THORACIC & WALL - University of Kansas Medical Center
... Breast extends from 2nd-3rd rib superiorly to 6th-7th costal cartilage inferiorly. Extends from lateral border of sternum to beyond the anterior axillary fold. ...
... Breast extends from 2nd-3rd rib superiorly to 6th-7th costal cartilage inferiorly. Extends from lateral border of sternum to beyond the anterior axillary fold. ...
Disseminated T-cell lymphoma in a guinea pig
... were present in the lymph nodes, spleen, liver, lungs, heart, rhinarium, bone marrow, and kidneys. Bilateral infiltration of the eyes by neoplastic lymphoblasts was noted, which was more extensive on the right. The neoplastic cells stained immunohistochemically as T-lymphocytes using antibodies dire ...
... were present in the lymph nodes, spleen, liver, lungs, heart, rhinarium, bone marrow, and kidneys. Bilateral infiltration of the eyes by neoplastic lymphoblasts was noted, which was more extensive on the right. The neoplastic cells stained immunohistochemically as T-lymphocytes using antibodies dire ...
PAROTID GLANDS - Chennai City Branch Of ASI
... Pain and nodularity Involvement of skin & ulceration Involvement of masseter Involvement of facial nerve Involvement of neck lymph node ...
... Pain and nodularity Involvement of skin & ulceration Involvement of masseter Involvement of facial nerve Involvement of neck lymph node ...
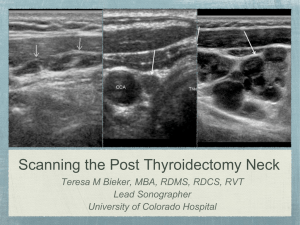
Scanning the Post Thyroidectomy Neck
... If Tg increases, it is likely caused by recurrent tumor Tg Antibodies Present in 20-25% of thyroid cancer patients If antibodies are positive, Tg levels are falsely decreased Tg antibodies typically decrease over several years When disease in present, antibodies can increase Thyroid Stimulating Horm ...
... If Tg increases, it is likely caused by recurrent tumor Tg Antibodies Present in 20-25% of thyroid cancer patients If antibodies are positive, Tg levels are falsely decreased Tg antibodies typically decrease over several years When disease in present, antibodies can increase Thyroid Stimulating Horm ...
Atlas of Procedures in Surgical Oncology: With Critical, Evideence
... node dissection: a prospective randomized study. Breast Cancer Res Treat ...
... node dissection: a prospective randomized study. Breast Cancer Res Treat ...
Bovine mammary glands
... The inguinal canal -orifice in the body cavity in the inguinal region where blood vessels, lymph vessels and nerves enter and leave the body wall to supply the skin in the posterior part of the animal. As the external pudic artery passes out of the body cavity it becomes the mammary artery. Onc ...
... The inguinal canal -orifice in the body cavity in the inguinal region where blood vessels, lymph vessels and nerves enter and leave the body wall to supply the skin in the posterior part of the animal. As the external pudic artery passes out of the body cavity it becomes the mammary artery. Onc ...
Document
... Radula: A toothed chitinous ribbon used for scraping up food into the mouth. Unique to all molluscs except bivalves. Visceral Mass: Dorsal concentration of internal organs. Gills: A large surface-area tissue used for exchanging gases. Found in molluscs with open or closed circulatory systems. ...
... Radula: A toothed chitinous ribbon used for scraping up food into the mouth. Unique to all molluscs except bivalves. Visceral Mass: Dorsal concentration of internal organs. Gills: A large surface-area tissue used for exchanging gases. Found in molluscs with open or closed circulatory systems. ...
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE OF ABDOMEN
... cava near the level of the superior mesenteric artery • Receive lymph from efferent lymphatic vessels from the celiac nodes and superior mesenteric nodes ...
... cava near the level of the superior mesenteric artery • Receive lymph from efferent lymphatic vessels from the celiac nodes and superior mesenteric nodes ...
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE OF ABDOMEN
... aorta and the inferior vena cava near the level of the superior mesenteric artery Receive lymph from efferent lymphatic vessels from the celiac nodes and superior mesenteric nodes ...
... aorta and the inferior vena cava near the level of the superior mesenteric artery Receive lymph from efferent lymphatic vessels from the celiac nodes and superior mesenteric nodes ...
Module 21 / Gross Anatomy of the Integumentary System
... (papillary) and a dense irregular layer (reticular). Both layers of the dermis contain connective tissue components (collagen, elastin, fibroblasts), plus blood vessels, sensory receptors and lymphatics. The dermis is a "functional" layer. The dermis is connective tissue that can stretch and retract ...
... (papillary) and a dense irregular layer (reticular). Both layers of the dermis contain connective tissue components (collagen, elastin, fibroblasts), plus blood vessels, sensory receptors and lymphatics. The dermis is a "functional" layer. The dermis is connective tissue that can stretch and retract ...
