Learning - Purdue Psychological Sciences
... Skinner believed in inner thought processes and biological underpinnings, but did not feel it was necessary to consider them seriously in psychology (because they were unobservable). ...
... Skinner believed in inner thought processes and biological underpinnings, but did not feel it was necessary to consider them seriously in psychology (because they were unobservable). ...
File - Ms. G`s Classroom
... someone else’s actions into the motor program you would use to do the same thing may enable imitation, language training, & empathy ...
... someone else’s actions into the motor program you would use to do the same thing may enable imitation, language training, & empathy ...
Guide 29
... thought of as the "real" reason something occurred. Example: Why did the ship sink? Proximate cause: Because it was holed beneath the waterline, water entered the hull and the ship became denser than the water which supported it, so it couldn't stay afloat. Ultimate cause: Because the ship hit a roc ...
... thought of as the "real" reason something occurred. Example: Why did the ship sink? Proximate cause: Because it was holed beneath the waterline, water entered the hull and the ship became denser than the water which supported it, so it couldn't stay afloat. Ultimate cause: Because the ship hit a roc ...
General Psych Learning Classical Conditioning Pavlov
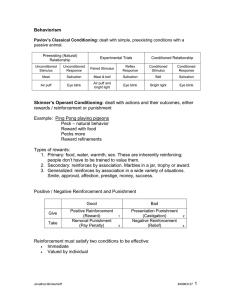
... Owner swats a dog who has chewed her slippers... Negative Punishment Removal of a reward (Negative) Teenager who stays out past curfew is not allowed to drive the family car for 2 weeks... Husband who forgets anniversary sleeps on couch for a week... Difficulties in Punishment Learner may not unders ...
... Owner swats a dog who has chewed her slippers... Negative Punishment Removal of a reward (Negative) Teenager who stays out past curfew is not allowed to drive the family car for 2 weeks... Husband who forgets anniversary sleeps on couch for a week... Difficulties in Punishment Learner may not unders ...
Chapter Seven Part Two - K-Dub
... Latent Learning Rats appear to form cognitive maps. They can learn a maze just by wandering, with no cheese to reinforce their learning. Evidence of these maps is revealed once the cheese is placed somewhere in the maze. After only a few trials, these rats quickly catch up in maze-solving to ra ...
... Latent Learning Rats appear to form cognitive maps. They can learn a maze just by wandering, with no cheese to reinforce their learning. Evidence of these maps is revealed once the cheese is placed somewhere in the maze. After only a few trials, these rats quickly catch up in maze-solving to ra ...
How To*s for Effective Functional Behavior Assessments
... • Escape--The individual behaves in order to get out of doing something he/she does not want to do. • Stimulation--The individual behaves in a specific way because it feels good to them. • Seeking Access to Materials--The individual behaves in order to get a preferred item or participate in an enjoy ...
... • Escape--The individual behaves in order to get out of doing something he/she does not want to do. • Stimulation--The individual behaves in a specific way because it feels good to them. • Seeking Access to Materials--The individual behaves in order to get a preferred item or participate in an enjoy ...
Lecture Materials
... Further criticism extends to the presumption that behavior increases only when it is reinforced. This premise is at odds with research conducted by Albert Bandura at Stanford University. His findings indicate that violent behavior is imitated, without being reinforced, in studies conducted with chil ...
... Further criticism extends to the presumption that behavior increases only when it is reinforced. This premise is at odds with research conducted by Albert Bandura at Stanford University. His findings indicate that violent behavior is imitated, without being reinforced, in studies conducted with chil ...
Fall 2014 10-2 Chapter 7 Pt 2
... At home: In children, reinforcing good behavior increases the occurrence of these behaviors. Ignoring unwanted behavior decreases their occurrence. Credit: Worth Publishers ...
... At home: In children, reinforcing good behavior increases the occurrence of these behaviors. Ignoring unwanted behavior decreases their occurrence. Credit: Worth Publishers ...
Learning Powerpoint
... Subject operates on the environment and produces a result that will influence whether he or she will operate in the same way in the future. ...
... Subject operates on the environment and produces a result that will influence whether he or she will operate in the same way in the future. ...
here
... The rats first accidentally pressed the levers in the cage, causing food or water to drop into a dish. After repeating the action, the rats saw that they could receive food and water by pressing the lever. (Learned this behaviour) So, when the rats were rewarded they were conditioned to repeat this ...
... The rats first accidentally pressed the levers in the cage, causing food or water to drop into a dish. After repeating the action, the rats saw that they could receive food and water by pressing the lever. (Learned this behaviour) So, when the rats were rewarded they were conditioned to repeat this ...
Memory - K-Dub
... Latent Learning Rats appear to form cognitive maps. They can learn a maze just by wandering, with no cheese to reinforce their learning. Evidence of these maps is revealed once the cheese is placed somewhere in the maze. After only a few trials, these rats quickly catch up in maze-solving to ra ...
... Latent Learning Rats appear to form cognitive maps. They can learn a maze just by wandering, with no cheese to reinforce their learning. Evidence of these maps is revealed once the cheese is placed somewhere in the maze. After only a few trials, these rats quickly catch up in maze-solving to ra ...
Behavior Analysis and Strategy Application after Brain Injury
... • In order to understand what is maintaining a particular behavior we not only need to look at the function of that behavior, but also the schedule on which it is being reinforced or maintained. • Behaviors within the same functional class can be sensitive to concurrent schedules of reinforcement, m ...
