a novel system for peptide bond formation on natural product
... NRP synthetase containing a single A and Reductase (R) domain but no C domains (SLI0883); instead, a homolog of the leucyl/phenylalanyl tRNA protein transferase (L/F transferase; SLI0884) could be annotated. L/F transferases catalyze the transfer of leucine or phenylalanine from an aminoacyl-tRNA to ...
... NRP synthetase containing a single A and Reductase (R) domain but no C domains (SLI0883); instead, a homolog of the leucyl/phenylalanyl tRNA protein transferase (L/F transferase; SLI0884) could be annotated. L/F transferases catalyze the transfer of leucine or phenylalanine from an aminoacyl-tRNA to ...
Enzyme Foldable
... - Obtain 3 sheets of computer paper. - Stagger the sheets so that there is a 1 inch separation. - Fold in half so that now you have 6 tabs. - Staple together at the top using only 2 staples. - Title Enzymes Flaps: 1. What is an enzyme? a. Write a 3 – 4 sentence summary of what is an enzyme. b. Lock ...
... - Obtain 3 sheets of computer paper. - Stagger the sheets so that there is a 1 inch separation. - Fold in half so that now you have 6 tabs. - Staple together at the top using only 2 staples. - Title Enzymes Flaps: 1. What is an enzyme? a. Write a 3 – 4 sentence summary of what is an enzyme. b. Lock ...
Name: Date: ______ Per: ______ Chemical Reactions and
... 11. Can one single enzyme catalyze many different types of substrates? Explain why? ...
... 11. Can one single enzyme catalyze many different types of substrates? Explain why? ...
Document
... Sources: liver, carrot, broccoli leaf, sweet potato, butter, kale, spinach, pumpkin, collard greens, Cheddar cheese, egg, milk ...
... Sources: liver, carrot, broccoli leaf, sweet potato, butter, kale, spinach, pumpkin, collard greens, Cheddar cheese, egg, milk ...
Unit1-KA5-Revision
... An enzyme is a biological catalyst made up by all living 3-State what an enzyme is. cells. It speeds up reactions and is left unchanged. 4-Which part of the enzyme binds The active site. The shape of the active site is to the substrate? complementary to that of its specific substrate. 5-Explain the ...
... An enzyme is a biological catalyst made up by all living 3-State what an enzyme is. cells. It speeds up reactions and is left unchanged. 4-Which part of the enzyme binds The active site. The shape of the active site is to the substrate? complementary to that of its specific substrate. 5-Explain the ...
1.3 Enzymes supplemental work
... The students conducted experiments to study digestive enzyme activity. In the first experiment, the students observed the rate at which salivary amylase breaks down starch (the substrate) in solutions with different pH values. The students then performed the same type of experiment with pepsin. The ...
... The students conducted experiments to study digestive enzyme activity. In the first experiment, the students observed the rate at which salivary amylase breaks down starch (the substrate) in solutions with different pH values. The students then performed the same type of experiment with pepsin. The ...
Proteins and Nucleic Acids
... protein…this is known as DENATURATION. So if the shape changes, what’s affected? The Function of the Protein! Other Causes of Protein Denaturation salt concentration and environmental factors ...
... protein…this is known as DENATURATION. So if the shape changes, what’s affected? The Function of the Protein! Other Causes of Protein Denaturation salt concentration and environmental factors ...
this lecture as PDF here
... Enzymes undergo physical changes during the reaction but revert to their original form at the end of the reaction. ...
... Enzymes undergo physical changes during the reaction but revert to their original form at the end of the reaction. ...
Document
... Deamination – replacement of an amine group (NH2) with an oxygen (O) atom N-, O-, or S-Dealkylation – replacement of an alkyl group (e.g., CH3) with a hydrogen atom. Typically, the alkyl group in the parent molecule is bonded to a N, O, or S atom. Aliphatic or aromatic hydroxylation – addition ...
... Deamination – replacement of an amine group (NH2) with an oxygen (O) atom N-, O-, or S-Dealkylation – replacement of an alkyl group (e.g., CH3) with a hydrogen atom. Typically, the alkyl group in the parent molecule is bonded to a N, O, or S atom. Aliphatic or aromatic hydroxylation – addition ...
Amino acid chains may form helices as parts of the corresponding
... Enzymes can also catalyse reactions that will not run by themselves, but then energy needs to be supplied. This is often provided by ATP. One or more phosphate group in ATP is hydrolysed off, and the energy released is used to catalyse the reaction that would otherwise not run. A typical example is ...
