Practice questions for centripetal motion
... on him is 620N. What will the normal force be if the velocity is doubled? 7. A car of mass 938kg travels around a banked curve of radius 91m. The banking is at an angle of 19° to the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the road and the tires is 0.32. a) What forces provide the cen ...
... on him is 620N. What will the normal force be if the velocity is doubled? 7. A car of mass 938kg travels around a banked curve of radius 91m. The banking is at an angle of 19° to the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the road and the tires is 0.32. a) What forces provide the cen ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation Jeopardy Review Game
... related to a job of converting speech from one language to another.) ...
... related to a job of converting speech from one language to another.) ...
More Exam Review SPH 4U1
... Note that this distance, being positive, is above the starting point. The spring will have expanded 0.10 m to its normal length, so that the marble is 12.7 m above the top of the now-uncompressed spring. ...
... Note that this distance, being positive, is above the starting point. The spring will have expanded 0.10 m to its normal length, so that the marble is 12.7 m above the top of the now-uncompressed spring. ...
Circular Motion and Gravity Jeopardy
... related to a job of converting speech from one language to another.) ...
... related to a job of converting speech from one language to another.) ...
Thompson Teaching
... • (320 km/h is the answer, but as a note, because of air resistance she would probably have reached an actual terminal velocity of about 200 km/h) ...
... • (320 km/h is the answer, but as a note, because of air resistance she would probably have reached an actual terminal velocity of about 200 km/h) ...
Problem sheet 2
... 1.- Two infinite, grounded, conducting planes are located at x = a/2 and x = −a/2. A point charge q is placed between the planes at the point (x0 , y 0 , z 0 ), where −a/2 < x0 < a/2. Find the location an magnitude of all the image charges needed to satisfy the boundary conditions on the potential a ...
... 1.- Two infinite, grounded, conducting planes are located at x = a/2 and x = −a/2. A point charge q is placed between the planes at the point (x0 , y 0 , z 0 ), where −a/2 < x0 < a/2. Find the location an magnitude of all the image charges needed to satisfy the boundary conditions on the potential a ...
3-Newton`s law of gravity قانون نيوتن للثقالة
... • We have used the same symbol نفس الرمزg for gravitational field magnitude that we used earlier for the acceleration of free fall. The units of the two quantities are the same الكميتان لهما نفس الوحدات. ...
... • We have used the same symbol نفس الرمزg for gravitational field magnitude that we used earlier for the acceleration of free fall. The units of the two quantities are the same الكميتان لهما نفس الوحدات. ...
M2 Not-Formula Book
... object being spun on a string, this force is tension in the string; in the case of a planet in orbit, the force is gravitational attraction; in the case of a car driving around a corner, this force is friction between the tyres and the road. ...
... object being spun on a string, this force is tension in the string; in the case of a planet in orbit, the force is gravitational attraction; in the case of a car driving around a corner, this force is friction between the tyres and the road. ...
Example: The gravitational force of attraction between Earth and the
... just the distance from the surface not the center) (3316 N) 18. Trivia Question: What is the closest star to Earth? 19. The Sun has a mass of 2 x 1030 kg and a radius of 6.96 x 108 m. What would be the acceleration due to gravity experienced at the surface of the sun if something could actually get ...
... just the distance from the surface not the center) (3316 N) 18. Trivia Question: What is the closest star to Earth? 19. The Sun has a mass of 2 x 1030 kg and a radius of 6.96 x 108 m. What would be the acceleration due to gravity experienced at the surface of the sun if something could actually get ...
SAT Subject Physics Formula Reference
... For more than one pair of charges, use this formula for each pair, then add all the UE ’s. The potential difference ∆V between two points is defined as the negative of the work done by the electric field per unit charge as charge q moves from one point to the other. Alternately, it is the change in ...
... For more than one pair of charges, use this formula for each pair, then add all the UE ’s. The potential difference ∆V between two points is defined as the negative of the work done by the electric field per unit charge as charge q moves from one point to the other. Alternately, it is the change in ...
Universal Gravitation Worksheet
... 1. Two students are sitting 1.50m apart. One student has a mass of 70.0kg and the other has a mass of 52.0kg. What is the gravitational force between them? (1.08x10-7N) 2. What gravitational force does the moon produce on the earth if the centers of the moon and earth are 3.88x108m apart and the moo ...
... 1. Two students are sitting 1.50m apart. One student has a mass of 70.0kg and the other has a mass of 52.0kg. What is the gravitational force between them? (1.08x10-7N) 2. What gravitational force does the moon produce on the earth if the centers of the moon and earth are 3.88x108m apart and the moo ...
force
... with the same force as the apple nor did it fall with the same gravitational acceleration. Why not? 1. The moon was much farther away from the Earth than an apple on the surface. 2. The moon was much larger than the apple. ...
