I. Introduction to class - Los Angeles Mission College
... Vaccine: Prevents chickenpox in 70-90% of recipients. First dose given between 12 and 18 months, second dose at 4 to 6 years. May help prevent shingles in adults. Adults get two shots 4 to 8 weeks apart. Shingles (Herpes Zoster): Recurrence of latent herpes zoster infection. Epidemiology: Occurs in ...
... Vaccine: Prevents chickenpox in 70-90% of recipients. First dose given between 12 and 18 months, second dose at 4 to 6 years. May help prevent shingles in adults. Adults get two shots 4 to 8 weeks apart. Shingles (Herpes Zoster): Recurrence of latent herpes zoster infection. Epidemiology: Occurs in ...
Health STI/HIV PPT - Gordon State College
... The vaccine now in use requires a series of 3 shots over a one-year period. It has been approved by the FDA and should be covered by most insurance. The American Cancer Society recommends the vaccine for girls when they are 11 or 12, before they begin having sex. It is also recommended as a “catch u ...
... The vaccine now in use requires a series of 3 shots over a one-year period. It has been approved by the FDA and should be covered by most insurance. The American Cancer Society recommends the vaccine for girls when they are 11 or 12, before they begin having sex. It is also recommended as a “catch u ...
Paramyxoviridae family – Lecture Notes
... They are an important cause of respiratory disease Most people are infected by age 5 They cause epidemic and sporadic infections Seasonality: fall and early winter Type 1 & 2 cause epidemics in fall and early winter Type 3 & 4 cause some sort of sporadic infection Stable on surfaces (up to 10 hours) ...
... They are an important cause of respiratory disease Most people are infected by age 5 They cause epidemic and sporadic infections Seasonality: fall and early winter Type 1 & 2 cause epidemics in fall and early winter Type 3 & 4 cause some sort of sporadic infection Stable on surfaces (up to 10 hours) ...
Infection Control
... Cell-Mediated Defenses T-cell system – exposure to antigen causes release into lymph system 1. Helper 2. Cytotoxic 3. Suppressor ...
... Cell-Mediated Defenses T-cell system – exposure to antigen causes release into lymph system 1. Helper 2. Cytotoxic 3. Suppressor ...
Slide 1 - UAB School of Optometry
... Slide 41: These are just some images of VZV. Left: young child with typical chickenpox lesions. Middle: newborn (more severe because of immature immune system). Right: typical case of shingles. Slide 42: For chickenpox in children, normally supportive care is sufficient. There is a vaccine approved. ...
... Slide 41: These are just some images of VZV. Left: young child with typical chickenpox lesions. Middle: newborn (more severe because of immature immune system). Right: typical case of shingles. Slide 42: For chickenpox in children, normally supportive care is sufficient. There is a vaccine approved. ...
Acyclovir infiltrate
... Oral acyclovir 400 mg - 5 times daily for 10 days ; oral acyclovir is the preferred treatment in patients unable to tolerate topical medications. Dermatological emergencies. Erythema multiforme. Authoritative facts about the skin from DermNet New Zealand. Skinnontumor / Clinical dermatology - Herpes ...
... Oral acyclovir 400 mg - 5 times daily for 10 days ; oral acyclovir is the preferred treatment in patients unable to tolerate topical medications. Dermatological emergencies. Erythema multiforme. Authoritative facts about the skin from DermNet New Zealand. Skinnontumor / Clinical dermatology - Herpes ...
STI Powerpoint
... • Infants born to females with HPV may develop warts in their throats, blocking breathing passages, which can be life-threatening. • Warts may not appear for months after infection (virus can still be passed.) • Applications can treat warts but virus remains in body forever. ...
... • Infants born to females with HPV may develop warts in their throats, blocking breathing passages, which can be life-threatening. • Warts may not appear for months after infection (virus can still be passed.) • Applications can treat warts but virus remains in body forever. ...
Common skin infections
... • Measles: caused by Rubeola virus, is a systemic infection characterized by a skin rash. - It is an endemic childhood disease, complications of measles infection can be quite serious (ear infection, respiratory tract infection). - There is no treatment for measles. A vaccine has been available sin ...
... • Measles: caused by Rubeola virus, is a systemic infection characterized by a skin rash. - It is an endemic childhood disease, complications of measles infection can be quite serious (ear infection, respiratory tract infection). - There is no treatment for measles. A vaccine has been available sin ...
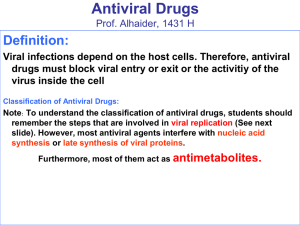
Antiviral Drugs
... They can’t effect human cells because they need viral enzymes, so they are more effective in infective pt ...
... They can’t effect human cells because they need viral enzymes, so they are more effective in infective pt ...
Virus - Kory Trosclair
... Signs are a skin rash similar to measles. Serious cases can cause death from bleeding and lower blood cell counts. Most common in tropical locations (Pacific islands, Latin America). ...
... Signs are a skin rash similar to measles. Serious cases can cause death from bleeding and lower blood cell counts. Most common in tropical locations (Pacific islands, Latin America). ...
Sports Related Skin Infections Position Statement and
... These are viral infections, which are transmitted by skin-to-skin contact. Lesions on exposed areas of skin that are not covered by clothing, uniform or equipment require the player to be withdrawn from any activity that may result in direct skin-to-skin contact with another participant. Covering in ...
... These are viral infections, which are transmitted by skin-to-skin contact. Lesions on exposed areas of skin that are not covered by clothing, uniform or equipment require the player to be withdrawn from any activity that may result in direct skin-to-skin contact with another participant. Covering in ...
