Newton`s Second Law
... Newton's first law of motion predicts the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are Teacher's Guide balanced. The first law - sometimes referred to as the law of inertia - states that if the forces acting upon an object are balanced, then the acceleration of that object will be 0 m/s/s. ...
... Newton's first law of motion predicts the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are Teacher's Guide balanced. The first law - sometimes referred to as the law of inertia - states that if the forces acting upon an object are balanced, then the acceleration of that object will be 0 m/s/s. ...
27. Gravitation
... field for different bodies Gravitational field E due to a spherical shell of mass M and radius R at a point distant r from the centre. (a) When r > R ...
... field for different bodies Gravitational field E due to a spherical shell of mass M and radius R at a point distant r from the centre. (a) When r > R ...
Non-Linear Motion
... • However, for very long range projectiles the curvature of Earth’s surface must be taken into account. • If an object is projected fast enough, it will fall around the Earth and become an Earth satellite. • An Earth satellite, such as the space shuttle or the moon, is simply a projectile traveling ...
... • However, for very long range projectiles the curvature of Earth’s surface must be taken into account. • If an object is projected fast enough, it will fall around the Earth and become an Earth satellite. • An Earth satellite, such as the space shuttle or the moon, is simply a projectile traveling ...
Chapter 8 and 9 Study Guide 2016-2017
... Suppose a girl is standing on a pond where there is no friction between her feet and the ice. In order to get off the ice, she can a. bend over touching the ice in front of her and then bring her feet to her hands. b. walk very slowly on tiptoe. c. get on her hands and knees and crawl off the ice. ...
... Suppose a girl is standing on a pond where there is no friction between her feet and the ice. In order to get off the ice, she can a. bend over touching the ice in front of her and then bring her feet to her hands. b. walk very slowly on tiptoe. c. get on her hands and knees and crawl off the ice. ...
TAKS Physics Review (Objective 5)
... The student knows the effects of waves on everyday life. The student is expected to (A) demonstrate wave types and their characteristics through a variety of activities such as modeling with ropes and coils, activating tuning forks, and interpreting data on seismic waves. (10th only) (B) demonstrate ...
... The student knows the effects of waves on everyday life. The student is expected to (A) demonstrate wave types and their characteristics through a variety of activities such as modeling with ropes and coils, activating tuning forks, and interpreting data on seismic waves. (10th only) (B) demonstrate ...
Chapter 8 and 9 Study Guide
... 2. A 30-kg girl and a 50-kg boy face each other on friction-free roller skates. The girl pushes the boy, who moves away at a speed of 3 m/s. What is the girl's speed? 3. A 40-kg football player leaps through the air to collide with and tackle a 50-kg player heading toward him, also in the air. If th ...
... 2. A 30-kg girl and a 50-kg boy face each other on friction-free roller skates. The girl pushes the boy, who moves away at a speed of 3 m/s. What is the girl's speed? 3. A 40-kg football player leaps through the air to collide with and tackle a 50-kg player heading toward him, also in the air. If th ...
P1710_MWF09
... • Newton’s Laws of Motion are: (1) Acceleration (or deceleration) occurs if and only if there is a net external force. (2) a = F/m [Note this is a vector eqn.] (3) The force exerted by a first object on a second is always equal and opposite the the force exerted by the second on the first. F12 = ...
... • Newton’s Laws of Motion are: (1) Acceleration (or deceleration) occurs if and only if there is a net external force. (2) a = F/m [Note this is a vector eqn.] (3) The force exerted by a first object on a second is always equal and opposite the the force exerted by the second on the first. F12 = ...
Slide 1
... • For the spring example, the mass is pulled down to y = -A and then released. • Two forces are working on the mass: gravity (weight) and the spring. ...
... • For the spring example, the mass is pulled down to y = -A and then released. • Two forces are working on the mass: gravity (weight) and the spring. ...
Document
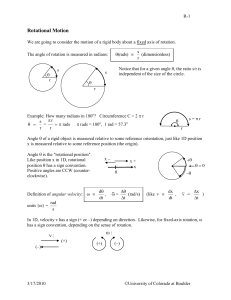
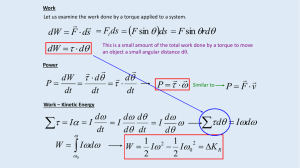
... The majority of motion we have been discussing is translational motion. We have recently been exploring rotational motion. Now we will look at both together. If a wheel is placed on a flat surface and a force is applied at the center of the wheel what will it do? It will translate and rotate. Why do ...
... The majority of motion we have been discussing is translational motion. We have recently been exploring rotational motion. Now we will look at both together. If a wheel is placed on a flat surface and a force is applied at the center of the wheel what will it do? It will translate and rotate. Why do ...