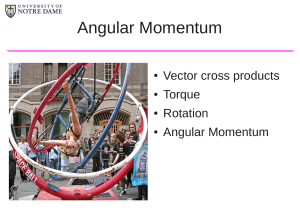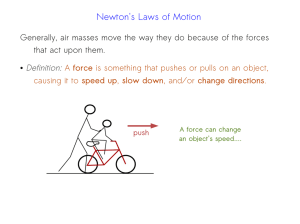
Newtons` First and Second Laws
... At this level students will takes notes on Newton’s Second Law of motion. While they are taking notes I will make connections to their labs and everyday life. Specifically I will explain to them F=ma and specifically what acceleration is. How Force is required to accelerate something. Students will ...
... At this level students will takes notes on Newton’s Second Law of motion. While they are taking notes I will make connections to their labs and everyday life. Specifically I will explain to them F=ma and specifically what acceleration is. How Force is required to accelerate something. Students will ...
SPRING 2016 PHYS 1211 (as of Jan. 11/2016)
... 4. Re-read chapter carefully after class. 5. Do assigned homework. 6. Solve as many end-of-chapter problems as possible. 7. Concepts first. Do NOT plug-and-chug. 8. Use a buddy system: find a friend with whom to discuss physics. 9. Think about physics on a regular basis. 10. If everything fails, con ...
... 4. Re-read chapter carefully after class. 5. Do assigned homework. 6. Solve as many end-of-chapter problems as possible. 7. Concepts first. Do NOT plug-and-chug. 8. Use a buddy system: find a friend with whom to discuss physics. 9. Think about physics on a regular basis. 10. If everything fails, con ...
Chapter 1
... C4. Consider the sine of any angle between 30° and 40°. If the angle were doubled, what would happen to the sine of the angle? a. It would double. b. It would more than double. c. It would increase but be less than double. d. In different cases, it could do any of the above. C5. There are other ways ...
... C4. Consider the sine of any angle between 30° and 40°. If the angle were doubled, what would happen to the sine of the angle? a. It would double. b. It would more than double. c. It would increase but be less than double. d. In different cases, it could do any of the above. C5. There are other ways ...
Introduction to Modern Physics PHYX 2710
... • Fancy Science: Vector analysis of complex force problems is facilitated by use of a free body diagram. • Common Sense: A picture is worth a 100 words. (A scale picture is worth an A!) • Key is to: • Isolate a single body and draw all the forces acting on it. • Add up all the arrows (vectors). Intr ...
... • Fancy Science: Vector analysis of complex force problems is facilitated by use of a free body diagram. • Common Sense: A picture is worth a 100 words. (A scale picture is worth an A!) • Key is to: • Isolate a single body and draw all the forces acting on it. • Add up all the arrows (vectors). Intr ...
1301Lab7 - U of M Physics
... Describing rotations requires applying the physics concepts you have already been studying – position, velocity, acceleration, force, mass, kinetic energy, and momentum to objects that can rotate. However, as we have seen, a modified set of kinematic quantities is sometimes easier to apply to object ...
... Describing rotations requires applying the physics concepts you have already been studying – position, velocity, acceleration, force, mass, kinetic energy, and momentum to objects that can rotate. However, as we have seen, a modified set of kinematic quantities is sometimes easier to apply to object ...
Forces and Motion Scripted - UTeach Outreach
... velocity in the absence of external forces. Here, the wooden block has zero velocity, and without an external force it will never change. Image from Forces and Motion simulation The modern equations of motion proposed by Sir Isaac Newton (1643 – 1727) in 1686 form the basis of classical mechanics, t ...
... velocity in the absence of external forces. Here, the wooden block has zero velocity, and without an external force it will never change. Image from Forces and Motion simulation The modern equations of motion proposed by Sir Isaac Newton (1643 – 1727) in 1686 form the basis of classical mechanics, t ...
Impulse and Momentum
... Impulse and Momentum • Objectives – Compare the system before and after an event in momentum problems – Define the momentum of an object – Determine the impulse given to an object – Recognize that impulse equals the change in momentum of an object ...
... Impulse and Momentum • Objectives – Compare the system before and after an event in momentum problems – Define the momentum of an object – Determine the impulse given to an object – Recognize that impulse equals the change in momentum of an object ...
Ch6 - Force and Motion-II
... Two specially prepared metal surfaces can cold-weld together and become impossible to slide, because there is so much contact between the surfaces Greater force normal to the contact plane increases the friction because the surfaces are pressed together and make ...
... Two specially prepared metal surfaces can cold-weld together and become impossible to slide, because there is so much contact between the surfaces Greater force normal to the contact plane increases the friction because the surfaces are pressed together and make ...
Section Check
... Newton’s 3rd law tell you that there must be a second horizontal force acting on the couch, one that opposes your force and is equal in size. This force is static friction, which is the force exerted on one surface by another when there is no motion between the two. ...
... Newton’s 3rd law tell you that there must be a second horizontal force acting on the couch, one that opposes your force and is equal in size. This force is static friction, which is the force exerted on one surface by another when there is no motion between the two. ...
Period 5 Activity Sheet Solutions: Forces and Newton’s Laws
... by forming the ratio of the force required to drag the cart divided by the weight of the cart. Coefficient of friction = force to pull cart across smooth board weight of cart 4) Drag the cart upside down at a constant velocity across the rough board. How much force is required to move the cart at a ...
... by forming the ratio of the force required to drag the cart divided by the weight of the cart. Coefficient of friction = force to pull cart across smooth board weight of cart 4) Drag the cart upside down at a constant velocity across the rough board. How much force is required to move the cart at a ...
Unit 4 Packet (Labs)
... 2. What would happen to your experimental results if you entered the wrong mass for the ball in this experiment? 3. Predict what would happen in a similar experiment using a bouncing ball. To do this, you would mount the Motion Detector high and pointed downward so it can follow the ball through sev ...
... 2. What would happen to your experimental results if you entered the wrong mass for the ball in this experiment? 3. Predict what would happen in a similar experiment using a bouncing ball. To do this, you would mount the Motion Detector high and pointed downward so it can follow the ball through sev ...
Word Format
... your knees. In order for you to stand, it is necessary that the friction between bones of the knee be very large otherwise you would wobble like a newborn colt. However, you require a much smaller frictional force between the knee joints in order to walk. The knee changes its frictional force by sec ...
... your knees. In order for you to stand, it is necessary that the friction between bones of the knee be very large otherwise you would wobble like a newborn colt. However, you require a much smaller frictional force between the knee joints in order to walk. The knee changes its frictional force by sec ...