Document
... Example : Two boxes and a pulley. Two boxes are connected by a cord running over a pulley. The coefficient of kinetic friction between box A and the table is 0.20. We ignore the mass of the cord and pulley and any friction in the pulley, which means we can assume that a force applied to one end of ...
... Example : Two boxes and a pulley. Two boxes are connected by a cord running over a pulley. The coefficient of kinetic friction between box A and the table is 0.20. We ignore the mass of the cord and pulley and any friction in the pulley, which means we can assume that a force applied to one end of ...
PPT
... Restating Newton’s Second Law “The rate of change of momentum of an object is equal to the net force applied to it” ...
... Restating Newton’s Second Law “The rate of change of momentum of an object is equal to the net force applied to it” ...
introduction and basic concepts
... The unit kilogram (kg) is the mass unit in the SI system, and it is sometimes called kg-mass, whereas kgforce (kgf) is a force unit. One kg-force is the force required to accelerate a 1-kg mass by 9.807 m/s2. In other words, the weight of 1-kg mass at sea level on earth is 1 kg-force. Discussion dim ...
... The unit kilogram (kg) is the mass unit in the SI system, and it is sometimes called kg-mass, whereas kgforce (kgf) is a force unit. One kg-force is the force required to accelerate a 1-kg mass by 9.807 m/s2. In other words, the weight of 1-kg mass at sea level on earth is 1 kg-force. Discussion dim ...
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Shahrood University of
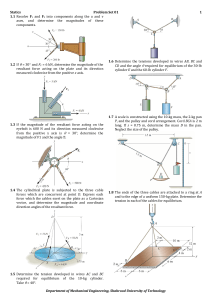
... = 0.6 at B. Neglect the friction are weight of the blocks. 7.6 The truck has a mass of 1.25 Mg and a center of mass at G. Determine the greatest load it can pull if (a) the truck has rear-wheel drive while the front wheels are free to roll, and (b) the truck has four-wheel drive. The coefficient of ...
... = 0.6 at B. Neglect the friction are weight of the blocks. 7.6 The truck has a mass of 1.25 Mg and a center of mass at G. Determine the greatest load it can pull if (a) the truck has rear-wheel drive while the front wheels are free to roll, and (b) the truck has four-wheel drive. The coefficient of ...
AP Physics C - Mechanics Spring and a Block
... elastic spring that is extended from its equilibrium (rest position - where it is neither stretched nor compressed). If the spring is stretched in the positive x direction, a restorative force will act to bring it back to its equilibrium point - a negative force: ...
... elastic spring that is extended from its equilibrium (rest position - where it is neither stretched nor compressed). If the spring is stretched in the positive x direction, a restorative force will act to bring it back to its equilibrium point - a negative force: ...
chapter11
... A non-zero torque produces a change in the angular momentum The result of the change in angular momentum is a precession about the z axis The direction of the angular momentum is changing The precessional motion is the motion of the symmetry axis about the vertical The precession is usually slow rel ...
... A non-zero torque produces a change in the angular momentum The result of the change in angular momentum is a precession about the z axis The direction of the angular momentum is changing The precessional motion is the motion of the symmetry axis about the vertical The precession is usually slow rel ...
FINAL EXAM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS
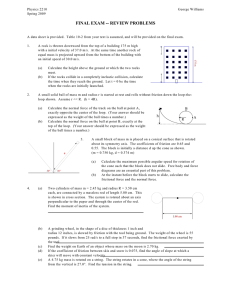
... A block of mass m is given an initial velocity by the spring. The spring has a spring constant k, and is squeezed 0.200 m when the block is at A. Between A and B the slope has friction coefficients :s = 0.75 and :k = 0.65. After point B the system is frictionless. The block goes around the circular ...
... A block of mass m is given an initial velocity by the spring. The spring has a spring constant k, and is squeezed 0.200 m when the block is at A. Between A and B the slope has friction coefficients :s = 0.75 and :k = 0.65. After point B the system is frictionless. The block goes around the circular ...
Force and Motion
... The book was initially moving forward (because it was on a moving bus). When the bus stopped, the book continued moving forward, which was its initial state of motion, and therefore it slid forward off the seat. Follow-up: What is the force that usually keeps the book on the seat? ...
... The book was initially moving forward (because it was on a moving bus). When the bus stopped, the book continued moving forward, which was its initial state of motion, and therefore it slid forward off the seat. Follow-up: What is the force that usually keeps the book on the seat? ...
Kinetic Energy and Work
... masses) can be thought of as having two components: kinetic and potential – Kinetic energy is energy of motion – Potential energy is energy of position ...
... masses) can be thought of as having two components: kinetic and potential – Kinetic energy is energy of motion – Potential energy is energy of position ...
Ex 1 - SharpSchool
... McMurray to Edmonton. It encounters a wind velocity of 43.2 km/h. What is the velocity of the airplane relative to an observer on the ground if, 1) the wind is south wind blowing to the north. ...
... McMurray to Edmonton. It encounters a wind velocity of 43.2 km/h. What is the velocity of the airplane relative to an observer on the ground if, 1) the wind is south wind blowing to the north. ...
SPH4U: Forces
... Reason. Emmy says, “Since the skydiver is moving downwards, the net force should be downwards.” Do you agree or disagree with Emmy? Explain. ...
... Reason. Emmy says, “Since the skydiver is moving downwards, the net force should be downwards.” Do you agree or disagree with Emmy? Explain. ...
here.
... m (E − V(x )) One may wonder how this formula for energy arose from Newton’s equation. Let us consider one degree of freedom. We wish to integrate m ẍ = − dV dx with respect to time in order to solve the equation of motion. To do so we notice that ẋ is an integrating factor. For, multiplying the e ...
... m (E − V(x )) One may wonder how this formula for energy arose from Newton’s equation. Let us consider one degree of freedom. We wish to integrate m ẍ = − dV dx with respect to time in order to solve the equation of motion. To do so we notice that ẋ is an integrating factor. For, multiplying the e ...