Newton`s Laws of Motion
... published them in his book Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (mathematic principles of natural philosophy) in 1687. Today these laws are known as Newton’s Laws of Motion and describe the motion of all objects on the scale we experience in our everyday lives. ...
... published them in his book Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (mathematic principles of natural philosophy) in 1687. Today these laws are known as Newton’s Laws of Motion and describe the motion of all objects on the scale we experience in our everyday lives. ...
True or False - Hauserphysics
... 36. _____If a hockey puck slides on a perfectly frictionless surface, it will eventually slow down because of its inertia. 37. _____Inertia is the resistance any material object has to a change in its state of motion. 38. _____Gravitational force acting between two objects is directly proportional t ...
... 36. _____If a hockey puck slides on a perfectly frictionless surface, it will eventually slow down because of its inertia. 37. _____Inertia is the resistance any material object has to a change in its state of motion. 38. _____Gravitational force acting between two objects is directly proportional t ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Inertia Galileo came up with the definitions of FORCE and FRICTION. Force is any push or pull. Friction is the name given to the force that acts between materials that touch as they move past each other. Galileo was concerned with how things move rather than why they move. Galileo stated that ev ...
... Inertia Galileo came up with the definitions of FORCE and FRICTION. Force is any push or pull. Friction is the name given to the force that acts between materials that touch as they move past each other. Galileo was concerned with how things move rather than why they move. Galileo stated that ev ...
Force
... The book slides and then stops because of In space there is no a resistant force called resistance to cause friction. Friction is friction, so a bowling force that opposes ball would stay in motion. motion ...unless another object got in the way… ...
... The book slides and then stops because of In space there is no a resistant force called resistance to cause friction. Friction is friction, so a bowling force that opposes ball would stay in motion. motion ...unless another object got in the way… ...
Newtons laws ppt
... •The more moving components, the greater the force of friction will be (usually. •The smaller the frictional force, the farther your supply of energy will propel your vehicle. •Slow-moving cars have a smaller force of air resistance and travel farther than faster-moving ...
... •The more moving components, the greater the force of friction will be (usually. •The smaller the frictional force, the farther your supply of energy will propel your vehicle. •Slow-moving cars have a smaller force of air resistance and travel farther than faster-moving ...
inertia Forces can change velocity!
... each other – Universal Law of Gravity • Your weight is the attractive force that the earth exerts on you- it’s what makes things ...
... each other – Universal Law of Gravity • Your weight is the attractive force that the earth exerts on you- it’s what makes things ...
Document
... This unbalanced force is friction. This force is everywhere & affects our daily life constantly. ...
... This unbalanced force is friction. This force is everywhere & affects our daily life constantly. ...
Physics Final Review Problems 2014 *Note: the following problems
... e) Be able to do the above with graphical representations as well (position vs time graphs, velocity vs time graphs) f) Calculate velocity, position, and acceleration using the appropriate formulas. 1. What is the difference between distance and displacement? Speed and velocity? 2. What type of moti ...
... e) Be able to do the above with graphical representations as well (position vs time graphs, velocity vs time graphs) f) Calculate velocity, position, and acceleration using the appropriate formulas. 1. What is the difference between distance and displacement? Speed and velocity? 2. What type of moti ...
Physics Final Review Problems 2013 *Note: the following problems
... e) Be able to do the above with graphical representations as well (position vs time graphs, velocity vs time graphs) f) Calculate velocity, position, and acceleration using the appropriate formulas. 1. What is the difference between distance and displacement? Speed and velocity? 2. What type of moti ...
... e) Be able to do the above with graphical representations as well (position vs time graphs, velocity vs time graphs) f) Calculate velocity, position, and acceleration using the appropriate formulas. 1. What is the difference between distance and displacement? Speed and velocity? 2. What type of moti ...
Science-8-LEQ-5-1
... what is the force that slows your bike down? A –flow B –friction C –stress D –feet ...
... what is the force that slows your bike down? A –flow B –friction C –stress D –feet ...
Friction and Gravity
... The SI unit of mass is the KILOGRAM MORE mass and SHORTER distance means greater gravitational force. ...
... The SI unit of mass is the KILOGRAM MORE mass and SHORTER distance means greater gravitational force. ...
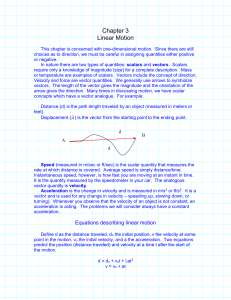
Notes - SFA Physics and Astronomy
... In many cases we are at liberty to start measuring at zero (do = 0) and the motion begins at rest (vo = 0), in which case these equations become d = ½at2 v = at , but these are not new equations, merely adaptations of the general forms. ...
... In many cases we are at liberty to start measuring at zero (do = 0) and the motion begins at rest (vo = 0), in which case these equations become d = ½at2 v = at , but these are not new equations, merely adaptations of the general forms. ...
Slide 1
... Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1727) • Laws of motion, law of gravitation, telescopes, properties of light, calculus, etc. ...
... Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1727) • Laws of motion, law of gravitation, telescopes, properties of light, calculus, etc. ...
VI. Newton`s Third Law
... Third Law of Motion When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal but opposite force on the first. ...
... Third Law of Motion When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal but opposite force on the first. ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation
... is not an interaction between 2 objects, and therefore not a real force. Nothing pulls an object away from the center of the circle. ...
... is not an interaction between 2 objects, and therefore not a real force. Nothing pulls an object away from the center of the circle. ...