Core versus Risk-Based Vaccinations Source: Southern Equine
... mares, weak maladjusted foals at birth, or a neurological form of disease. As with other species of animals, the Herpes virus may establish a unique latent infection in horses. These horses may shed the virus to susceptible animals when their immune system is stressed, making it difficult to control ...
... mares, weak maladjusted foals at birth, or a neurological form of disease. As with other species of animals, the Herpes virus may establish a unique latent infection in horses. These horses may shed the virus to susceptible animals when their immune system is stressed, making it difficult to control ...
Infectious mononucleosis (IM) and Epstein
... Acute infection is characterised by IgM antibodies against the viral capsid, antibodies to EBV early antigen and the initial absence of antibodies to EBV nuclear antigen (anti-EBNA). Seroconversion of anti-EBNA at approximately1 month after the initial illness may confirm the diagnosis in retrospect ...
... Acute infection is characterised by IgM antibodies against the viral capsid, antibodies to EBV early antigen and the initial absence of antibodies to EBV nuclear antigen (anti-EBNA). Seroconversion of anti-EBNA at approximately1 month after the initial illness may confirm the diagnosis in retrospect ...
mikroorganisme penyebab infeksi mata
... lymphatics and veins. Both systemic (chills, fever, malaise, leukocytosis) and local (tenderness, voluntary limitations of extraocular movements) symptoms may arise in periorbital ...
... lymphatics and veins. Both systemic (chills, fever, malaise, leukocytosis) and local (tenderness, voluntary limitations of extraocular movements) symptoms may arise in periorbital ...
STI Handout
... Viral infection/inflammation of the liver 90-95% of adults will recover completely on their own, but 5-10% will develop a chronic liver infection, which increases their risk for liver disease and liver cancer. Hep B is highly infectious and can be transmitted via semen, vaginal fluids, saliva, urine ...
... Viral infection/inflammation of the liver 90-95% of adults will recover completely on their own, but 5-10% will develop a chronic liver infection, which increases their risk for liver disease and liver cancer. Hep B is highly infectious and can be transmitted via semen, vaginal fluids, saliva, urine ...
Bacterial keratitis
... 2 - oral ciprofloxacin : 750 mg t.d may indicated in juxtalimbal ulcer . 3 – Atropine: to prevent formation of posterior synichia 4 – Steroid therapy: reduced necrosis & scar formation Disadvantage: increase risk of perforation and exacerbate infection Viral infection : Herpes simplex keratitis (h.s ...
... 2 - oral ciprofloxacin : 750 mg t.d may indicated in juxtalimbal ulcer . 3 – Atropine: to prevent formation of posterior synichia 4 – Steroid therapy: reduced necrosis & scar formation Disadvantage: increase risk of perforation and exacerbate infection Viral infection : Herpes simplex keratitis (h.s ...
Infections and Infestations Dr Iain Henderson GP Scotstoun Hospital Practitioner, Western Infirmary
... • The itch will continue 4-6 weeks • Repeat treatment one week later – overuse will cause dermatitis • Oral Ivermectin is now considered treatment of choice for crusted scabies and other resistant cases. ...
... • The itch will continue 4-6 weeks • Repeat treatment one week later – overuse will cause dermatitis • Oral Ivermectin is now considered treatment of choice for crusted scabies and other resistant cases. ...
VIRAL INFECTIONS
... Usually this is clinically obvious from the classical appearance of the rash . Aspiration of vesicular fluid and PCR or tissue culture will confirm the diagnosis. Electron microscopy cannot distinguish HSV from VZV. Serological examination for rising titres of antibody is only useful in primar ...
... Usually this is clinically obvious from the classical appearance of the rash . Aspiration of vesicular fluid and PCR or tissue culture will confirm the diagnosis. Electron microscopy cannot distinguish HSV from VZV. Serological examination for rising titres of antibody is only useful in primar ...
Lecture 12 - Viral Diseases 2 slides per page
... attenuated vaccine recently introduced treatment (influenza specific medications) amantadine, rimantadine ‐ interfere with uncoating process neuraminidase inhibitors (Tamiflu, Relenza) ...
... attenuated vaccine recently introduced treatment (influenza specific medications) amantadine, rimantadine ‐ interfere with uncoating process neuraminidase inhibitors (Tamiflu, Relenza) ...
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
... Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD’s) or Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI’s) refer to diseases which are spread by a bacteria or virus that is passed from one person to another during sexual contact or exposure to infected body fluids. Some STI’s are curable, while others are not. Many have seri ...
... Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD’s) or Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI’s) refer to diseases which are spread by a bacteria or virus that is passed from one person to another during sexual contact or exposure to infected body fluids. Some STI’s are curable, while others are not. Many have seri ...
Skin Clinical
... Skin can become infected by microorganisms that spread from another infected site in 3 ways o Direct extension o Hematogeneous Spread o Spread along neurons ...
... Skin can become infected by microorganisms that spread from another infected site in 3 ways o Direct extension o Hematogeneous Spread o Spread along neurons ...
Ch. 19 Warm-up
... What you must know: The components of a virus. The differences between lytic and lysogenic cycles. ...
... What you must know: The components of a virus. The differences between lytic and lysogenic cycles. ...
Human Herpesviruses
... During latent infection: the only region of genome to be trancribed generates latency associated transcripts(LATs) and these RNAs are not translated in protein ...
... During latent infection: the only region of genome to be trancribed generates latency associated transcripts(LATs) and these RNAs are not translated in protein ...
HIV/AIDS M3 lecture - Creighton University
... – Integrity of the exposed site – Type of body fluid – Volume of body fluid ...
... – Integrity of the exposed site – Type of body fluid – Volume of body fluid ...
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease - Alabama Department of Public
... Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease What is Hand, Food, and Mouth Disease (HFMD)? HFMD is a viral disease that affects the hands, feet, and mouth. HFMD usually infects infants and children younger than 5 years old. However, it can sometimes occur in adults. How does HFMD spread? Person-to-person: Di ...
... Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease What is Hand, Food, and Mouth Disease (HFMD)? HFMD is a viral disease that affects the hands, feet, and mouth. HFMD usually infects infants and children younger than 5 years old. However, it can sometimes occur in adults. How does HFMD spread? Person-to-person: Di ...
Session 16 - Teaching Slides
... Herpes simplex (HSV): • Cluster of vesicles which rupture then scab, typically around mouth, anus, genitals • If spread to esophagus, can cause difficulty or pain in swallowing • Possible complications of encephalitis ...
... Herpes simplex (HSV): • Cluster of vesicles which rupture then scab, typically around mouth, anus, genitals • If spread to esophagus, can cause difficulty or pain in swallowing • Possible complications of encephalitis ...
Document
... C. vesicle fluid D. swab from ulcer bed 19. The primary means of spread of varicella zoster virus is: A. direct contact with lesions B. respiratory droplets C. saliva D. fecal-oral route 20. Which of the following viruses causes heterophile antibody-negative mononucleosis? A cytomegalovirus B. Epste ...
... C. vesicle fluid D. swab from ulcer bed 19. The primary means of spread of varicella zoster virus is: A. direct contact with lesions B. respiratory droplets C. saliva D. fecal-oral route 20. Which of the following viruses causes heterophile antibody-negative mononucleosis? A cytomegalovirus B. Epste ...
Sialodacryoadenitis Virus | Charles River Research Animal
... colonies. “Burn out” of an SDAV infection through deliberate spread of infection and cessation of breeding until all rats are infected and have had time to clear the virus has also been shown to be effective for immunocompetent rats. ...
... colonies. “Burn out” of an SDAV infection through deliberate spread of infection and cessation of breeding until all rats are infected and have had time to clear the virus has also been shown to be effective for immunocompetent rats. ...
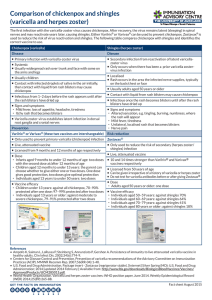
Comparison of chickenpox and shingles (varicella and herpes zoster)
... Rash occurs in the area the infected nerve supplies, typically on the back/chest or face Usually adults aged 50 years or older Contact with liquid from rash blisters may cause chickenpox Infectious once the rash becomes blisters until after the rash blisters have dried up ...
... Rash occurs in the area the infected nerve supplies, typically on the back/chest or face Usually adults aged 50 years or older Contact with liquid from rash blisters may cause chickenpox Infectious once the rash becomes blisters until after the rash blisters have dried up ...
Biohazard Sorting Application Form This form must be filled out
... cannot be started until this application has been reviewed and approved. Additional information may be requested before approval can be considered. Please allow at least one week for the review and approval process to be completed. Date: Project Title: ...
... cannot be started until this application has been reviewed and approved. Additional information may be requested before approval can be considered. Please allow at least one week for the review and approval process to be completed. Date: Project Title: ...
Microbial ecology of the lower genital tract in women with sexually
... changes or physical or emotional stress. When recurrences occur, the virus in a nerve cell (at their latency sites) becomes active and through the axon of the cell reaches the skin, where it infects cells locally entering a new replication cycle (Ryan & Ray, 2004). Symptoms of HSV infection include ...
