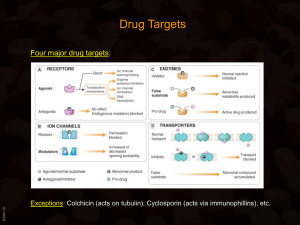
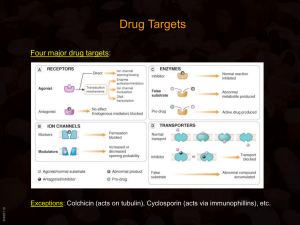
Physiologic factors related to drug absorption
... are more lipid soluble have a larger value of K The surface area, A, of the membrane also influences the rate of absorption. Drugs may be absorbed from most areas of the gastrointestinal tract. However, the duodenal area of the small intestine shows the most rapid drug absorption, due to such anat ...
... are more lipid soluble have a larger value of K The surface area, A, of the membrane also influences the rate of absorption. Drugs may be absorbed from most areas of the gastrointestinal tract. However, the duodenal area of the small intestine shows the most rapid drug absorption, due to such anat ...
C - ISpatula
... withstand large amounts of wear and tear, for example the inside of the mouth and oesophagus, and the vagina. In the skin the outer cells become filled with keratin, and then die and slough off from the outside. This type of epithelium is ...
... withstand large amounts of wear and tear, for example the inside of the mouth and oesophagus, and the vagina. In the skin the outer cells become filled with keratin, and then die and slough off from the outside. This type of epithelium is ...
C - ISpatula
... withstand large amounts of wear and tear, for example the inside of the mouth and oesophagus, and the vagina. In the skin the outer cells become filled with keratin, and then die and slough off from the outside. This type of epithelium is ...
... withstand large amounts of wear and tear, for example the inside of the mouth and oesophagus, and the vagina. In the skin the outer cells become filled with keratin, and then die and slough off from the outside. This type of epithelium is ...
Unit 2
... down their concentration gradients. Specialized membrane proteins transmit extracellular signals to the inside of the cell. 8. Describe factors that affect selective permeability of membranes. Factors that affect selective permeability of membranes include: * the hydrophobic core of the membrane * t ...
... down their concentration gradients. Specialized membrane proteins transmit extracellular signals to the inside of the cell. 8. Describe factors that affect selective permeability of membranes. Factors that affect selective permeability of membranes include: * the hydrophobic core of the membrane * t ...
Wednesday, September 20, 2006
... 2. Transport proteins can be saturated therefore, they have a maximum rate of moving stuff due to limited # of proteins within membrane 3. Transport proteins can be inhibited 4. ‘Catalyze’ physical movement of stuff that would not be able to cross membrane B. Molecules move down concentration gradie ...
... 2. Transport proteins can be saturated therefore, they have a maximum rate of moving stuff due to limited # of proteins within membrane 3. Transport proteins can be inhibited 4. ‘Catalyze’ physical movement of stuff that would not be able to cross membrane B. Molecules move down concentration gradie ...
Unit 2
... substances across a membrane down their concentration gradients. 20. Explain how large molecules are transported across the cell membrane. Large molecules are transported across the cell membrane through exocytosis and endocytosis. Exocytosis: transport vesicles migrate to the plasma membrane, fuse ...
... substances across a membrane down their concentration gradients. 20. Explain how large molecules are transported across the cell membrane. Large molecules are transported across the cell membrane through exocytosis and endocytosis. Exocytosis: transport vesicles migrate to the plasma membrane, fuse ...
11 Signal Transduction
... • Each TK adds a phosphate from an ATP to a tyrosine on the tail of the other polypeptide • The receptor is fully activated as a result ...
... • Each TK adds a phosphate from an ATP to a tyrosine on the tail of the other polypeptide • The receptor is fully activated as a result ...
Cell Biology
... • Most diverse and complex macromolecules in the cell • Used for structure, function and information • Made of linearly arranged amino acid residues – “folded” up with “active” regions ...
... • Most diverse and complex macromolecules in the cell • Used for structure, function and information • Made of linearly arranged amino acid residues – “folded” up with “active” regions ...
Cell Transport 2016 - Waterford Public Schools
... Example: water in blood forced out through capillaries , but blood cells and large particles in the plasma remain inside. -------------------------------------------------------------------------Example: Kidneys- pressure forces solute from the blood across a membrane and into the nephron ...
... Example: water in blood forced out through capillaries , but blood cells and large particles in the plasma remain inside. -------------------------------------------------------------------------Example: Kidneys- pressure forces solute from the blood across a membrane and into the nephron ...
Cell structure Part 1
... the outside and inside of the membrane. This allows the integral proteins to act as transport channels. Fluid mosaic modelUsed to describe the cell membrane. Phospholipidshas a polar and nonpolar end. The polar end likes water and the nonpolar end hates water. ...
... the outside and inside of the membrane. This allows the integral proteins to act as transport channels. Fluid mosaic modelUsed to describe the cell membrane. Phospholipidshas a polar and nonpolar end. The polar end likes water and the nonpolar end hates water. ...
cell membrane
... Cell Membrane Regulates passage of materials into and out of the cell Parts of the membrane: A) lipid bilayer (2 layers) B) proteins C) cholesterol D) carbohydrate chains copyright cmassengale ...
