infectious diseases. • Methods of transmittal include: ▫ coughing ▫ Sneezing ▫ Contaminated food or water ...