Slide 1
... Any periodic motion where the restoring force is proportional to the displacement is called simple harmonic motion ...
... Any periodic motion where the restoring force is proportional to the displacement is called simple harmonic motion ...
Self Assessment
... 12. – 13. Name two ways to increase friction and two ways to decrease friction ...
... 12. – 13. Name two ways to increase friction and two ways to decrease friction ...
Newton`s Second Law Questions
... 6. A 4.46 kg block located on a horizontal frictionless floor is pulled by a cord that exerts a force of 12.9 N at an angle of 26.5o above the horizontal. What is the acceleration of the block when the force is applied? ...
... 6. A 4.46 kg block located on a horizontal frictionless floor is pulled by a cord that exerts a force of 12.9 N at an angle of 26.5o above the horizontal. What is the acceleration of the block when the force is applied? ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... golf ball will sit on the tee until acted upon by an outside force. Once hit, it will travel until fluid friction and gravity slow it down. IF…their was no atmosphere or gravity to slow it down it would continue on forever in the direction it was hit. ...
... golf ball will sit on the tee until acted upon by an outside force. Once hit, it will travel until fluid friction and gravity slow it down. IF…their was no atmosphere or gravity to slow it down it would continue on forever in the direction it was hit. ...
Chapter 10.3-10.5
... to move at a constant velocity until a force acts to change either its speed or direction. • Gravity and friction are unbalanced forces that often change an object’s motion. ...
... to move at a constant velocity until a force acts to change either its speed or direction. • Gravity and friction are unbalanced forces that often change an object’s motion. ...
Do now
... have with the net force for a given mass. Explain this relationship by writing the formula and then explaining if there is a direct or inverse relationship between the force and the acceleration (1 pt), what happens to the acceleration if the mass changes (1 pt), and then explain what conditions mus ...
... have with the net force for a given mass. Explain this relationship by writing the formula and then explaining if there is a direct or inverse relationship between the force and the acceleration (1 pt), what happens to the acceleration if the mass changes (1 pt), and then explain what conditions mus ...
Chapter 12
... • What happens when an object exerts a force on another object? • How do you calculate the momentum of an object? • What is the total momentum after objects ...
... • What happens when an object exerts a force on another object? • How do you calculate the momentum of an object? • What is the total momentum after objects ...
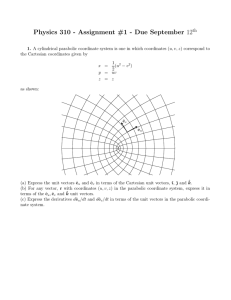
Physics 310 - Assignment #1 - Due September 12
... a fluid that produces both linear and quadratic fiscous drag, that is, find x(t) when the only forces acting on the object are Fdrag = −c1 v − c2 v|v|. Consider separately the two cases when the initial velocity is v0 > 0 and v0 < 0. 3. A box of mass M sits on an frictionless incline plane attached ...
... a fluid that produces both linear and quadratic fiscous drag, that is, find x(t) when the only forces acting on the object are Fdrag = −c1 v − c2 v|v|. Consider separately the two cases when the initial velocity is v0 > 0 and v0 < 0. 3. A box of mass M sits on an frictionless incline plane attached ...
Chapter 12 - Forces - Riverdale High School
... • CLE.3202.3.2: Investigate and apply Newton’s three laws of motion • CLE.3202.4.1: Explore the difference between mass and weight • CLE.3202.4.2: Relate gravitational force to mass • CLE.3202.3.3: Examine the Law of Conservation of Momentum in real-world situations • CLE.3202.Math.1: Understand the ...
... • CLE.3202.3.2: Investigate and apply Newton’s three laws of motion • CLE.3202.4.1: Explore the difference between mass and weight • CLE.3202.4.2: Relate gravitational force to mass • CLE.3202.3.3: Examine the Law of Conservation of Momentum in real-world situations • CLE.3202.Math.1: Understand the ...
Inertia and Newton’s First Law of Motion
... A curling rock moving along a rink eventually comes to a stop. Does this disagree with Newton’s first law of motion? Explain your answer. Draw an FBD for the birdie in each case: A. A badminton racket makes contact with a ...
... A curling rock moving along a rink eventually comes to a stop. Does this disagree with Newton’s first law of motion? Explain your answer. Draw an FBD for the birdie in each case: A. A badminton racket makes contact with a ...
Force and Motion Unit Plan
... 7.7A: Contrast situations where work is done with different amounts of force to situations where no work is done such as moving a box with a ramp and without a ramp, or standing still. 7.7C: Demonstrate and illustrate forces that affect motion in everyday life, such as emergence of seedlings, turgor ...
... 7.7A: Contrast situations where work is done with different amounts of force to situations where no work is done such as moving a box with a ramp and without a ramp, or standing still. 7.7C: Demonstrate and illustrate forces that affect motion in everyday life, such as emergence of seedlings, turgor ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation
... is not an interaction between 2 objects, and therefore not a real force. Nothing pulls an object away from the center of the circle. ...
... is not an interaction between 2 objects, and therefore not a real force. Nothing pulls an object away from the center of the circle. ...
Newton`s 1st, 2nd and 3rd Law
... boy push off of each other. The boy accelerates at 2m/s2. Find the girl’s ...
... boy push off of each other. The boy accelerates at 2m/s2. Find the girl’s ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion What force causes an object to have centripetal acceleration? Centripetal force - net force necessary to cause centripetal acceleration. ...
... Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion What force causes an object to have centripetal acceleration? Centripetal force - net force necessary to cause centripetal acceleration. ...
Some Introductory Concepts for Energy
... – body at rest tends to stay at rest and body in uniform motion will stay in straight line uniform motion unless acted upon by an outside force ...
... – body at rest tends to stay at rest and body in uniform motion will stay in straight line uniform motion unless acted upon by an outside force ...