... Cell Membrane Regulates passage of materials into and out of the cell Parts of the membrane: A) lipid bilayer (2 layers) B) proteins C) cholesterol D) carbohydrate chains copyright cmassengale ...
Publications de l`équipe
... Exosome secretion: molecular mechanisms and roles in immune responses. Traffic (Copenhagen, Denmark) : 1659-68 : DOI : 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01225.x ...
... Exosome secretion: molecular mechanisms and roles in immune responses. Traffic (Copenhagen, Denmark) : 1659-68 : DOI : 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01225.x ...
Nobel Prize for of Cholesterol
... working hard to ensure that the Congress is highly successful and hopes to welcome a large number of physiologists from all over the world to Vancouver in 1986. For further information write to IUPS Secretariat, ...
... working hard to ensure that the Congress is highly successful and hopes to welcome a large number of physiologists from all over the world to Vancouver in 1986. For further information write to IUPS Secretariat, ...
Transport Proteins
... – _____________________, the control of water balance, is a necessary adaptation for life in such environments – The protist Paramecium, which is hypertonic to its pond water environment, has a contractile vacuole that acts as a pump • Water Balance of Cells with Walls – __________________ help main ...
... – _____________________, the control of water balance, is a necessary adaptation for life in such environments – The protist Paramecium, which is hypertonic to its pond water environment, has a contractile vacuole that acts as a pump • Water Balance of Cells with Walls – __________________ help main ...
Signaling-dependent immobilization of acylated proteins in the inner
... a combination of bright-field and confocal fluorescence microscopy, we were able to establish that the mobility of saturated lipids is drastically reduced at the phagocytic cup by a process that requires receptor-induced tyrosine phosphorylation. ...
... a combination of bright-field and confocal fluorescence microscopy, we were able to establish that the mobility of saturated lipids is drastically reduced at the phagocytic cup by a process that requires receptor-induced tyrosine phosphorylation. ...
Plasma Membrane Discussion
... Protective barrier Regulate transport in & out of cell (selectively permeable) Allow cell recognition Provide anchoring sites for filaments of cytoskeleton ...
... Protective barrier Regulate transport in & out of cell (selectively permeable) Allow cell recognition Provide anchoring sites for filaments of cytoskeleton ...
Lecture 4
... – Nuclear receptors: Lipid soluble ligand that crosses the cell membrane and acts on an intracellular receptor ...
... – Nuclear receptors: Lipid soluble ligand that crosses the cell membrane and acts on an intracellular receptor ...
No Slide Title
... – Nuclear receptors: Lipid soluble ligand that crosses the cell membrane and acts on an intracellular receptor ...
... – Nuclear receptors: Lipid soluble ligand that crosses the cell membrane and acts on an intracellular receptor ...
Cell Boundaries - Duplin County Schools
... random motion, a solute will undergo DIFFUSION-movement of solute particles from area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration; diffusion continues until it reaches EQUILIBRIUM-concentrations are the same throughout ...
... random motion, a solute will undergo DIFFUSION-movement of solute particles from area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration; diffusion continues until it reaches EQUILIBRIUM-concentrations are the same throughout ...
chapter_4_2007
... A set of folded membranes and tubes throughout the cell. Provides a large surface area for important chemical reactions. ...
... A set of folded membranes and tubes throughout the cell. Provides a large surface area for important chemical reactions. ...
TRANSPORT - TeacherWeb
... This picture shows diffusion of molecules (without a membrane present): ...
... This picture shows diffusion of molecules (without a membrane present): ...
Slide 1
... – primary active transport establishes high [Na] outside the cell - creates a Na gradient -diffusion of Na back into the cell allows the movement of a second ion – either in the same direction as the Na+ (symporter) or in the opposite direction (antiporter) e.g. Na+/Ca2+ antiporter – opposite direct ...
... – primary active transport establishes high [Na] outside the cell - creates a Na gradient -diffusion of Na back into the cell allows the movement of a second ion – either in the same direction as the Na+ (symporter) or in the opposite direction (antiporter) e.g. Na+/Ca2+ antiporter – opposite direct ...
Lecture 1 Cell Biology
... substance will diffuse from where it is more concentrated to where it is less concentrated. ...
... substance will diffuse from where it is more concentrated to where it is less concentrated. ...
Lipid raft
The plasma membranes of cells contain combinations of glycosphingolipids and protein receptors organized in glycolipoprotein microdomains termed lipid rafts. These specialized membrane microdomains compartmentalize cellular processes by serving as organizing centers for the assembly of signaling molecules, influencing membrane fluidity and membrane protein trafficking, and regulating neurotransmission and receptor trafficking. Lipid rafts are more ordered and tightly packed than the surrounding bilayer, but float freely in the membrane bilayer. Although more common in plasma membrane, lipid rafts have also been reported in other parts of the cell, such as Golgi and lysosomes.