... Enzymes can also catalyse reactions that will not run by themselves, but then energy needs to be supplied. This is often provided by ATP. One or more phosphate group in ATP is hydrolysed off, and the energy released is used to catalyse the reaction that would otherwise not run. A typical example is ...
Enzymes
... particular configuration of the active site into which the substrate molecules fit like a key, giving rise to the lock and key hypothesis. This hypothesis has been modified to the induced fit hypothesis, where it is thought that when a Substrate combines with an enzyme, it induces the enzyme structu ...
... particular configuration of the active site into which the substrate molecules fit like a key, giving rise to the lock and key hypothesis. This hypothesis has been modified to the induced fit hypothesis, where it is thought that when a Substrate combines with an enzyme, it induces the enzyme structu ...
Enzymes
... Enzymes must have a precise shape to work properly. Cells can control when an enzyme is active by altering its shape. ...
... Enzymes must have a precise shape to work properly. Cells can control when an enzyme is active by altering its shape. ...
Enzymes
... • Reverse Transcriptase – creates DNA from RNA • DNA Polymerase – makes new DNA for you • Lipase – Helps break down fats • Alcohol Dehyrogenase – breaks down alcohol in the body (makes it non toxic) There is an enzyme for just about any of your life needs!! ...
... • Reverse Transcriptase – creates DNA from RNA • DNA Polymerase – makes new DNA for you • Lipase – Helps break down fats • Alcohol Dehyrogenase – breaks down alcohol in the body (makes it non toxic) There is an enzyme for just about any of your life needs!! ...
The enzyme
... Enzymes as the biocatalysts (3) • Relationship of initial velocity (V0) and substrate concentration (S) was examined. • A mathematical description was established for the kinetics of enzyme action (Michaelis and Menten, 1913). Before it was known that enzymes are proteins!!! • Weak-bonding interact ...
... Enzymes as the biocatalysts (3) • Relationship of initial velocity (V0) and substrate concentration (S) was examined. • A mathematical description was established for the kinetics of enzyme action (Michaelis and Menten, 1913). Before it was known that enzymes are proteins!!! • Weak-bonding interact ...
Enzyme Puzzle Activity
... enzyme with a matching active site, and reactants that are formed after the enzyme speeds up the reaction. If you have problems, refer to page 76 in your biology book. 2) You will have to name your enzyme. Usually, enzymes end in ‘ase.” For example, catalase is an enzyme used frequently in the lab. ...
... enzyme with a matching active site, and reactants that are formed after the enzyme speeds up the reaction. If you have problems, refer to page 76 in your biology book. 2) You will have to name your enzyme. Usually, enzymes end in ‘ase.” For example, catalase is an enzyme used frequently in the lab. ...
chapter 20
... 3. What is the active site of an enzyme? Be able to predict types of interactions between amino acids in the enzyme active site and amino acids in the substrate (as was done in the web animation). 4. Discuss the difference between the “lock and key” and “induced fit” models of enzyme catalysis. 5. W ...
... 3. What is the active site of an enzyme? Be able to predict types of interactions between amino acids in the enzyme active site and amino acids in the substrate (as was done in the web animation). 4. Discuss the difference between the “lock and key” and “induced fit” models of enzyme catalysis. 5. W ...
ENZYMES Worksheet 1. What is an enzyme?
... 6. the break-down of complex molecules into simple molecules ...
... 6. the break-down of complex molecules into simple molecules ...
Enzymes
... 4. In the osmosis demo with the 10% and 60% glucose solutions, which one had the greatest amount of water that diffused into the osmometer and WHY? This is a two part question. 5. Molecules diffuse from an area of [high] [low] OR [low] [high]? (note [ ] = concentration) 6. What is an enzyme? 7. ...
... 4. In the osmosis demo with the 10% and 60% glucose solutions, which one had the greatest amount of water that diffused into the osmometer and WHY? This is a two part question. 5. Molecules diffuse from an area of [high] [low] OR [low] [high]? (note [ ] = concentration) 6. What is an enzyme? 7. ...
Biochemistry - CPBiologyMTHS
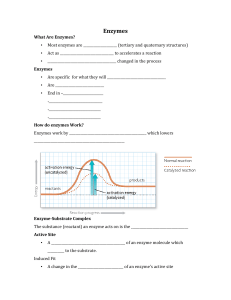
... 1. Speeds up a reaction by lowering the activation energy 2. Not consumed by the reaction ...
... 1. Speeds up a reaction by lowering the activation energy 2. Not consumed by the reaction ...