Pharynx and Larynx
... The digestive and respiratory systems merge briefly in the pharynx, which is subdivided into nasal, oral, and laryngeal parts. The pharyngeal walls basically consist of three strata: a mucosa, a muscularis, and an adventitia. The most superior part, the nasopharynx, is directly continuous with the n ...
... The digestive and respiratory systems merge briefly in the pharynx, which is subdivided into nasal, oral, and laryngeal parts. The pharyngeal walls basically consist of three strata: a mucosa, a muscularis, and an adventitia. The most superior part, the nasopharynx, is directly continuous with the n ...
1. A woman with breast cancer subsequently develops metastases
... However, these lymphatic channels are not the major way that cancer would be transmitted to the internal vertebral venous plexus. This plexus of veins would be most likely to receive cancer cells transmitted through the blood. The internal thoracic vein drains some blood from the breast, but it woul ...
... However, these lymphatic channels are not the major way that cancer would be transmitted to the internal vertebral venous plexus. This plexus of veins would be most likely to receive cancer cells transmitted through the blood. The internal thoracic vein drains some blood from the breast, but it woul ...
9/30/09 Abdomen Continued Ureters: They are muscular ducts
... arterial branches of the abdominal aorta are described as visceral or parietal and also paired on unpaired. Unpaired visceral arteries include the celiac trunk along with SMA (superiormesenteric artery) & IMS (inferiomesenteric artery). Paired visceral arteries include the suprarenal arteries and th ...
... arterial branches of the abdominal aorta are described as visceral or parietal and also paired on unpaired. Unpaired visceral arteries include the celiac trunk along with SMA (superiormesenteric artery) & IMS (inferiomesenteric artery). Paired visceral arteries include the suprarenal arteries and th ...
ENT_examination
... Onset – course of the disease – other symptoms that may arise from the same organ. - What increase or relieve the symptoms? - History of same disease before. And what medications given and what was the results of investigations? ...
... Onset – course of the disease – other symptoms that may arise from the same organ. - What increase or relieve the symptoms? - History of same disease before. And what medications given and what was the results of investigations? ...
Guidelines for Extremity Examination
... 2-Expose the inguinal region well 3-Palpate above and below the inguinal ligament 4-Examine both sides and comment as mentioned above. Lymph Nodes in the Axilla: 1-Examine the patient from the front 2- Insert his/her right hand into the patient's left axilla 3-The patients arms are adducted and his/ ...
... 2-Expose the inguinal region well 3-Palpate above and below the inguinal ligament 4-Examine both sides and comment as mentioned above. Lymph Nodes in the Axilla: 1-Examine the patient from the front 2- Insert his/her right hand into the patient's left axilla 3-The patients arms are adducted and his/ ...
Exam 1 Study Guide - Dr. Stuart Sumida
... The return of lymphatic fluid to the venous circulation from most of the body is: a) at the junction of the right subclavian and right jugular veins. b) via the thoracic duct. c) into the cysterna chyli. d) at the junction of the right and left brachiocephalic veins. e) greater when a person is calm ...
... The return of lymphatic fluid to the venous circulation from most of the body is: a) at the junction of the right subclavian and right jugular veins. b) via the thoracic duct. c) into the cysterna chyli. d) at the junction of the right and left brachiocephalic veins. e) greater when a person is calm ...
Identifying pericardial recesses on computed tomography : is it
... - Inferiorly : It is attached to the central tendon of the diaphragm - Anteriorly : It is attached to the sternum by the superior and the inferior pericardial ligaments and is covered by the parietal mediastinal pleura Serosal pericardium - A single layer of flat cells on a thin subserosal layer of ...
... - Inferiorly : It is attached to the central tendon of the diaphragm - Anteriorly : It is attached to the sternum by the superior and the inferior pericardial ligaments and is covered by the parietal mediastinal pleura Serosal pericardium - A single layer of flat cells on a thin subserosal layer of ...
segmented.ppt fall 2012
... 3. Intestine: long intestine stretches length of body to aid in digestion of soil 4. Ganglion: brain-like organ 5. Aortic Arches: Heart of worm; really 5 enlarged blood vessels. ...
... 3. Intestine: long intestine stretches length of body to aid in digestion of soil 4. Ganglion: brain-like organ 5. Aortic Arches: Heart of worm; really 5 enlarged blood vessels. ...
Lymph Node Levels
... sternocleidomastoid muscle,, whereas the level V nodes are located posterior p to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Regional lymph node (N) cl classification for all head and neck cancer sites except nasopharynxx aand thyroid cancers. : N1 - <3 cm ipsi N2a - 3-6 cm ipsi single le N2b - 3-6 cm ipsi mul ...
... sternocleidomastoid muscle,, whereas the level V nodes are located posterior p to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Regional lymph node (N) cl classification for all head and neck cancer sites except nasopharynxx aand thyroid cancers. : N1 - <3 cm ipsi N2a - 3-6 cm ipsi single le N2b - 3-6 cm ipsi mul ...