Avian Encephalomyelitis
... immunohistochemical staining is a reliable method of diagnosis. The major differential diagnosis for neurologic signs in very young chicks is bacterial or mycotic encephalitis. Rickets and nutritional encephalomalacia are next in the list of differential diagnoses, although the clinical manifestatio ...
... immunohistochemical staining is a reliable method of diagnosis. The major differential diagnosis for neurologic signs in very young chicks is bacterial or mycotic encephalitis. Rickets and nutritional encephalomalacia are next in the list of differential diagnoses, although the clinical manifestatio ...
Document
... Virus in herpes family; Epstein-Barr can cause mononucleosis in adolescents or young adulthood ...
... Virus in herpes family; Epstein-Barr can cause mononucleosis in adolescents or young adulthood ...
Primary varicella infection associated with Steven
... erosions of conjunctiva, mouth and genitilia with skin lesions in the form of erythematous macules, papules and target lesions involving less than 10% of body surface area. Varicella is caused by varicella zoster virus. It is a primary infection with a viraemic stage after which the virus persists i ...
... erosions of conjunctiva, mouth and genitilia with skin lesions in the form of erythematous macules, papules and target lesions involving less than 10% of body surface area. Varicella is caused by varicella zoster virus. It is a primary infection with a viraemic stage after which the virus persists i ...
Virology Seminars Spring 2005 - University of Edinburgh: Virology
... 14th March Frank Jiggins Institute for Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh Genetic variation in the susceptibility of Drosophila to viruses 21st March Alan Barrett University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, Texas West Nile virus 18th April David Blackbourn Institute for Cancer Studies, ...
... 14th March Frank Jiggins Institute for Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh Genetic variation in the susceptibility of Drosophila to viruses 21st March Alan Barrett University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, Texas West Nile virus 18th April David Blackbourn Institute for Cancer Studies, ...
a patient with haemorrhagic bullae
... body, in conjunction with the immunosuppressive treatment, made us think of an opportunistic infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The haemorrhagic aspect was suggested to be caused by the underlying thrombocytopenia, which initially persisted despite therapy with rituximab. A polymerase chai ...
... body, in conjunction with the immunosuppressive treatment, made us think of an opportunistic infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The haemorrhagic aspect was suggested to be caused by the underlying thrombocytopenia, which initially persisted despite therapy with rituximab. A polymerase chai ...
hales_ith15e_powerpoint_lectures_chapter16
... Virus in herpes family; Epstein-Barr can cause mononucleosis in adolescents or young adulthood ...
... Virus in herpes family; Epstein-Barr can cause mononucleosis in adolescents or young adulthood ...
DNA viruses: Adeno-, Pox-Papilloma
... descendant of related marriages – They develop wide spread of scaly macules and papules, particularly on the face, hands and feet – It is typically associated with HPV types 5 and 8 ...
... descendant of related marriages – They develop wide spread of scaly macules and papules, particularly on the face, hands and feet – It is typically associated with HPV types 5 and 8 ...
Communicable Disease Review Game
... Which stage of syphilis causes a skin rash, fever, headaches, sore throat, loss of hair/weight? Primary Secondary Latent Late or tertiary ...
... Which stage of syphilis causes a skin rash, fever, headaches, sore throat, loss of hair/weight? Primary Secondary Latent Late or tertiary ...
Herpes simplex
.jpg?width=300)
Herpes simplex (Greek: ἕρπης herpēs, ""creeping"" or ""latent"") is a viral disease caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected. Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups often called cold sores or fever blisters or may just cause a sore throat. Genital herpes, often simply known as herpes, may have minimal symptoms or form blisters that break open and result in small ulcers. These typically heal over two to four weeks. Tingling or shooting pains may occur before the blisters appear. Herpes cycles between periods of active disease followed by periods without symptoms. The first episode is often more severe and may be associated with fever, muscle pains, swollen lymph nodes and headaches. Over time, episodes of active disease decrease in frequency and severity. Other disorders caused by herpes simplex include: herpetic whitlow when it involves the fingers, herpes of the eye, herpes infection of the brain, and neonatal herpes when it affects a newborn, among others.There are two types of herpes simplex virus, type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2). HSV-1 more commonly causes oral infections while HSV-2 more commonly causes genital infections. They are transmitted by direct contact with body fluids or lesions of an infected individual. Transmission may still occur when symptoms are not present. Genital herpes is classified as a sexually transmitted infection. It may be spread to an infant during childbirth. After infection, the viruses are transported along sensory nerves to the nerve cell bodies, where they reside lifelong. Causes of recurrence may include: decreased immune function, stress, and sunlight exposure. Oral and genital herpes is usually diagnosed based on the presenting symptoms. The diagnosis may be confirmed by viral culture or detecting herpes DNA in fluid from blisters. Testing the blood for antibodies against the virus can confirm a previous infection but will be negative in new infections.The most effective method of avoiding genital infections is by avoiding vaginal, oral and anal sex. Condom use decreases the risk somewhat. Daily antiviral medication taken by someone who has the infection can also reduce spread. There is no available vaccine and once infected, there is no cure. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) and topical lidocaine may be used to help with the symptoms. Treatments with antiviral medication such as aciclovir or valaciclovir can lessen the severity of symptomatic episodes.Worldwide rates of either HSV-1 or HSV-2 are between 60% and 95% in adults. HSV-1 is usually acquired during childhood. Rates of both increase as people age. Rates of HSV-1 are between 70% and 80% in populations of low socioeconomic status and 40% to 60% in populations of improved socioeconomic status. An estimated 536 million people worldwide (16% of the population) were infected with HSV-2 as of 2003 with greater rates among women and those in the developing world. Most people with HSV-2 do not realize that they are infected.