* Proteins, or polypeptides, are polymers made of monomers called
... your body, and your body has to maintain a stable internal environment (homeostasis) to keep its enzymes working ...
... your body, and your body has to maintain a stable internal environment (homeostasis) to keep its enzymes working ...
Reading Guide for Essay Name What Happens to the Food You Eat
... After chewing and mechanically breaking down food, how are large molecules broken down into smaller ones? ...
... After chewing and mechanically breaking down food, how are large molecules broken down into smaller ones? ...
Enzymes: The Biological Catalysts
... D. When an enzyme binds with the substrate, the bonded substrate interacts with the enzyme causing it to change shape. This change in shape facilitates the chemical reaction to occur. This is called the induced fit. ...
... D. When an enzyme binds with the substrate, the bonded substrate interacts with the enzyme causing it to change shape. This change in shape facilitates the chemical reaction to occur. This is called the induced fit. ...
Enzymes
... enzymes is 7. Exceptions :Pepsin (gastric protease) Trypsin (intestinal protease) Pepsin works best at pH of 3 ...
... enzymes is 7. Exceptions :Pepsin (gastric protease) Trypsin (intestinal protease) Pepsin works best at pH of 3 ...
Document
... _____________________- energy needed to start a chemical reaction _____________________- newly formed substance _____________________- Pentose sugar, phosphate, base _____________________- Ribonucleic acid, single strand, key role in manufacturing protein _____________________- an enzyme that breaks ...
... _____________________- energy needed to start a chemical reaction _____________________- newly formed substance _____________________- Pentose sugar, phosphate, base _____________________- Ribonucleic acid, single strand, key role in manufacturing protein _____________________- an enzyme that breaks ...
How do Enzymes work?
... depending upon the shape their substrate has, this helps their individual substrate to fit in perfectly with the shape of the enzyme. The enzyme and the substrate together are known as the EnzymeSubstrate Complex. When the subtracts are close together in the enzyme, their actually energy to perform ...
... depending upon the shape their substrate has, this helps their individual substrate to fit in perfectly with the shape of the enzyme. The enzyme and the substrate together are known as the EnzymeSubstrate Complex. When the subtracts are close together in the enzyme, their actually energy to perform ...
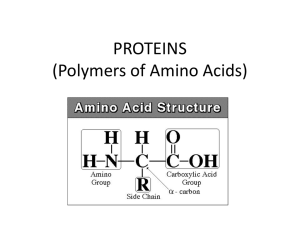
(most also have sulfur) The monomers of proteins are amino acids.
... • 20 different amino acids are found in nature. • Since the R-group varies, it allows for much variety. That is why proteins have so many functions. ...
... • 20 different amino acids are found in nature. • Since the R-group varies, it allows for much variety. That is why proteins have so many functions. ...
Lesson 2 – Carbohydrates
... 2. pH – the pH affects the activity of enzymes so controlling the pH will change which enzymes are active. 3. Temperature – the temperature affects the activity of enzymes so controlling the temperature will change which enzymes are active. 4. Cofactors – some enzymes require another non-protein mol ...
... 2. pH – the pH affects the activity of enzymes so controlling the pH will change which enzymes are active. 3. Temperature – the temperature affects the activity of enzymes so controlling the temperature will change which enzymes are active. 4. Cofactors – some enzymes require another non-protein mol ...
RACC BIO Organic Molecules
... Hemoglobin, transports oxygen in the blood. Hormonal proteins Insulin helps regulate the concentration of sugar in the blood Defensive proteins Antibodies combat bacteria and viruses Enzymatic Proteins are probably the most important type of protein Enzymes regulate metabolism by speed ...
... Hemoglobin, transports oxygen in the blood. Hormonal proteins Insulin helps regulate the concentration of sugar in the blood Defensive proteins Antibodies combat bacteria and viruses Enzymatic Proteins are probably the most important type of protein Enzymes regulate metabolism by speed ...
Interfering with enzymes (poisons and drugs)
... • “A non-protein organic molecule that forms a permanent part of a functioning protein molecule.” • E.g. zinc-based prosthetic group in carbonic anhydrase – where have we met this enzyme? ...
... • “A non-protein organic molecule that forms a permanent part of a functioning protein molecule.” • E.g. zinc-based prosthetic group in carbonic anhydrase – where have we met this enzyme? ...
