An Introduction to Medical Ethics
... o In order to determine if the action is permissible, consider: • The nature of the act must be good or neutral, it cannot be intrinsically wrong • The agent intends the good effect and not the bad either as a means to the good or as an end itself • The good effect must outweigh the evil that is per ...
... o In order to determine if the action is permissible, consider: • The nature of the act must be good or neutral, it cannot be intrinsically wrong • The agent intends the good effect and not the bad either as a means to the good or as an end itself • The good effect must outweigh the evil that is per ...
ETHICS AND SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY
... Ethics - the moral principles and values that govern the actions and decisions of an individual or group. Ethics are different from laws. Laws - society’s standards and values that are enforceable in court. Three factors typically influence a business person’s ethical decisions: 1. Societal Culture ...
... Ethics - the moral principles and values that govern the actions and decisions of an individual or group. Ethics are different from laws. Laws - society’s standards and values that are enforceable in court. Three factors typically influence a business person’s ethical decisions: 1. Societal Culture ...
Ethical Theories
... no set of values ought to be applied to all Objections: (Naturalistic Fallacy) • The existence of moral differences does not justify them (“is does not imply ought”) • If a culture’s values were always “right,” there could be no moral development or progress • We would have to tolerate even cruel cu ...
... no set of values ought to be applied to all Objections: (Naturalistic Fallacy) • The existence of moral differences does not justify them (“is does not imply ought”) • If a culture’s values were always “right,” there could be no moral development or progress • We would have to tolerate even cruel cu ...
Universal Ethical Egoism
... completely, responsible for their own lives…” (Hinman 121) This viewpoint can lead to a lack of compassion. For example, when the Jewish people were placed into concentration camps during World War II, they certainly did not bring their fate on themselves. According to the doctrine of ethical egoism ...
... completely, responsible for their own lives…” (Hinman 121) This viewpoint can lead to a lack of compassion. For example, when the Jewish people were placed into concentration camps during World War II, they certainly did not bring their fate on themselves. According to the doctrine of ethical egoism ...
2. NOTIONS OF MORALITY (notes)
... Act only according to that maxim by which you can also will that it would become a universal law. Act in such a way that you always treat humanity, whether in your own person or in the person of any other, never simply as a means, but always at the same time as an end. Act as though you were through ...
... Act only according to that maxim by which you can also will that it would become a universal law. Act in such a way that you always treat humanity, whether in your own person or in the person of any other, never simply as a means, but always at the same time as an end. Act as though you were through ...
moral values - Academic Home Page
... have to deal with an unpleasant or ugly truth, like a serious illness. Respect for persons We must respect the wishes of others. How the other person feels about being lied to is more important than how the potential liar feels about lying. Immanuel Kant: “It is immoral to use other people solely an ...
... have to deal with an unpleasant or ugly truth, like a serious illness. Respect for persons We must respect the wishes of others. How the other person feels about being lied to is more important than how the potential liar feels about lying. Immanuel Kant: “It is immoral to use other people solely an ...
Ethical Egoism
... The needs of others are also deemed important, and when we can help others—especially at little cost to ourselves—we sense that we should do so. This is based on the assumption that we have duties to others simply because they are people who could be helped or harmed by what we do. ...
... The needs of others are also deemed important, and when we can help others—especially at little cost to ourselves—we sense that we should do so. This is based on the assumption that we have duties to others simply because they are people who could be helped or harmed by what we do. ...
Ethical Theory and Business
... • They then enter the market and are free to bargain in an open, free and competitive market environment. • Thus competition among rational and selfinterested individuals will continuously work to promote the greatest overall good ...
... • They then enter the market and are free to bargain in an open, free and competitive market environment. • Thus competition among rational and selfinterested individuals will continuously work to promote the greatest overall good ...
Introduction to Philosophy: Major Concepts and Problems
... 3. Ethical theories: virtue ethics, 'love thy neighbour' ethics, ethics of natural rights, ethics of the social contract. Theory of the development of moral competences by L. Kohlberg. 4. Introduction to the political and social philosophy. Doctrines in political philosophy: conservatism, liberalism ...
... 3. Ethical theories: virtue ethics, 'love thy neighbour' ethics, ethics of natural rights, ethics of the social contract. Theory of the development of moral competences by L. Kohlberg. 4. Introduction to the political and social philosophy. Doctrines in political philosophy: conservatism, liberalism ...
Stages of Moral Development
... 2. Stages cannot be skipped (ie., jumping from stage 2 to 4 without experiencing stage 3) 3. Most adults do not advance past stage 4 in their development 4. Studying ethical cases can help individuals develop their moral senses and thus advance B. Level One--preconventional morality 1. Stage 1-- Pun ...
... 2. Stages cannot be skipped (ie., jumping from stage 2 to 4 without experiencing stage 3) 3. Most adults do not advance past stage 4 in their development 4. Studying ethical cases can help individuals develop their moral senses and thus advance B. Level One--preconventional morality 1. Stage 1-- Pun ...
Chapter 6
... • Goodness theories typically focus on the end result of actions and the goodness or happiness created by them • Obligation theories emphasize the means and motives by which actions are justified. – Teleology and Deontology ...