Neck
... Two lobes joined together by an isthmus Excretes hormones Thyroxine (T4)- body growth/ metabolism Triiodothyronine (T3)growth/ metabolism Calcitonin- < blood calcium to promote bone formation ...
... Two lobes joined together by an isthmus Excretes hormones Thyroxine (T4)- body growth/ metabolism Triiodothyronine (T3)growth/ metabolism Calcitonin- < blood calcium to promote bone formation ...
female genitalia
... Vascularization: arterial supply – mostly from the two vaginal arteries; the internal pudendal and the middle rectal arteries can also supply the vagina. Venous drainage – vaginal venous plexuses which drain into the internal iliac veins. Innervation: vaginal nerves derived from the uterovaginal ...
... Vascularization: arterial supply – mostly from the two vaginal arteries; the internal pudendal and the middle rectal arteries can also supply the vagina. Venous drainage – vaginal venous plexuses which drain into the internal iliac veins. Innervation: vaginal nerves derived from the uterovaginal ...
document
... The tissue fluid is mostly taken up by the blood capillaries, partly by the lymphatic capillaries. Composition Lymphatic system consists of the lymph conducting channels, lymphoid tissues and lymphoid organs. Lymph tissues: contain lymphocytes. Diffused lymphoid tissues and lymph nodules. Such as ag ...
... The tissue fluid is mostly taken up by the blood capillaries, partly by the lymphatic capillaries. Composition Lymphatic system consists of the lymph conducting channels, lymphoid tissues and lymphoid organs. Lymph tissues: contain lymphocytes. Diffused lymphoid tissues and lymph nodules. Such as ag ...
The Regional Anatomy of the Upper limb
... (2) The second part lies deep to the pectoralis minor; behind, related to the subscapularis; laterally, posteriorly, medially, related to the lateral cord, posterioe cord and medial cord respectively; The branch--The thoracoacromial a. To pierces clavipectoral fascia and divides into 3 bran ...
... (2) The second part lies deep to the pectoralis minor; behind, related to the subscapularis; laterally, posteriorly, medially, related to the lateral cord, posterioe cord and medial cord respectively; The branch--The thoracoacromial a. To pierces clavipectoral fascia and divides into 3 bran ...
dr.mohamed saad eldeen
... ipsilateral bronchial stump; exclude contralateral hilum and supraclavicular lymph nodes unless involved. ...
... ipsilateral bronchial stump; exclude contralateral hilum and supraclavicular lymph nodes unless involved. ...
Language of Anatomy and Organ systems Lab
... Hypochondriac (L & R) Inguinal (L & R) Lumbar ( L & R) ...
... Hypochondriac (L & R) Inguinal (L & R) Lumbar ( L & R) ...
Lymphatic system

The lymphatic system is part of the circulatory system and a vital part of the immune system, comprising a network of lymphatic vessels that carry a clear fluid called lymph (from Latin lympha meaning water) directionally towards the heart. The lymphatic system was first described in the seventeenth century independently by Olaus Rudbeck and Thomas Bartholin. Unlike the cardiovascular system, the lymphatic system is not a closed system. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma while leaving the blood cells. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered plasma are reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres remain in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymph system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres.The other main function is that of defense in the immune system. Lymph is very similar to blood plasma: it contains lymphocytes and other white blood cells. It also contains waste products and debris of cells together with bacteria and protein. Associated organs composed of lymphoid tissue are the sites of lymphocyte production. Lymphocytes are concentrated in the lymph nodes. The spleen and the thymus are also lymphoid organs of the immune system. The tonsils are lymphoid organs that are also associated with the digestive system. Lymphoid tissues contain lymphocytes, and also contain other types of cells for support. The system also includes all the structures dedicated to the circulation and production of lymphocytes (the primary cellular component of lymph), which also includes the bone marrow, and the lymphoid tissue associated with the digestive system.The blood does not come into direct contact with the parenchymal cells and tissues in the body (except in case of an injury causing rupture of one or more blood vessels), but constituents of the blood first exit the microvascular exchange blood vessels to become interstitial fluid, which comes into contact with the parenchymal cells of the body. Lymph is the fluid that is formed when interstitial fluid enters the initial lymphatic vessels of the lymphatic system. The lymph is then moved along the lymphatic vessel network by either intrinsic contractions of the lymphatic passages or by extrinsic compression of the lymphatic vessels via external tissue forces (e.g., the contractions of skeletal muscles), or by lymph hearts in some animals. The organization of lymph nodes and drainage follows the organization of the body into external and internal regions; therefore, the lymphatic drainage of the head, limbs, and body cavity walls follows an external route, and the lymphatic drainage of the thorax, abdomen, and pelvic cavities follows an internal route. Eventually, the lymph vessels empty into the lymphatic ducts, which drain into one of the two subclavian veins, near their junction with the internal jugular veins.