Overview of Anatomy and Physiology 5
... – Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to blood – Disposes of debris from lymphatic stream – Houses white blood cells involved with immunity ...
... – Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to blood – Disposes of debris from lymphatic stream – Houses white blood cells involved with immunity ...
Thorax
... -progressive cough, hoarseness, and swelling of the face and arms. - On examination: plethoric, with a ruddy complexion, suffusion, pitting edema of the face and upper torso, and prominent spidery telangiectasia on his face and chest (Panel A). The jugular veins were nonpulsatile and distended. - Co ...
... -progressive cough, hoarseness, and swelling of the face and arms. - On examination: plethoric, with a ruddy complexion, suffusion, pitting edema of the face and upper torso, and prominent spidery telangiectasia on his face and chest (Panel A). The jugular veins were nonpulsatile and distended. - Co ...
digestive sys 212 (M..
... peritoneum Serous membranes lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities and covers the related organs. It is attached to the stomach curves. Lesser omentum; attaches the liver to the lesser curvature. Greater omentum; attaches the greater curvature to the transverse colon, and then to the poste ...
... peritoneum Serous membranes lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities and covers the related organs. It is attached to the stomach curves. Lesser omentum; attaches the liver to the lesser curvature. Greater omentum; attaches the greater curvature to the transverse colon, and then to the poste ...
pdf
... Fig. 17: T4N2b supraglottic tumor (T). Level III large lymph node with necrosis and fixation sign in the anterior wall of the IJV (red arrows) References: Radiology Department, Hospital Clinic Barcelona The depression and fixation sign of the IJV may be useful to identify pathologic lymph nodes wit ...
... Fig. 17: T4N2b supraglottic tumor (T). Level III large lymph node with necrosis and fixation sign in the anterior wall of the IJV (red arrows) References: Radiology Department, Hospital Clinic Barcelona The depression and fixation sign of the IJV may be useful to identify pathologic lymph nodes wit ...
digestive system
... peritoneum Serous membranes lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities and covers the related organs. It is attached to the stomach curves. Lesser omentum; attaches the liver to the lesser curvature. Greater omentum; attaches the greater curvature to the transverse colon, and then to the poste ...
... peritoneum Serous membranes lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities and covers the related organs. It is attached to the stomach curves. Lesser omentum; attaches the liver to the lesser curvature. Greater omentum; attaches the greater curvature to the transverse colon, and then to the poste ...
Anatomy and Physiology II MED 165 Blood Vessels System
... List all of the components of systemic circulation? What are three layers of all arteries and veins? What tissue is found in the three layers? Which direction do arteries transport blood? Is arterial blood oxygenated, deoxygenated or it depends on the type of circulation? What are the two types of a ...
... List all of the components of systemic circulation? What are three layers of all arteries and veins? What tissue is found in the three layers? Which direction do arteries transport blood? Is arterial blood oxygenated, deoxygenated or it depends on the type of circulation? What are the two types of a ...
The thymus
... • T4 converted to more active T3 by tissue deiodinases • T4 and T3 accelerated metabolism, increase oxygen consumption, important for growth and development of the ...
... • T4 converted to more active T3 by tissue deiodinases • T4 and T3 accelerated metabolism, increase oxygen consumption, important for growth and development of the ...
COMPARING INVERTEBRATES
... flatworms ingest food and expel wastes through a single opening. Some cells of the gastrovascular cavity secrete enzymes and absorb digested food. Other cells surround food particles and digest them in vacuoles. More complex animals digest food in a tube called the digestive tract, which may have sp ...
... flatworms ingest food and expel wastes through a single opening. Some cells of the gastrovascular cavity secrete enzymes and absorb digested food. Other cells surround food particles and digest them in vacuoles. More complex animals digest food in a tube called the digestive tract, which may have sp ...
Anatomy introduction11
... • TISSUES: group of cells with similar structure and function. There are four groups of tissues: 1. Epithelial tissues: cover or line body surfaces, some are capable of producing secretions with specific functions. ...
... • TISSUES: group of cells with similar structure and function. There are four groups of tissues: 1. Epithelial tissues: cover or line body surfaces, some are capable of producing secretions with specific functions. ...
Human Anatomy - Perry Local Schools
... Body Regions body regions identified on the surface specific local areas of the body internal organs located in each region clinical importance of organs pelvic, abdominal, upper & lower extremities Body Cavities and Membranes connective & epithelial tissues compartmentalization of vis ...
... Body Regions body regions identified on the surface specific local areas of the body internal organs located in each region clinical importance of organs pelvic, abdominal, upper & lower extremities Body Cavities and Membranes connective & epithelial tissues compartmentalization of vis ...
Intercostal Muscles
... Organs • the primary organs of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems ...