... • Goodness theories typically focus on the end result of actions and the goodness or happiness created by them • Obligation theories emphasize the means and motives by which actions are justified. – Teleology and Deontology ...
Egoism and Altruism - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... What is the difference between Psychological Egoism and Ethical Egoism? ...
... What is the difference between Psychological Egoism and Ethical Egoism? ...
Collective Good
... “It is possible to measure progress because of the persistence throughout the whole course of human history of certain identical interests and purposes. When such an interest or purpose is sufficiently broad in scope, and gets itself permanently embodied, it is called an institution. Thus government ...
... “It is possible to measure progress because of the persistence throughout the whole course of human history of certain identical interests and purposes. When such an interest or purpose is sufficiently broad in scope, and gets itself permanently embodied, it is called an institution. Thus government ...
What are Egoism & Altruism? - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Based more on the question of what is in our natures Do we naturally act for ourselves or for others? Is it possible to act for others’ interests? ...
... Based more on the question of what is in our natures Do we naturally act for ourselves or for others? Is it possible to act for others’ interests? ...
Consequentialist Theories
... “Everyone should always establish and follow that rule or rules that will bring about the greatest good for all concerned.” There is a presumption, as Thiroux puts it, that “it is foolish and dangerous to leave moral actions up to individuals without providing them with some guidance and without try ...
... “Everyone should always establish and follow that rule or rules that will bring about the greatest good for all concerned.” There is a presumption, as Thiroux puts it, that “it is foolish and dangerous to leave moral actions up to individuals without providing them with some guidance and without try ...
303WrightComunitrnV2
... the state cannot be limited (so perpetual peace is unattainable) o The state must promote the economic interests of its society, which may cause conflict o The state protects self as an entity, rather than the individuals or property within it o War is a necessary feature in a world where you can't ...
... the state cannot be limited (so perpetual peace is unattainable) o The state must promote the economic interests of its society, which may cause conflict o The state protects self as an entity, rather than the individuals or property within it o War is a necessary feature in a world where you can't ...
kohlberg`s stages of moral development
... • That is to say most people take their moral views from those around them and only a minority think through ethical principles for themselves. ...
... • That is to say most people take their moral views from those around them and only a minority think through ethical principles for themselves. ...
Morality and Self
... ► Why do we form a society? ► On the benefits of forming a society, rather than remaining in the state of nature ...
... ► Why do we form a society? ► On the benefits of forming a society, rather than remaining in the state of nature ...
Ethical Egoism
... owners to pursue their own interest of maximum financial gain by capitalizing on what others are willing to pay to pursue their own interest of survival in the wake of natural ...
... owners to pursue their own interest of maximum financial gain by capitalizing on what others are willing to pay to pursue their own interest of survival in the wake of natural ...
003. Chapter 2
... Democracies/western democracies: usually have a foundation of individualism (but can contain collectivism as well, especially economically) o The One instead of the many Political freedom to inalienable human rights – fundamentally important Right winged – neo conservative thinking (political ...
... Democracies/western democracies: usually have a foundation of individualism (but can contain collectivism as well, especially economically) o The One instead of the many Political freedom to inalienable human rights – fundamentally important Right winged – neo conservative thinking (political ...
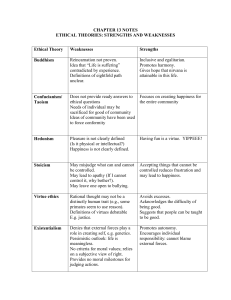
Chapter 13 Theories Strengths and Weaknesses
... Denies that external forces play a role in creating self, e.g. genetics. Pessimistic outlook: life is meaningless. No criteria for moral values; relies on a subjective view of right. Provides no moral milestones for judging actions. ...
... Denies that external forces play a role in creating self, e.g. genetics. Pessimistic outlook: life is meaningless. No criteria for moral values; relies on a subjective view of right. Provides no moral milestones for judging actions. ...
Egoism and Altruism
... • Acting for the sake of other people’s interests • Altruism can be divided into two theses: psychological altruism (people “naturally act” for each other’s sake) and ethical altruism (people ought to act with each other’s interests in mind) • Ethical altruism is perhaps best summarized in the so-ca ...
... • Acting for the sake of other people’s interests • Altruism can be divided into two theses: psychological altruism (people “naturally act” for each other’s sake) and ethical altruism (people ought to act with each other’s interests in mind) • Ethical altruism is perhaps best summarized in the so-ca ...
Philosophies in Grendel Chapter One Orphism: the teachings of an
... agent's self-interest may be incidentally detrimental to, beneficial to, or neutral in its effect on others. It allows for the possibility of either as long as what is chosen is efficacious in satisfying self-interest of the agent. Ethical egoism is sometimes the philosophical basis for people's sup ...
... agent's self-interest may be incidentally detrimental to, beneficial to, or neutral in its effect on others. It allows for the possibility of either as long as what is chosen is efficacious in satisfying self-interest of the agent. Ethical egoism is sometimes the philosophical basis for people's sup ...