02 Cell. Cell metabolism
... neither rigid nor static in structure but is highly flexible and can change its shape and composition through time. The lipid bilayer functions as a liquid in which other molecules such as proteins are suspended. ...
... neither rigid nor static in structure but is highly flexible and can change its shape and composition through time. The lipid bilayer functions as a liquid in which other molecules such as proteins are suspended. ...
Document
... c. Main responsibility: ensure the composition of extracellular fluid is not the same as the composition of the intracellular fluid d. Water-soluble substances (salts, nutrients) cross membrane with aid of protein channels, which are selective about what can pass through e. Lipids can pass directly ...
... c. Main responsibility: ensure the composition of extracellular fluid is not the same as the composition of the intracellular fluid d. Water-soluble substances (salts, nutrients) cross membrane with aid of protein channels, which are selective about what can pass through e. Lipids can pass directly ...
Lectures 6 & 7: Powerpoint
... Membranes of adjacent cells glued together by proteins and carbohydrates Tight junction: Cells sealed together with proteins ...
... Membranes of adjacent cells glued together by proteins and carbohydrates Tight junction: Cells sealed together with proteins ...
The Cell Membrane
... All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane (also called the plasma membrane). This is a biological membrane or biomembrane consisting of a double layer of lipids in which proteins are located. The cell membrane keeps the components of the cell isolated from the external environment. It also serves ...
... All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane (also called the plasma membrane). This is a biological membrane or biomembrane consisting of a double layer of lipids in which proteins are located. The cell membrane keeps the components of the cell isolated from the external environment. It also serves ...
Document
... interconnected tubes and flattened sacs that begin at the nucleus and ramble throughout the cytoplasm • Flattened channel, starts at nuclear envelope and folds back on itself repeatedly in cytoplasm ...
... interconnected tubes and flattened sacs that begin at the nucleus and ramble throughout the cytoplasm • Flattened channel, starts at nuclear envelope and folds back on itself repeatedly in cytoplasm ...
multiscale modeling of the organizations of receptor transmembrane
... Significant differences with ErbB2 Minimal response to the change of thickness At low tilt angles protein precession entropy is significant Lee and Im, Phys. Rev. Lett. (2008) ...
... Significant differences with ErbB2 Minimal response to the change of thickness At low tilt angles protein precession entropy is significant Lee and Im, Phys. Rev. Lett. (2008) ...
CHEM 260 | ELEMENTS OF BIOCHEMISTRY L/L
... Metabolism - Protein Metabolism - Lipids and Membranes - Lipid Metabolism - Aerobic Metabolism - Nucleic Acids - Genetic Information ...
... Metabolism - Protein Metabolism - Lipids and Membranes - Lipid Metabolism - Aerobic Metabolism - Nucleic Acids - Genetic Information ...
The structure and function of the Mitochondrion
... References: Modified image of the mitochondrion - http://www.grayfoxpartners.com/Rates.html Text-Campbell, Reece (2008) Biology, 8th ed. Pearson Modified image of the Endosymbiotic - theory http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/cells/organelles/ ...
... References: Modified image of the mitochondrion - http://www.grayfoxpartners.com/Rates.html Text-Campbell, Reece (2008) Biology, 8th ed. Pearson Modified image of the Endosymbiotic - theory http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/cells/organelles/ ...
3-20
... • Nucleus = genetic material of cell • Cytoplasm = everything between the membrane and the nucleus – cytosol = intracellular fluid – organelles = subcellular structures with specific functions ...
... • Nucleus = genetic material of cell • Cytoplasm = everything between the membrane and the nucleus – cytosol = intracellular fluid – organelles = subcellular structures with specific functions ...
Cell Membranes Review
... molecules? How does water react with non-polar molecules, such as lipids or fats? Explain how water’s polarity results in a high surface tension and high heat capacity. What does this mean for living organisms that are made mostly of water? 4. Water is called the “universal solvent.” What aspect of ...
... molecules? How does water react with non-polar molecules, such as lipids or fats? Explain how water’s polarity results in a high surface tension and high heat capacity. What does this mean for living organisms that are made mostly of water? 4. Water is called the “universal solvent.” What aspect of ...
READ THIS!
... get dressed are in one place. All the items you need for studying are in another place. This compartmentalization improves efficiency. Cells also need organization to improve efficiency. The compartmentalization of cells is achieved by dividing up areas in the cell with membranes. A plasma membrane ...
... get dressed are in one place. All the items you need for studying are in another place. This compartmentalization improves efficiency. Cells also need organization to improve efficiency. The compartmentalization of cells is achieved by dividing up areas in the cell with membranes. A plasma membrane ...
Membrane Structure and Function Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid
... – Binding to external structures – Binding to other cells ...
... – Binding to external structures – Binding to other cells ...
chapter05
... Biological membranes do not have free ends and can round up into a vesicle. MEMBRANE PROTEINS INTEGRAL MEMBRANE PROTEINS are embedded in the bilayer with the hydrophilic side exposed to the aqueous environment and the hydrophobic side inside the bilayer. TRANSMEMBRANE PROTEINS are integral proteins ...