... Organs • the primary organs of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems ...
The Circulatory System
... Development of the human body from the fertilized egg-cell to the adult form which includes the next stages: prenatal ontogenesis (embryonic, fetal); organization of embryo body (ectoderm, entoderm, dorsal and ventral mesoderm; somites and their components), postnatal ontogenesis. The Locomotion App ...
... Development of the human body from the fertilized egg-cell to the adult form which includes the next stages: prenatal ontogenesis (embryonic, fetal); organization of embryo body (ectoderm, entoderm, dorsal and ventral mesoderm; somites and their components), postnatal ontogenesis. The Locomotion App ...
Canine Lymphosarcoma (Lymphoma, LSA)
... and as such is not really viewed to “spread” to other organs. This tumor is not generally viewed as a curable tumor in dogs, although occasional dogs will experience what seems to be a cure with appropriate treatment (see below). A dog can start with one stage of the disease and progress over time t ...
... and as such is not really viewed to “spread” to other organs. This tumor is not generally viewed as a curable tumor in dogs, although occasional dogs will experience what seems to be a cure with appropriate treatment (see below). A dog can start with one stage of the disease and progress over time t ...
OMM54-TheVentilatedPatient - UNT Health Science Center
... i. Exits skull at jugular foramen ii. Ganglion nodosum of vagus lies in fascias on anterior surface of OA and AA (also helps treat the brainstem) b. Increase parasympathetic tone i. Bronchoconstriction ii. Vasodilation c. Treatment Goals i. Normalize vagal tone 1. prevent bronchoconstriction, decrea ...
... i. Exits skull at jugular foramen ii. Ganglion nodosum of vagus lies in fascias on anterior surface of OA and AA (also helps treat the brainstem) b. Increase parasympathetic tone i. Bronchoconstriction ii. Vasodilation c. Treatment Goals i. Normalize vagal tone 1. prevent bronchoconstriction, decrea ...
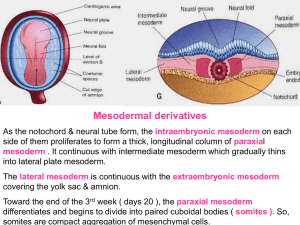
07 - mesodermal
... 2- Small cavities appear within the blood islands. 3- Angioblastic flatten and arrange themselves around the cavities to form endothelial cells of blood vessels. ...
... 2- Small cavities appear within the blood islands. 3- Angioblastic flatten and arrange themselves around the cavities to form endothelial cells of blood vessels. ...
Document
... • The lymph vessels from the medial quadrants of the breast pierce the second, third, and fourth intercostal spaces and enter the thorax to drain into the lymph nodes alongside the internal thoracic artery. • The lymph vessels from the lateral quadrants of the breast drain into the anterior or pecto ...
... • The lymph vessels from the medial quadrants of the breast pierce the second, third, and fourth intercostal spaces and enter the thorax to drain into the lymph nodes alongside the internal thoracic artery. • The lymph vessels from the lateral quadrants of the breast drain into the anterior or pecto ...
Skin of the Neck
... Contents of the posterior triangle: A) Nerves and Plexuses: 1. Cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus (supraclavicular nerve, lesser occipital nerve, greater auricular nerve and transverse cervical nerve) enter the posterior triangle by piercing the fascia over its floor, and run for some dista ...
... Contents of the posterior triangle: A) Nerves and Plexuses: 1. Cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus (supraclavicular nerve, lesser occipital nerve, greater auricular nerve and transverse cervical nerve) enter the posterior triangle by piercing the fascia over its floor, and run for some dista ...
Lobes of thyroid gland and carotid sheath (with its contents).
... 1. Superior thyroid artery from external carotid artery. 2. Inferior thyroid artery from thyrocervical trunk from 1st part of subclavian artery. 3. Thyroidea ima artery from brachiocephalic or arch of aorta. Venous drainage: 1. Superior thyroid vein to internal jugular vein. 2. Middle thyroid vein t ...
... 1. Superior thyroid artery from external carotid artery. 2. Inferior thyroid artery from thyrocervical trunk from 1st part of subclavian artery. 3. Thyroidea ima artery from brachiocephalic or arch of aorta. Venous drainage: 1. Superior thyroid vein to internal jugular vein. 2. Middle thyroid vein t ...
Slide () - CHEST Journal
... From: Diagnosing and Staging Lung Cancer Involving the Mediastinum Chest. 2015;147(5):1401-1412. doi:10.1378/chest.14-1355 ...
... From: Diagnosing and Staging Lung Cancer Involving the Mediastinum Chest. 2015;147(5):1401-1412. doi:10.1378/chest.14-1355 ...
