Chapter 22 Three Dimensional Rotations and Gyroscopes
... Most of the examples and applications we have considered concerned the rotation of rigid bodies about a fixed axis. However, there are many examples of rigid bodies that rotate about an axis that is changing its direction. A turning bicycle wheel, a gyroscope, the earth’s precession about its axis, ...
... Most of the examples and applications we have considered concerned the rotation of rigid bodies about a fixed axis. However, there are many examples of rigid bodies that rotate about an axis that is changing its direction. A turning bicycle wheel, a gyroscope, the earth’s precession about its axis, ...
Physics 121C Mechanics
... Work Done by a Constant Force If there is more than one force acting on an object, we can find the work done by each force, and also the work done by the net force: ...
... Work Done by a Constant Force If there is more than one force acting on an object, we can find the work done by each force, and also the work done by the net force: ...
Ch4 - Department of Engineering and Physics
... • Every body in the universe attracts every other body with a mutually attracting force. • For two bodies, this force is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance separating them, m1 m2 F=G ...
... • Every body in the universe attracts every other body with a mutually attracting force. • For two bodies, this force is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance separating them, m1 m2 F=G ...
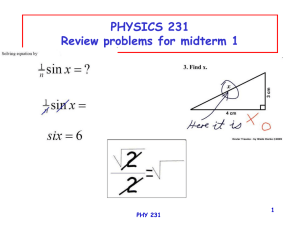
PHYSICS 231 Review problems for midterm 1 1 PHY 231
... Initially, the velocity is pointing up, but is decreasing in magnitude (speed is decreasing) since the gravitational force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the spee ...
... Initially, the velocity is pointing up, but is decreasing in magnitude (speed is decreasing) since the gravitational force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the spee ...
report
... When a ball is at rest the only force applied on it is static friction. This is the friction (force that resists relative motion) that exists between a stationary object and the surface on which it is resting. When this occurs, there is no pushing or pulling force, the forces are balanced, thus no a ...
... When a ball is at rest the only force applied on it is static friction. This is the friction (force that resists relative motion) that exists between a stationary object and the surface on which it is resting. When this occurs, there is no pushing or pulling force, the forces are balanced, thus no a ...
AP Physics Review - stoweschools.com
... Weight = Force due to Gravity = product of mass and acceleration due to gravity Universal Gravitational Force is directly proportional to the universal gravitational constant, the mass of one object, the mass of another object and inversely proportional to the distance between the center of the obje ...
... Weight = Force due to Gravity = product of mass and acceleration due to gravity Universal Gravitational Force is directly proportional to the universal gravitational constant, the mass of one object, the mass of another object and inversely proportional to the distance between the center of the obje ...