... Biological membranes do not have free ends and can round up into a vesicle. MEMBRANE PROTEINS INTEGRAL MEMBRANE PROTEINS are embedded in the bilayer with the hydrophilic side exposed to the aqueous environment and the hydrophobic side inside the bilayer. TRANSMEMBRANE PROTEINS are integral proteins ...
Outline
... down a concentration gradient. Small, nonpolar molecules (e.g. O2, CO2) can get through the phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion. Diffusion doesn’t have to have a membrane (perfume). ...
... down a concentration gradient. Small, nonpolar molecules (e.g. O2, CO2) can get through the phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion. Diffusion doesn’t have to have a membrane (perfume). ...
07 Cell Transport - Crestwood Local Schools
... Also found in the cell membrane are certain proteins, which play an important part in the cell by: 1) Coordinating cell-to-cell behaviors. 2) Adjusting the cells metabolism rates. 3) Initiating growth & division times. ...
... Also found in the cell membrane are certain proteins, which play an important part in the cell by: 1) Coordinating cell-to-cell behaviors. 2) Adjusting the cells metabolism rates. 3) Initiating growth & division times. ...
Online Activity: Types of Transport
... The small circles represents dissolved solutes like salt, glucose, and amino acids. You can assume that the additional space surrounding the solutes is water. hypotonic - __________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ...
... The small circles represents dissolved solutes like salt, glucose, and amino acids. You can assume that the additional space surrounding the solutes is water. hypotonic - __________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ...
Answer Key - TeacherWeb
... 8. Phospholipids are molecules that contain phosphate, have polar heads & nonpolar tails and form the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane. p.81 9. The double membrane surrounding the nucleus is called the lipid bilayer (nuclear envelope is okay too). 10. One important organelle that helps maintain ho ...
... 8. Phospholipids are molecules that contain phosphate, have polar heads & nonpolar tails and form the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane. p.81 9. The double membrane surrounding the nucleus is called the lipid bilayer (nuclear envelope is okay too). 10. One important organelle that helps maintain ho ...
Parts of the Cell
... Cell Membrane: controls substances that pass in and out of the cell. a. Selectively permeable: membrane that keeps out some materials but allows others to pass. b. All membranes are made of lipids and proteins i. Phospholipid bilayer: hydrophilic heads point outward while hydrophobic tails are point ...
... Cell Membrane: controls substances that pass in and out of the cell. a. Selectively permeable: membrane that keeps out some materials but allows others to pass. b. All membranes are made of lipids and proteins i. Phospholipid bilayer: hydrophilic heads point outward while hydrophobic tails are point ...
Macromolecules & the Cell Membrane
... – Hypotonic: solution outside of the cell is LESS concentrated; water enters the cell ...
... – Hypotonic: solution outside of the cell is LESS concentrated; water enters the cell ...
The Human Cell Membrane
... All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane (also called the plasma membrane). This is a biological membrane or biomembrane consisting of a double layer of lipids in which proteins are located. The cell membrane keeps the components of the cell isolated from the external environment. It also serves ...
... All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane (also called the plasma membrane). This is a biological membrane or biomembrane consisting of a double layer of lipids in which proteins are located. The cell membrane keeps the components of the cell isolated from the external environment. It also serves ...
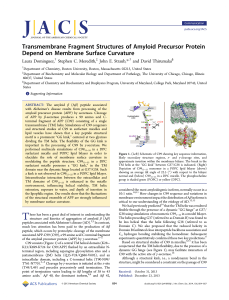
Transmembrane Fragment Structures of Amyloid Precursor Protein
... derived from the PDB structures (orange lines in Figure 5) lead to a significantly shorter average distance. Interestingly, the distances reported for the WT peptide in 1:4 POPG:POPC lipid vesicles6 are consistent with a more modest bend near a hinge located at G37/G3814 and in agreement with our sim ...
... derived from the PDB structures (orange lines in Figure 5) lead to a significantly shorter average distance. Interestingly, the distances reported for the WT peptide in 1:4 POPG:POPC lipid vesicles6 are consistent with a more modest bend near a hinge located at G37/G3814 and in agreement with our sim ...
Model lipid bilayer
A model lipid bilayer is any bilayer assembled in vitro, as opposed to the bilayer of natural cell membranes or covering various sub-cellular structures like the nucleus. A model bilayer can be made with either synthetic or natural lipids. The simplest model systems contain only a single pure synthetic lipid. More physiologically relevant model bilayers can be made with mixtures of several synthetic or natural lipids.There are many different types of model bilayers, each having experimental advantages and disadvantages. The first system developed was the black lipid membrane or “painted” bilayer, which allows simple electrical characterization of bilayers but is short-lived and can be difficult to work with. Supported bilayers are anchored to a solid substrate, increasing stability and allowing the use of characterization tools not possible in bulk solution. These advantages come at the cost of unwanted substrate interactions which can denature membrane proteins.