Chapter 6 Forces in Motion
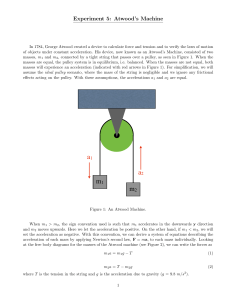
... • As an object falls, air resistance continues to increase until it exactly matches the downward force of gravity. The object has then reached its terminal velocity…or a net force of zero ...
... • As an object falls, air resistance continues to increase until it exactly matches the downward force of gravity. The object has then reached its terminal velocity…or a net force of zero ...
What makes one thing more energy efficient than another. Energy
... on it and changes the current motion 2. Force is always equal to the mass of the object times the acceleration 3. for every force applied to an object the object will apply an equal counter force ...
... on it and changes the current motion 2. Force is always equal to the mass of the object times the acceleration 3. for every force applied to an object the object will apply an equal counter force ...
Unit 4 SG
... 5. Draw a velocity versus time graph showing the following: A zebra moves from rest to a constant speed of 2 m/s for 2 seconds, then it stops for 4 seconds to drink water, and then takes off running at 4 m/s for 2 ...
... 5. Draw a velocity versus time graph showing the following: A zebra moves from rest to a constant speed of 2 m/s for 2 seconds, then it stops for 4 seconds to drink water, and then takes off running at 4 m/s for 2 ...
Newton`s Laws
... an object is directly related to the net force and inversely related to its mass. When figuring the acceleration of object, there are two factors to consider - force and mass. The elephant experiences a much greater force which will produce larger accelerations. BUT the mass of an object resists acc ...
... an object is directly related to the net force and inversely related to its mass. When figuring the acceleration of object, there are two factors to consider - force and mass. The elephant experiences a much greater force which will produce larger accelerations. BUT the mass of an object resists acc ...
Physics 130 - UND: University of North Dakota
... HW 10/9 “Skidding Objects” due Friday 10/11 Exam 2 Thursday, 10/17 5-7 Wit 116 6-8 Wit 114 (only if needed) Please send email if other time needed ...
... HW 10/9 “Skidding Objects” due Friday 10/11 Exam 2 Thursday, 10/17 5-7 Wit 116 6-8 Wit 114 (only if needed) Please send email if other time needed ...
Physics 130 - University of North Dakota
... g is always a “field strength”, not an acceleration! It tells us how much force (in Newtons) is on an object and depends on the object’s mass. Weight = mass x g W = mg An object in free fall (or in projectile motion) has only the weight force on it as nothing else is touching it. ...
... g is always a “field strength”, not an acceleration! It tells us how much force (in Newtons) is on an object and depends on the object’s mass. Weight = mass x g W = mg An object in free fall (or in projectile motion) has only the weight force on it as nothing else is touching it. ...
Simple Harmonic Motion
... Simple Harmonic Motion Definitions of Terms • Amplitude = A = the maximum displacement of the moving object from its equilibrium position. • (unit = m) • Period = T = the time it takes the object to complete one full cycle of motion. • (unit = s) • Frequency = f = the number of cycles or vibration ...
... Simple Harmonic Motion Definitions of Terms • Amplitude = A = the maximum displacement of the moving object from its equilibrium position. • (unit = m) • Period = T = the time it takes the object to complete one full cycle of motion. • (unit = s) • Frequency = f = the number of cycles or vibration ...
5.2 Newton`s First Law
... Motion only changes through the action of a net force. If the net force is zero – there can be no changes in motion. ...
... Motion only changes through the action of a net force. If the net force is zero – there can be no changes in motion. ...
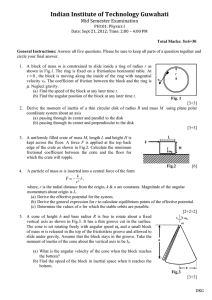
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
... Date: Sept 21, 2012; Time: 2:00 – 4:00 PM Total Marks: 5×6=30 ...
... Date: Sept 21, 2012; Time: 2:00 – 4:00 PM Total Marks: 5×6=30 ...