... • In order to understand what is maintaining a particular behavior we not only need to look at the function of that behavior, but also the schedule on which it is being reinforced or maintained. • Behaviors within the same functional class can be sensitive to concurrent schedules of reinforcement, m ...
Chapter 15 Learning Behaviorism Historical Perspective
... A bar to press and a chute for delivering food pellets Pigeon would be bumping around and eventually pushes the bar resulting in a food pellet down the chute The pigeon eats it and continues with what it’s doing Eventually the pigeon catches on and hits the bar more often resulting in persistent hit ...
... A bar to press and a chute for delivering food pellets Pigeon would be bumping around and eventually pushes the bar resulting in a food pellet down the chute The pigeon eats it and continues with what it’s doing Eventually the pigeon catches on and hits the bar more often resulting in persistent hit ...
Learning Learning: A relatively permanent change of an organism`s
... --Asserted that Intrinsic Motivation was another important factor to learning. --Motivation: must be motivated to imitate the behavior that has been modeled --Reinforcers play an important role in motivation. While experiencing these motivators can be highly effective, so can observing these reinfor ...
... --Asserted that Intrinsic Motivation was another important factor to learning. --Motivation: must be motivated to imitate the behavior that has been modeled --Reinforcers play an important role in motivation. While experiencing these motivators can be highly effective, so can observing these reinfor ...
Conditioning
... behavior. • only works when guaranteed • severe punishments may cause a person to simply leave the situation • Context must always be apparent • sometimes is accompanied by unseen benefits that make the behavior increase rather than decrease ...
... behavior. • only works when guaranteed • severe punishments may cause a person to simply leave the situation • Context must always be apparent • sometimes is accompanied by unseen benefits that make the behavior increase rather than decrease ...
Operant Conditioning (Hockenbury pg
... Variable-interval schedules – Reinforce the first response after time intervals. The unpredictable pop quiz that reinforces studying. Produces and responses. Cognition & Operant Conditioning Skinner and Thorndike felt that cognitions or thoughts, perceptions and expectations have place in psycho ...
... Variable-interval schedules – Reinforce the first response after time intervals. The unpredictable pop quiz that reinforces studying. Produces and responses. Cognition & Operant Conditioning Skinner and Thorndike felt that cognitions or thoughts, perceptions and expectations have place in psycho ...
Behaviorism
... No homework / dismiss early for recess Intrinsic rewards – the right thing to do; this builds class esprit de corps ...
... No homework / dismiss early for recess Intrinsic rewards – the right thing to do; this builds class esprit de corps ...
Learning - AP Psychology
... through the use of this “baby box,” which maintained the temperature of a child’s environment. Crib was humidity and temperature controlled. Skinner believed it would keep his second daughter from getting cold at night and crying. A fan pushed air from the outside through a surface, adjusting the te ...
... through the use of this “baby box,” which maintained the temperature of a child’s environment. Crib was humidity and temperature controlled. Skinner believed it would keep his second daughter from getting cold at night and crying. A fan pushed air from the outside through a surface, adjusting the te ...
File
... through the use of this “baby box,” which maintained the temperature of a child’s environment. Crib was humidity and temperature controlled. Skinner believed it would keep his second daughter from getting cold at night and crying. A fan pushed air from the outside through a surface, adjusting the te ...
... through the use of this “baby box,” which maintained the temperature of a child’s environment. Crib was humidity and temperature controlled. Skinner believed it would keep his second daughter from getting cold at night and crying. A fan pushed air from the outside through a surface, adjusting the te ...
Woolfolk, A. (2010). Chapter 6: Behavioral Views of Learning. In A
... A. Steps In Behavior analysis: 1. Specify the behavior to be changed and determine current level. 2. Determine an intervention using your antecedents and consequences. 3. Monitor the results and modify as necessary. B. Use Premack to identify reinforcers C. Use ...
... A. Steps In Behavior analysis: 1. Specify the behavior to be changed and determine current level. 2. Determine an intervention using your antecedents and consequences. 3. Monitor the results and modify as necessary. B. Use Premack to identify reinforcers C. Use ...
Learning/Conditioning + Memory – (textbook chapters 8 + 9)
... 5. Maya wants to train her cat to use the toilet instead of the litter box. Describe how she might use shaping to train her cat in five steps/stages to exhibit toilet-using behavior. ...
... 5. Maya wants to train her cat to use the toilet instead of the litter box. Describe how she might use shaping to train her cat in five steps/stages to exhibit toilet-using behavior. ...
Fall 2015 10-6 Chapter 7 Pt 2
... At home: In children, reinforcing good behavior increases the occurrence of these behaviors. Ignoring unwanted behavior decreases their occurrence. Credit: Worth Publishers ...
... At home: In children, reinforcing good behavior increases the occurrence of these behaviors. Ignoring unwanted behavior decreases their occurrence. Credit: Worth Publishers ...
MS Word - Christian Counseling Resources
... clinical populations. I treat children and adults from the “womb to the tomb.” The techniques I have in my clinical “toolkit” can be applied to just about any type of problem I encounter in my private practice. One important area of training that I have not discussed with you yet is that of behavior ...
... clinical populations. I treat children and adults from the “womb to the tomb.” The techniques I have in my clinical “toolkit” can be applied to just about any type of problem I encounter in my private practice. One important area of training that I have not discussed with you yet is that of behavior ...