... changes or physical or emotional stress. When recurrences occur, the virus in a nerve cell (at their latency sites) becomes active and through the axon of the cell reaches the skin, where it infects cells locally entering a new replication cycle (Ryan & Ray, 2004). Symptoms of HSV infection include ...
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES (STDS) A sexually
... Careless consumption of alcohol often leads to unprotected sex with virtual strangers. Even though condom use is increasing, unprotected sex still occurs frequently among international travellers especially those who want to experience the culture of the local people! STDs, which are normally transm ...
... Careless consumption of alcohol often leads to unprotected sex with virtual strangers. Even though condom use is increasing, unprotected sex still occurs frequently among international travellers especially those who want to experience the culture of the local people! STDs, which are normally transm ...
POWERPOINT JEOPARDY
... infection control practices and when they should be used. • Identify at least one problem about the use, overuse or misuse of antibiotics ...
... infection control practices and when they should be used. • Identify at least one problem about the use, overuse or misuse of antibiotics ...
HSV by FS and MB
... URTIvirus spreads to sensory nerve endingstransport to cell bodies and resides theregenome of virus into nucleus of neuronpi of any of three branches of V can result in si in any of branches (backdoor spread)!!! ...
... URTIvirus spreads to sensory nerve endingstransport to cell bodies and resides theregenome of virus into nucleus of neuronpi of any of three branches of V can result in si in any of branches (backdoor spread)!!! ...
Antifungal Drugs
... resistant to acyclovir), CMV (including ganciclovirresistant ones). ADR. Toxicity of foscarnet is high: Kidney damages—renal diabetes-like condition, acute renal Anaemia, phlebitis, tremor, convulsions Neurological as well as constitutional symptoms due to hypocalcaemia ...
... resistant to acyclovir), CMV (including ganciclovirresistant ones). ADR. Toxicity of foscarnet is high: Kidney damages—renal diabetes-like condition, acute renal Anaemia, phlebitis, tremor, convulsions Neurological as well as constitutional symptoms due to hypocalcaemia ...
Herpes simplex
.jpg?width=300)
Herpes simplex (Greek: ἕρπης herpēs, ""creeping"" or ""latent"") is a viral disease caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected. Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups often called cold sores or fever blisters or may just cause a sore throat. Genital herpes, often simply known as herpes, may have minimal symptoms or form blisters that break open and result in small ulcers. These typically heal over two to four weeks. Tingling or shooting pains may occur before the blisters appear. Herpes cycles between periods of active disease followed by periods without symptoms. The first episode is often more severe and may be associated with fever, muscle pains, swollen lymph nodes and headaches. Over time, episodes of active disease decrease in frequency and severity. Other disorders caused by herpes simplex include: herpetic whitlow when it involves the fingers, herpes of the eye, herpes infection of the brain, and neonatal herpes when it affects a newborn, among others.There are two types of herpes simplex virus, type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2). HSV-1 more commonly causes oral infections while HSV-2 more commonly causes genital infections. They are transmitted by direct contact with body fluids or lesions of an infected individual. Transmission may still occur when symptoms are not present. Genital herpes is classified as a sexually transmitted infection. It may be spread to an infant during childbirth. After infection, the viruses are transported along sensory nerves to the nerve cell bodies, where they reside lifelong. Causes of recurrence may include: decreased immune function, stress, and sunlight exposure. Oral and genital herpes is usually diagnosed based on the presenting symptoms. The diagnosis may be confirmed by viral culture or detecting herpes DNA in fluid from blisters. Testing the blood for antibodies against the virus can confirm a previous infection but will be negative in new infections.The most effective method of avoiding genital infections is by avoiding vaginal, oral and anal sex. Condom use decreases the risk somewhat. Daily antiviral medication taken by someone who has the infection can also reduce spread. There is no available vaccine and once infected, there is no cure. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) and topical lidocaine may be used to help with the symptoms. Treatments with antiviral medication such as aciclovir or valaciclovir can lessen the severity of symptomatic episodes.Worldwide rates of either HSV-1 or HSV-2 are between 60% and 95% in adults. HSV-1 is usually acquired during childhood. Rates of both increase as people age. Rates of HSV-1 are between 70% and 80% in populations of low socioeconomic status and 40% to 60% in populations of improved socioeconomic status. An estimated 536 million people worldwide (16% of the population) were infected with HSV-2 as of 2003 with greater rates among women and those in the developing world. Most people with HSV-2 do not realize that they are infected.