
Hooke`s Law Simple Harmonic Motion
... It is possible to compensate for the loss of energy in a damped system by applying an external sinusoidal force (with angular frequency ω) The amplitude of the motion remains constant if the energy input per cycle exactly equals the decrease in mechanical energy in each cycle that results from resis ...
... It is possible to compensate for the loss of energy in a damped system by applying an external sinusoidal force (with angular frequency ω) The amplitude of the motion remains constant if the energy input per cycle exactly equals the decrease in mechanical energy in each cycle that results from resis ...
AB_Activity_03
... lab problem: Force and Motion. It is the first lab that addresses the physics concept of force. This particular set of solutions was from 2004. During the semester you will collect your students’ answers to the lab problem warm-up questions 1-2 days prior to teaching the lab. Collecting the answers ...
... lab problem: Force and Motion. It is the first lab that addresses the physics concept of force. This particular set of solutions was from 2004. During the semester you will collect your students’ answers to the lab problem warm-up questions 1-2 days prior to teaching the lab. Collecting the answers ...
Chapter 7:Rotation of a Rigid Body
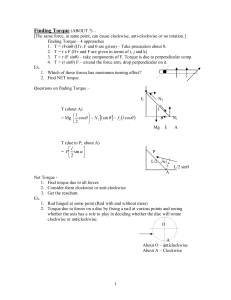
... counterbalanced by a body of weight, W1 as shown in Figure 8.9. If the mass of the beam is 3.0 kg, calculate a. the weight, W1 needed, b. the force exerted on the beam at point O. ...
... counterbalanced by a body of weight, W1 as shown in Figure 8.9. If the mass of the beam is 3.0 kg, calculate a. the weight, W1 needed, b. the force exerted on the beam at point O. ...
Projectile Motion
... Many would insist that there is a horizontal force acting upon the ball since it has a horizontal motion. This is simply not the case. The horizontal motion of the ball is the result of its own inertia. When projected from the truck, the ball already possessed a horizontal motion, and thus will main ...
... Many would insist that there is a horizontal force acting upon the ball since it has a horizontal motion. This is simply not the case. The horizontal motion of the ball is the result of its own inertia. When projected from the truck, the ball already possessed a horizontal motion, and thus will main ...
Momentum
... earlier unit, a vector quantity is a quantity which is fully described by both magnitude and direction. To fully describe the momentum of a 5-kg bowling ball moving westward at 2 m/s, you must include information about both the magnitude and the direction of the bowling ball. It is not enough to say ...
... earlier unit, a vector quantity is a quantity which is fully described by both magnitude and direction. To fully describe the momentum of a 5-kg bowling ball moving westward at 2 m/s, you must include information about both the magnitude and the direction of the bowling ball. It is not enough to say ...
Chapter 4: Forces and Newton`s Laws of Motion
... The free body diagram (FBD) is a simplified representation of an object, and the forces acting on it. It is called free because the diagram will show the object without its surroundings; i.e. the body is “free” of its environment. We will consider only the forces acting on our object of interest. Th ...
... The free body diagram (FBD) is a simplified representation of an object, and the forces acting on it. It is called free because the diagram will show the object without its surroundings; i.e. the body is “free” of its environment. We will consider only the forces acting on our object of interest. Th ...
Wednesday, Mar. 27, 2002
... Since the individual angular momentum can change, the total angular momentum of the system can change. Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let’s consider a two particle system ...
... Since the individual angular momentum can change, the total angular momentum of the system can change. Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let’s consider a two particle system ...
PHYSICS 231 Review problems for midterm 1
... Use 2) for rock 1 (upward) and realize that y(t)=0 when the rock lands: 0 = 100 + 15t-0.5x9.81t2 t=6.27 s (quadratic equation, disregard negative answer) Use 2 for rock 2 (dropped) to find the time it takes to reach the ground 0=100 +0t -0.5x9.81t2 t=4.515 s. So if he drops rock 2 6.27-4.52=1.75 s l ...
... Use 2) for rock 1 (upward) and realize that y(t)=0 when the rock lands: 0 = 100 + 15t-0.5x9.81t2 t=6.27 s (quadratic equation, disregard negative answer) Use 2 for rock 2 (dropped) to find the time it takes to reach the ground 0=100 +0t -0.5x9.81t2 t=4.515 s. So if he drops rock 2 6.27-4.52=1.75 s l ...
PSE4_Lecture_Ch11 - Angular Momentum
... Conceptual Example 11-7: A particle’s angular momentum. What is the angular momentum of a particle of mass m moving with speed v in a circle of radius r in a counterclockwise direction? ...
... Conceptual Example 11-7: A particle’s angular momentum. What is the angular momentum of a particle of mass m moving with speed v in a circle of radius r in a counterclockwise direction? ...
Playing with Pulleys!
... a. What is the uncertainty in your results for mechanical advantage and efficiency? b. What is the relationship between the number of supporting ropes and the mechanical advantage? c. Why would someone want to use a single fixed pulley if there is no mechanical advantage? d. As the number of pulleys ...
... a. What is the uncertainty in your results for mechanical advantage and efficiency? b. What is the relationship between the number of supporting ropes and the mechanical advantage? c. Why would someone want to use a single fixed pulley if there is no mechanical advantage? d. As the number of pulleys ...
















![04 Forces WS08 [v6.0]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017538421_1-2d2da7feadc016eec54eb7cdf19da8aa-300x300.png)




