Chapter 7
... • When a wheel of radius r rotates about an axis whose direction is fixed, a point on the rim of the wheel is described in terms of the circumferential distance l it has moved, its tangential speed v, and its tangential acceleration aT. • These quantities are related to the angular quantities q, w, ...
... • When a wheel of radius r rotates about an axis whose direction is fixed, a point on the rim of the wheel is described in terms of the circumferential distance l it has moved, its tangential speed v, and its tangential acceleration aT. • These quantities are related to the angular quantities q, w, ...
Newton’s Laws of Motion and Gravity
... Law of Conservation of Momentum • The momentum of an object doesn’t change unless its mass, velocity, or both change. • Momentum, however, can be transferred from one object to another. • The law of conservation of momentum states that if a group of objects exerts forces only on each other, their to ...
... Law of Conservation of Momentum • The momentum of an object doesn’t change unless its mass, velocity, or both change. • Momentum, however, can be transferred from one object to another. • The law of conservation of momentum states that if a group of objects exerts forces only on each other, their to ...
Multiple choice questions [60 points]
... When the potential energy U(r) is given as in Figure A, then the force is given in Figure B by curve A. 1 B. 2 ...
... When the potential energy U(r) is given as in Figure A, then the force is given in Figure B by curve A. 1 B. 2 ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion Powerpoint
... • Clothes on the floor of your room will stay there unless you pick them up. • If an object is already moving, it will continue to move at a constant velocity until a force acts to change either its speed or direction. ...
... • Clothes on the floor of your room will stay there unless you pick them up. • If an object is already moving, it will continue to move at a constant velocity until a force acts to change either its speed or direction. ...
Newton s Second and Third Laws and Gravity
... • a car decreasing speed on a straight road • a car traveling with constant speed on a straight road • a planet traveling around a Sun ...
... • a car decreasing speed on a straight road • a car traveling with constant speed on a straight road • a planet traveling around a Sun ...
Second Law teacher power point
... Newton’s First law of Motion I. Every object in a state of uniform motion tends to remain in that state of motion unless an external force is applied to it. Newton's Second Law of Motion: II. The relationship between an object's mass m, its acceleration a, and the applied force F is F = ma. Accelera ...
... Newton’s First law of Motion I. Every object in a state of uniform motion tends to remain in that state of motion unless an external force is applied to it. Newton's Second Law of Motion: II. The relationship between an object's mass m, its acceleration a, and the applied force F is F = ma. Accelera ...
Newton`s Second Law:
... During his training, 50lbs mock-up with a mass of 23kg was used Although this strategy effectively simulated the reduced weight, it did not correctly mimic the unchanging mass It was more difficult to accelerate the 135 kg unit (perhaps by jumping or twisting suddenly) on the moon than it was to acc ...
... During his training, 50lbs mock-up with a mass of 23kg was used Although this strategy effectively simulated the reduced weight, it did not correctly mimic the unchanging mass It was more difficult to accelerate the 135 kg unit (perhaps by jumping or twisting suddenly) on the moon than it was to acc ...
impulse - sportscoachinghigher
... When the force of gravity acts on a body, it acts through the centre of gravity and always moves towards the centre of the earth. Symmetrical objects like balls and cubes have their CoG in the exact centre of the object. Objects are 3 dimensional, so the CoG will be at the point where the axes of al ...
... When the force of gravity acts on a body, it acts through the centre of gravity and always moves towards the centre of the earth. Symmetrical objects like balls and cubes have their CoG in the exact centre of the object. Objects are 3 dimensional, so the CoG will be at the point where the axes of al ...
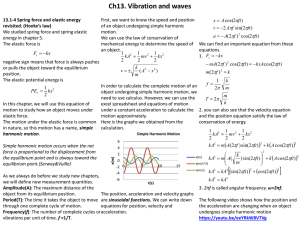
13.1-4 Spring force and elastic energy revisited. (Hooke’s law)
... excel spreadsheet and equations of motion motion to study how an object moves under under a constant acceleration to calculate the 2. you can also see that the velocity equation elastic force. motion approximately. and the position equation satisfy the law of The motion under the elastic force is co ...
... excel spreadsheet and equations of motion motion to study how an object moves under under a constant acceleration to calculate the 2. you can also see that the velocity equation elastic force. motion approximately. and the position equation satisfy the law of The motion under the elastic force is co ...
Document
... When the force of gravity acts on a body, it acts through the centre of gravity and always moves towards the centre of the earth. Symmetrical objects like balls and cubes have their CoG in the exact centre of the object. Objects are 3 dimensional, so the CoG will be at the point where the axes of al ...
... When the force of gravity acts on a body, it acts through the centre of gravity and always moves towards the centre of the earth. Symmetrical objects like balls and cubes have their CoG in the exact centre of the object. Objects are 3 dimensional, so the CoG will be at the point where the axes of al ...
Student Notes
... motion unless outsides forces act upon it - Sometimes referred to as the “Law of Inertia” - INTERTIA ...
... motion unless outsides forces act upon it - Sometimes referred to as the “Law of Inertia” - INTERTIA ...
Force Worksheet
... 6) A dancer lifts his partner above his head with an acceleration of 2.8m/s2. The dancer exerts a force of 230N. What is the mass of the partner? ...
... 6) A dancer lifts his partner above his head with an acceleration of 2.8m/s2. The dancer exerts a force of 230N. What is the mass of the partner? ...

![Multiple choice questions [60 points]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002785313_1-b2734444f348f25d9b46ea15f542520b-300x300.png)