... with the same force as the apple nor did it fall with the same gravitational acceleration. Why not? 1. The moon was much farther away from the Earth than an apple on the surface. 2. The moon was much larger than the apple. ...
What is Circular Motion?
... or oily, this friction force will not be available. The car will not be able to move in a circle, it will keep going in a straight line and therefore go off the road. ...
... or oily, this friction force will not be available. The car will not be able to move in a circle, it will keep going in a straight line and therefore go off the road. ...
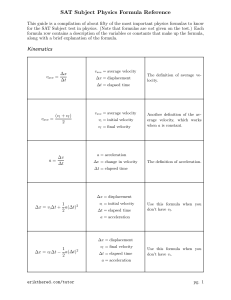
SAT Subject Physics Formula Reference Kinematics
... A charge q, when placed in an electric field E, will feel a force on it, given by this formula (q is sometimes called a “test” charge, since it tests the electric field strength). This formula gives the electric field due to a charge q at a distance r from the charge. Unlike the “test” charge, the c ...
... A charge q, when placed in an electric field E, will feel a force on it, given by this formula (q is sometimes called a “test” charge, since it tests the electric field strength). This formula gives the electric field due to a charge q at a distance r from the charge. Unlike the “test” charge, the c ...
Force and Motion
... a physics textbook is motionless on the top of a table. If you give it a hard push with your hand, it slides across the table and slowly comes to a stop. Use Newton’s 3 Laws to answer the ...
... a physics textbook is motionless on the top of a table. If you give it a hard push with your hand, it slides across the table and slowly comes to a stop. Use Newton’s 3 Laws to answer the ...
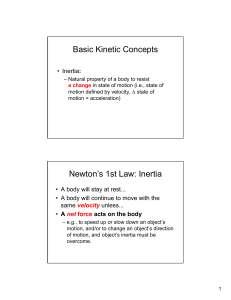
Chapter 11: Circular Motion
... 2. Describe the following quantities as they relate to uniform circular motion: speed, velocity, acceleration, force(i.e. constant, changing, direction?) 3. What quantities determine centripetal acceleration? 4. What quantities determine centripetal force? How is it defined? 5. Give examples of cent ...
... 2. Describe the following quantities as they relate to uniform circular motion: speed, velocity, acceleration, force(i.e. constant, changing, direction?) 3. What quantities determine centripetal acceleration? 4. What quantities determine centripetal force? How is it defined? 5. Give examples of cent ...
The equivalence of real and reduced
... Section 2.3 of your textbook. Let's keep Newton's laws in mind as we examine the properties of real and reduced-mass orbits: forces, energies, angular momenta. Gravitational force ...
... Section 2.3 of your textbook. Let's keep Newton's laws in mind as we examine the properties of real and reduced-mass orbits: forces, energies, angular momenta. Gravitational force ...
FORCE:
... A center-seeking force that causes an object to follow a circular path. “Any force that is directed at right angles to the path of the moving body and produces circular motion.” The following formulas are similar to those for Newton’s First Law, but deal with mass in motion in a circular path: ...
... A center-seeking force that causes an object to follow a circular path. “Any force that is directed at right angles to the path of the moving body and produces circular motion.” The following formulas are similar to those for Newton’s First Law, but deal with mass in motion in a circular path: ...
Motion
... • For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction • All forces act in pairs. ...
... • For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction • All forces act in pairs. ...
1. What is the weight of a 200 kg object? 2. A woman - IES Al
... is the acceleration of the basket? 3. A 20.0 kg mass is pulled by along a surface by a horizontal force of 100 N. Friction is 20.0 N. What is the acceleration of the mass? 4. A 49-N block is pulled by a horizontal force of 50.0 N along a rough horizontal surface at a constant acceleration of 6 m/s/s ...
... is the acceleration of the basket? 3. A 20.0 kg mass is pulled by along a surface by a horizontal force of 100 N. Friction is 20.0 N. What is the acceleration of the mass? 4. A 49-N block is pulled by a horizontal force of 50.0 N along a rough horizontal surface at a constant acceleration of 6 m/s/s ...
Electrical field
... Ellipse: curve such that sum of a and b is constant Orbit of Mars an ellipse with Sun at a focus ...
... Ellipse: curve such that sum of a and b is constant Orbit of Mars an ellipse with Sun at a focus ...
Roche limit
The Roche limit (pronounced /ʁoʃ/ in IPA, similar to the sound of rosh), sometimes referred to as the Roche radius, is the distance within which a celestial body, held together only by its own gravity, will disintegrate due to a second celestial body's tidal forces exceeding the first body's gravitational self-attraction. Inside the Roche limit, orbiting material disperses and forms rings whereas outside the limit material tends to coalesce. The term is named after Édouard Roche, who is the French astronomer who first calculated this theoretical limit in 1848.