Fields and Forces Gravitational force and fields State Newton`s
... M= mass of object A m= mass of object B r= distance between the 2 objects 1.1.2. Define gravitational field strength Gravitational field: as regions of space where a mass experiences a force because of its mass. Gravitational field strength: as the force per unit mass experienced by a small test mas ...
... M= mass of object A m= mass of object B r= distance between the 2 objects 1.1.2. Define gravitational field strength Gravitational field: as regions of space where a mass experiences a force because of its mass. Gravitational field strength: as the force per unit mass experienced by a small test mas ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • So on the Moon, you would have the same mass as on Earth but weigh less on the Moon since the Moon is less massive than Earth • Mass in metric system is usually measured in kilograms ...
... • So on the Moon, you would have the same mass as on Earth but weigh less on the Moon since the Moon is less massive than Earth • Mass in metric system is usually measured in kilograms ...
click here - CAPSTONE 2010
... Circular velocity for the gravitational force Huygens showed (mid 17th century) that for objects in circular orbits, no matter the nature of the force constraining one body to orbit another, F=-mv2/r, where v is the velocity of the orbiting body and the other terms are as defined above. The minus s ...
... Circular velocity for the gravitational force Huygens showed (mid 17th century) that for objects in circular orbits, no matter the nature of the force constraining one body to orbit another, F=-mv2/r, where v is the velocity of the orbiting body and the other terms are as defined above. The minus s ...
May the Force Be Qith You!
... a)Contact Forces: affect things they touch – Tension – force in a wire or rope when pulled. – Friction – slows down motion by rubbing. – Elastic – spring-like object restores itself to its normal shape after alteration. ...
... a)Contact Forces: affect things they touch – Tension – force in a wire or rope when pulled. – Friction – slows down motion by rubbing. – Elastic – spring-like object restores itself to its normal shape after alteration. ...
Document
... due to Earth’s gravitational pull – weight due to surfaces in contact – normal force due to relative motion between surfaces of contact – friction due to rope/string holding (in suspension) a heavy object – ...
... due to Earth’s gravitational pull – weight due to surfaces in contact – normal force due to relative motion between surfaces of contact – friction due to rope/string holding (in suspension) a heavy object – ...
Centripetal Force Lab
... Materials: centripetal force kit, balance Procedure: 1. Measure the mass of a couple of washers on a balance. Record the WEIGHT in the data table...THIS IS YOUR CENTRIPETAL FORCE. ALSO measure the stopper's mass and record. MASS OF STOPPER_______________ 2. Practice swinging the stopper around so th ...
... Materials: centripetal force kit, balance Procedure: 1. Measure the mass of a couple of washers on a balance. Record the WEIGHT in the data table...THIS IS YOUR CENTRIPETAL FORCE. ALSO measure the stopper's mass and record. MASS OF STOPPER_______________ 2. Practice swinging the stopper around so th ...
Glossary of Terms Handout
... the masses' centers, and M is the mass of the primary body (e.g. a planet). At Earth's surface, the value of g = 9.8 meters per second per second (9.8m/s2). See also weight. Gamma rays -- Electromagnetic radiation in the neighborhood of 100 femtometers wavelength. Gravitation -- The mutual attractio ...
... the masses' centers, and M is the mass of the primary body (e.g. a planet). At Earth's surface, the value of g = 9.8 meters per second per second (9.8m/s2). See also weight. Gamma rays -- Electromagnetic radiation in the neighborhood of 100 femtometers wavelength. Gravitation -- The mutual attractio ...
Physics 50 Workshop
... 4. An electron travels in a straight line from the cathode of a vacuum tube to its anode (negative and positive ends, respectively) due to the electric field between the two ends of the tube. It travels a distance of 1.0 cm. The electron starts at rest and reaches the anode at a speed of 6.0 x 106 m ...
... 4. An electron travels in a straight line from the cathode of a vacuum tube to its anode (negative and positive ends, respectively) due to the electric field between the two ends of the tube. It travels a distance of 1.0 cm. The electron starts at rest and reaches the anode at a speed of 6.0 x 106 m ...
2nd trimester groupwork #1 Group 7A
... A solid conducting sphere of radius a is surrounded by a hollow conducting shell of inner radius b and outer radius c as shown above. The sphere and the shell each have a charge +Q, Express your answers to parts (a), (b) and (e) in terms of Q, a, b, c, and the Coulomb's law constant. ...
... A solid conducting sphere of radius a is surrounded by a hollow conducting shell of inner radius b and outer radius c as shown above. The sphere and the shell each have a charge +Q, Express your answers to parts (a), (b) and (e) in terms of Q, a, b, c, and the Coulomb's law constant. ...
Click here for a short consolidation presentation on the basics of
... The centre of mass is the point where all of the mass of the object is concentrated. When an object is supported at its centre of mass it will remain in equilibrium. If the object is uniform, for example a meter stick, the center of mass will be at the exact geometric center; if the object is irreg ...
... The centre of mass is the point where all of the mass of the object is concentrated. When an object is supported at its centre of mass it will remain in equilibrium. If the object is uniform, for example a meter stick, the center of mass will be at the exact geometric center; if the object is irreg ...
HW10 - University of St. Thomas
... outer conductor have effective linear charge densities of -56 nC/m and +56 nC/m, respectively, what is the magnitude of the potential difference between them? U3-VfEI06. Two conducting spheres are isolated from each other and other charges. The larger sphere has a radius of 30 cm, while the smaller ...