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM
... I. Lymphatic System A. Lymphatic vessels are found on the surface around the lungs and beneath the visceral pleura 1. found in dense connective tissue 2. primary function is to remove excess fluid from tissue B. Lymphatic vessels arise from loose space of the interstitium 1. vessels follow bronchial ...
... I. Lymphatic System A. Lymphatic vessels are found on the surface around the lungs and beneath the visceral pleura 1. found in dense connective tissue 2. primary function is to remove excess fluid from tissue B. Lymphatic vessels arise from loose space of the interstitium 1. vessels follow bronchial ...
15-Submandibular Region-II2010-10-01 03:4111.6 MB
... tongue (except the tip); the floor of the mouth & vestibule; and the gums. The efferent lymph vessels drain into the deep cervical lymph nodes. The submental lymph nodes are situated in the submental triangles. They receive lymph from tip of the tongue, floor of the mouth beneath the tip of the tong ...
... tongue (except the tip); the floor of the mouth & vestibule; and the gums. The efferent lymph vessels drain into the deep cervical lymph nodes. The submental lymph nodes are situated in the submental triangles. They receive lymph from tip of the tongue, floor of the mouth beneath the tip of the tong ...
Dissection of the Rat
... You may have to flush out your rat’s abdomen under flowing water in the sink to remove the fluid in the gastrovascular cavity. The abdominal organs may still be covered with a membrane, the peritoneum, (peritoneal membrane) but this usually comes off with the overlying layers. If necessary drain the ...
... You may have to flush out your rat’s abdomen under flowing water in the sink to remove the fluid in the gastrovascular cavity. The abdominal organs may still be covered with a membrane, the peritoneum, (peritoneal membrane) but this usually comes off with the overlying layers. If necessary drain the ...
32-innervation of abdomen & lymph drainage
... They join branches from the sympathetic plexuses to form the superior hypogastric plexus. ...
... They join branches from the sympathetic plexuses to form the superior hypogastric plexus. ...
Human Anatomy and Histology
... 136. Common and internal iliac arteries. 137. External iliac artery. Femoral artery. 138. Popliteal artery. Arteries of the leg and foot. 139. Arterial anastomoses (collateral circulation) of the lower limb. 140. Superior vena cava system – veins of the head and neck. 141. Veins of the upper limb. 1 ...
... 136. Common and internal iliac arteries. 137. External iliac artery. Femoral artery. 138. Popliteal artery. Arteries of the leg and foot. 139. Arterial anastomoses (collateral circulation) of the lower limb. 140. Superior vena cava system – veins of the head and neck. 141. Veins of the upper limb. 1 ...
Lymphatic system

The lymphatic system is part of the circulatory system and a vital part of the immune system, comprising a network of lymphatic vessels that carry a clear fluid called lymph (from Latin lympha meaning water) directionally towards the heart. The lymphatic system was first described in the seventeenth century independently by Olaus Rudbeck and Thomas Bartholin. Unlike the cardiovascular system, the lymphatic system is not a closed system. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma while leaving the blood cells. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered plasma are reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres remain in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymph system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres.The other main function is that of defense in the immune system. Lymph is very similar to blood plasma: it contains lymphocytes and other white blood cells. It also contains waste products and debris of cells together with bacteria and protein. Associated organs composed of lymphoid tissue are the sites of lymphocyte production. Lymphocytes are concentrated in the lymph nodes. The spleen and the thymus are also lymphoid organs of the immune system. The tonsils are lymphoid organs that are also associated with the digestive system. Lymphoid tissues contain lymphocytes, and also contain other types of cells for support. The system also includes all the structures dedicated to the circulation and production of lymphocytes (the primary cellular component of lymph), which also includes the bone marrow, and the lymphoid tissue associated with the digestive system.The blood does not come into direct contact with the parenchymal cells and tissues in the body (except in case of an injury causing rupture of one or more blood vessels), but constituents of the blood first exit the microvascular exchange blood vessels to become interstitial fluid, which comes into contact with the parenchymal cells of the body. Lymph is the fluid that is formed when interstitial fluid enters the initial lymphatic vessels of the lymphatic system. The lymph is then moved along the lymphatic vessel network by either intrinsic contractions of the lymphatic passages or by extrinsic compression of the lymphatic vessels via external tissue forces (e.g., the contractions of skeletal muscles), or by lymph hearts in some animals. The organization of lymph nodes and drainage follows the organization of the body into external and internal regions; therefore, the lymphatic drainage of the head, limbs, and body cavity walls follows an external route, and the lymphatic drainage of the thorax, abdomen, and pelvic cavities follows an internal route. Eventually, the lymph vessels empty into the lymphatic ducts, which drain into one of the two subclavian veins, near their junction with the internal jugular veins.