Chapter 4 Enzymes and Energy
... • Different organs may make different enzymes (isoenzymes) that have the same activity. – Differences in structure do not affect the active sites. ...
... • Different organs may make different enzymes (isoenzymes) that have the same activity. – Differences in structure do not affect the active sites. ...
Chapter 3-5 Organic Chemistry
... DNA serves as the genetic code for production of proteins. RNA- DNA’s helper ...
... DNA serves as the genetic code for production of proteins. RNA- DNA’s helper ...
Enzyme Webquest
... Post-Lab Discussion Remind students that most metabolic processes consist of several reactions. Ask, What happens if one enzyme in a pathway is missing or defective? The entire pathway is shut down. The products in the reaction before the blocked reaction will accumulate. These accumulated products ...
... Post-Lab Discussion Remind students that most metabolic processes consist of several reactions. Ask, What happens if one enzyme in a pathway is missing or defective? The entire pathway is shut down. The products in the reaction before the blocked reaction will accumulate. These accumulated products ...
Enzymes - CynthiaJankowski
... What are Enzymes? • Enzymes are substances called catalysts that speed up chemical rxns by decreasing the activation energy of the rxns. • Enzymes are mostly proteins. • Help maintain homeostasis as rxn in living things would not occur quickly enough to sustain life. • Enzymes usually end in ASE, l ...
... What are Enzymes? • Enzymes are substances called catalysts that speed up chemical rxns by decreasing the activation energy of the rxns. • Enzymes are mostly proteins. • Help maintain homeostasis as rxn in living things would not occur quickly enough to sustain life. • Enzymes usually end in ASE, l ...
PROTEINS (Polymers of Amino Acids)
... MOLECULAR STRUCTURE • TERTIARY – 3-D shape – Globular – (round clusters – hemoglobin) – Fibrous – (long threads – collegen) ...
... MOLECULAR STRUCTURE • TERTIARY – 3-D shape – Globular – (round clusters – hemoglobin) – Fibrous – (long threads – collegen) ...
Chapter 5 Enzymes, Coenzyme and Energy
... ◦ Too high of temperatures may cause the enzyme to change its shape, this is known as denaturing, where a protein structure is permanently changed ...
... ◦ Too high of temperatures may cause the enzyme to change its shape, this is known as denaturing, where a protein structure is permanently changed ...
Document
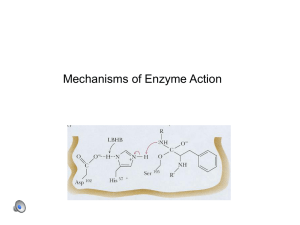
... electrons through +/- charges These effects reduce G(ES*): covalent bonds, acidbase catalysis, low-barrier hydrogen bonds, and metal ion catalysis Different classes of enzymes may use different mechanisms: 1. Oxidoreductases (oxidation-reduction reactions) 2. Transferases (transfer of functional gro ...
... electrons through +/- charges These effects reduce G(ES*): covalent bonds, acidbase catalysis, low-barrier hydrogen bonds, and metal ion catalysis Different classes of enzymes may use different mechanisms: 1. Oxidoreductases (oxidation-reduction reactions) 2. Transferases (transfer of functional gro ...
Clinical biochemistry (9) Enzymes and isoenzymes
... in minute quantity (c) being not consumed in the overall reaction. 3) They act as catalysts. 4) They are very specific for their substrates. 5) They possess active sites at which interaction with substrate occurs. 6) They are responsible for lowering activation energy. 7) Some enzymes are regulatory ...
... in minute quantity (c) being not consumed in the overall reaction. 3) They act as catalysts. 4) They are very specific for their substrates. 5) They possess active sites at which interaction with substrate occurs. 6) They are responsible for lowering activation energy. 7) Some enzymes are regulatory ...
Functional Groups Handout
... Functional Groups Organic molecules have two main parts. Carbon backbone: The carbon and hydrogen skeleton of a molecule Functional groups: groups of atoms/bonds that determine the physical and biological properties and reactivity of a molecule Memorization Alert: You will need to memorize function ...
... Functional Groups Organic molecules have two main parts. Carbon backbone: The carbon and hydrogen skeleton of a molecule Functional groups: groups of atoms/bonds that determine the physical and biological properties and reactivity of a molecule Memorization Alert: You will need to memorize function ...