... outer conductor have effective linear charge densities of -56 nC/m and +56 nC/m, respectively, what is the magnitude of the potential difference between them? U3-VfEI06. Two conducting spheres are isolated from each other and other charges. The larger sphere has a radius of 30 cm, while the smaller ...
Physics of body crashing
... The decelerating force Fd applied by the wall to the body (or to whatever body part which hits first) causes pressure Pd which causes deformation: ...
... The decelerating force Fd applied by the wall to the body (or to whatever body part which hits first) causes pressure Pd which causes deformation: ...
Quiz #3 - Dawson College
... b) must be moving in a vacuum or in the absence of air drag. c) has zero acceleration. d) has a net force acting upon it in the direction of motion. e) none of these 9. An archer shoots an arrow. Consider the action force to be the bowstring against the arrow. The reaction to this force is the a) ai ...
... b) must be moving in a vacuum or in the absence of air drag. c) has zero acceleration. d) has a net force acting upon it in the direction of motion. e) none of these 9. An archer shoots an arrow. Consider the action force to be the bowstring against the arrow. The reaction to this force is the a) ai ...
force
... with the same force as the apple nor did it fall with the same gravitational acceleration. Why not? 1. The moon was much farther away from the Earth than an apple on the surface. 2. The moon was much larger than the apple. ...
... with the same force as the apple nor did it fall with the same gravitational acceleration. Why not? 1. The moon was much farther away from the Earth than an apple on the surface. 2. The moon was much larger than the apple. ...
review 04 forces
... 20. If an object is in equilibrium on an inclined plane, state a formula for: a)the weight of the object b) the parallel component of weight c)the perpendicular component of weight d) the normal force e)the frictional (or applied) force ...
... 20. If an object is in equilibrium on an inclined plane, state a formula for: a)the weight of the object b) the parallel component of weight c)the perpendicular component of weight d) the normal force e)the frictional (or applied) force ...
Ch8-9
... holds the car in a curved path (Figure 8.37). If this friction is not great enough, the car fails to make the curve and the tires slide sideways; we say the car skids. ...
... holds the car in a curved path (Figure 8.37). If this friction is not great enough, the car fails to make the curve and the tires slide sideways; we say the car skids. ...
LECTURE 19: Universal Law of Gravitation
... WARM UP: What direction is the static friction pointing in if a car is going around a banked turn at the minimum speed possible? ...
... WARM UP: What direction is the static friction pointing in if a car is going around a banked turn at the minimum speed possible? ...
GRAVITY - the property of objects that have MASS
... - the only time something collapses is in the case of a black hole and burned out star ...
... - the only time something collapses is in the case of a black hole and burned out star ...
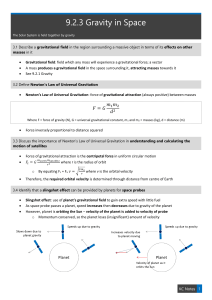
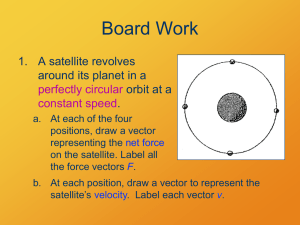
9.2.3 Gravity in Space
... The spin of the Earth generates a centrifuge effect, less gravity especially at equator o However, it is not acting as an inertial frame of reference ...
... The spin of the Earth generates a centrifuge effect, less gravity especially at equator o However, it is not acting as an inertial frame of reference ...
L23_gravity
... Properties of Gravity m1m2 F=G r2 • direction is toward the other object • magnitude decreases as (distance)2 increases • never becomes zero • infinite at zero separation (?!) ...
... Properties of Gravity m1m2 F=G r2 • direction is toward the other object • magnitude decreases as (distance)2 increases • never becomes zero • infinite at zero separation (?!) ...
Exploration of Space Lecture B
... So the expression 42K is proportional to mc where mc refers to the mass of the central body (like the sun or Earth). We can thus rewrite this expression as 42K = G mc. The value G is referred to as a universal gravitational constant. Henry Cavendish first experimentally measured it in 1798. Newton ...
... So the expression 42K is proportional to mc where mc refers to the mass of the central body (like the sun or Earth). We can thus rewrite this expression as 42K = G mc. The value G is referred to as a universal gravitational constant. Henry Cavendish first experimentally measured it in 1798. Newton ...
Forces Review
... (a) The values of g and G do not depend on location. (b) The values of g and G depend on location. (c) The value of G is the same everywhere in the universe, but the value of g is not. (d) The value of g is the same everywhere in the universe, but the value of G is not. (e) The values of g and G are ...
... (a) The values of g and G do not depend on location. (b) The values of g and G depend on location. (c) The value of G is the same everywhere in the universe, but the value of g is not. (d) The value of g is the same everywhere in the universe, but the value of G is not. (e) The values of g and G are ...
Roche limit
The Roche limit (pronounced /ʁoʃ/ in IPA, similar to the sound of rosh), sometimes referred to as the Roche radius, is the distance within which a celestial body, held together only by its own gravity, will disintegrate due to a second celestial body's tidal forces exceeding the first body's gravitational self-attraction. Inside the Roche limit, orbiting material disperses and forms rings whereas outside the limit material tends to coalesce. The term is named after Édouard Roche, who is the French astronomer who first calculated this theoretical limit in 1848.