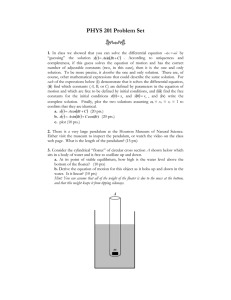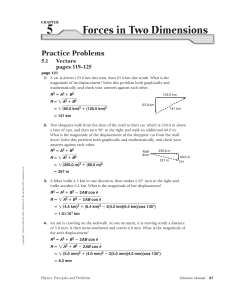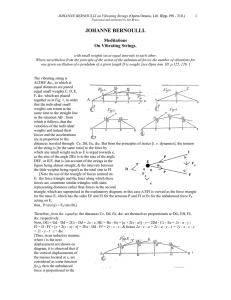
Mechanics Practice Problem Set
... a constant rate of 5.86 m/s2 until he comes to rest. If the cliff is 36.0 meters away, by how much does he overshoot the edge? Answer: 17.3 m 8. A rocket traveling at 88 m/s is accelerated to 132 m/s over a 15 second interval. What is its displacement in this time? Answer: 1650 m 9. A car sits in an ...
... a constant rate of 5.86 m/s2 until he comes to rest. If the cliff is 36.0 meters away, by how much does he overshoot the edge? Answer: 17.3 m 8. A rocket traveling at 88 m/s is accelerated to 132 m/s over a 15 second interval. What is its displacement in this time? Answer: 1650 m 9. A car sits in an ...
Review test # 2
... d. This cannot be determined without further information. The difference between speed and velocity is that velocity includes a. direction. c. time. b. distance. d. weight. Acceleration is defined as the change in velocity divided by a. speed. c. time. b. final velocity. d. distance. The SI unit for ...
... d. This cannot be determined without further information. The difference between speed and velocity is that velocity includes a. direction. c. time. b. distance. d. weight. Acceleration is defined as the change in velocity divided by a. speed. c. time. b. final velocity. d. distance. The SI unit for ...
momentum - Mrs. Brenner`s Biology
... Angular Momentum (Cont.) • Just as the linear momentum of an object changes when an impulse acts on it, the angular momentum of an object changes when an angular impulse acts on it. • Thus, the angular impulse on the object is equal to the change in the object’s angular momentum, which is called the ...
... Angular Momentum (Cont.) • Just as the linear momentum of an object changes when an impulse acts on it, the angular momentum of an object changes when an angular impulse acts on it. • Thus, the angular impulse on the object is equal to the change in the object’s angular momentum, which is called the ...
Gr 12 Physics Exam - Sample for Review
... a. a frozen turkey is carried upstairs b. a frozen turkey is carried on level ground c. a frozen turkey is dropped d. a frozen turkey is carried downstairs e. a frozen turkey is fired from a cannon ____ 47. When an object doubles its speed, the kinetic energy increases by a factor of a. 1 ...
... a. a frozen turkey is carried upstairs b. a frozen turkey is carried on level ground c. a frozen turkey is dropped d. a frozen turkey is carried downstairs e. a frozen turkey is fired from a cannon ____ 47. When an object doubles its speed, the kinetic energy increases by a factor of a. 1 ...
Chapter 7: Linear Momentum and Collisions
... 10. The total momentum of two moving objects can be zero because momentum is a vector, and two equal and opposite momenta will cancel each other. However, kinetic energy is a scalar quantity, and two moving objects will each have nonzero, positive kinetic energy that cannot cancel. Therefore, it doe ...
... 10. The total momentum of two moving objects can be zero because momentum is a vector, and two equal and opposite momenta will cancel each other. However, kinetic energy is a scalar quantity, and two moving objects will each have nonzero, positive kinetic energy that cannot cancel. Therefore, it doe ...
Chapter 1
... publisher, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms. More information on this license is available at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/ Material excluded and rights reserved Some material in this publication is not being made available under the term ...
... publisher, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms. More information on this license is available at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/ Material excluded and rights reserved Some material in this publication is not being made available under the term ...