
229_1.PDF
... INTRODUCTION At the nominal energy of 7 TeV each beam in the LHC stores energy of up to 0.35 GJ. The loss of only a fraction (10~8 ) of the beam can have a severe impact on the smooth machine operation. Therefore the beam loss detection system must fulfil several requirements, first: Protection: The ...
... INTRODUCTION At the nominal energy of 7 TeV each beam in the LHC stores energy of up to 0.35 GJ. The loss of only a fraction (10~8 ) of the beam can have a severe impact on the smooth machine operation. Therefore the beam loss detection system must fulfil several requirements, first: Protection: The ...
An Introduction to Kinetic Inductance Detectors
... To maximize the response, we need to maximize each of the following: 1) dθ/dω0 Make the change in phase for a given shift in resonant frequency as large as possible 2) dω0/dLtot Make the change I resonant frequency as large as possible for given change in inductance. 3) dLtot/dσ2 make the change in ...
... To maximize the response, we need to maximize each of the following: 1) dθ/dω0 Make the change in phase for a given shift in resonant frequency as large as possible 2) dω0/dLtot Make the change I resonant frequency as large as possible for given change in inductance. 3) dLtot/dσ2 make the change in ...
Noise in cavity ring-down spectroscopy caused by
... losses and due to this coherent transfer. Thus, we expect that the observed decay will generally no longer be a single exponential function and will decay faster than when the TEMnm mode is off resonance, if the energy in TEMnm is not totally collected by the detector. This clearly agrees with our o ...
... losses and due to this coherent transfer. Thus, we expect that the observed decay will generally no longer be a single exponential function and will decay faster than when the TEMnm mode is off resonance, if the energy in TEMnm is not totally collected by the detector. This clearly agrees with our o ...
EXPERIMENT 4-3 THE PHOTO-ELECTRIC EFFECT The
... electromagnetic wave. A photon incident on a metallic surface can interact with an atom in the metal, transferring all its energy to one of the atom's electrons. This electron may then escape through the electric field at the surface which keeps the less energetic electrons inside the metal. The ele ...
... electromagnetic wave. A photon incident on a metallic surface can interact with an atom in the metal, transferring all its energy to one of the atom's electrons. This electron may then escape through the electric field at the surface which keeps the less energetic electrons inside the metal. The ele ...
Module – 5
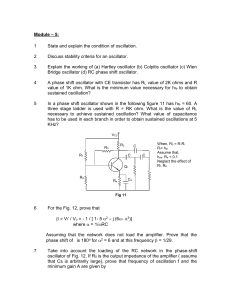
... Take into account the loading of the RC network in the phase-shift oscillator of Fig. 12. If R0 is the output impedance of the amplifier ( assume that Cs is arbitrarily large), prove that frequency of oscillation f and the minimum gain A are given by ...
... Take into account the loading of the RC network in the phase-shift oscillator of Fig. 12. If R0 is the output impedance of the amplifier ( assume that Cs is arbitrarily large), prove that frequency of oscillation f and the minimum gain A are given by ...
Lec 04
... an inductor! All the loops' contribution to the magnetic field add together to make a stronger field. Unlike capacitors and resistors, practical inductors are easy to make by hand. One can for instance spool some wire around a short wooden dowel, put the spool inside a plastic aspirin bottle with th ...
... an inductor! All the loops' contribution to the magnetic field add together to make a stronger field. Unlike capacitors and resistors, practical inductors are easy to make by hand. One can for instance spool some wire around a short wooden dowel, put the spool inside a plastic aspirin bottle with th ...
1D electromagnetic band gap structure formed by plasma
... structures have been intensively developed and investigated all over the world due to their unusual properties such as negative permittivity or permeability [1-3]. The possible applications of EBG structures in the microwave (MW) frequency range include such as power limiter, antennas, filters, mult ...
... structures have been intensively developed and investigated all over the world due to their unusual properties such as negative permittivity or permeability [1-3]. The possible applications of EBG structures in the microwave (MW) frequency range include such as power limiter, antennas, filters, mult ...
Principles of Electronic Communication Systems
... crystal oscillators but the convenience of incremental tuning over a broad frequency range. Frequency synthesizers provide an output that varies in fixed frequency increments over a wide range. In a transmitter, a frequency synthesizer provides ...
... crystal oscillators but the convenience of incremental tuning over a broad frequency range. Frequency synthesizers provide an output that varies in fixed frequency increments over a wide range. In a transmitter, a frequency synthesizer provides ...
Paper - Indico
... *sds@barc.gov.in Abstract Low energy high intensity proton accelerator (LEHIPA) at BARC requires a total of around 2.9 MW of radio frequency (RF) power at 352.2 MHz. This RF power is generated by three klystron based high power RF systems. Each of this 1 MW RF system uses high voltage bias supplies ...
... *sds@barc.gov.in Abstract Low energy high intensity proton accelerator (LEHIPA) at BARC requires a total of around 2.9 MW of radio frequency (RF) power at 352.2 MHz. This RF power is generated by three klystron based high power RF systems. Each of this 1 MW RF system uses high voltage bias supplies ...
Basic Circuitry2 - Electro Tech Online
... Some electrons on the outer orbits can jump from one atom to the next atom When an electron moves, it leaves a ‘hole’ in the orbit for another electron to jump into That electron leaves another hole, and so on When there is a large number electrons jumping from one atom to the next in the sa ...
... Some electrons on the outer orbits can jump from one atom to the next atom When an electron moves, it leaves a ‘hole’ in the orbit for another electron to jump into That electron leaves another hole, and so on When there is a large number electrons jumping from one atom to the next in the sa ...
ElectricEnergyModuleNotes - Western Michigan University
... This module contains copyrighted material from several sources as noted. 1. "How does this battery work? The Copper (Cu) atoms attract electrons more than do the Zinc (Zn) atoms. If you place a piece of copper and a piece of zinc in contact with each other, many electrons will pass from the zinc to ...
... This module contains copyrighted material from several sources as noted. 1. "How does this battery work? The Copper (Cu) atoms attract electrons more than do the Zinc (Zn) atoms. If you place a piece of copper and a piece of zinc in contact with each other, many electrons will pass from the zinc to ...
doc - University of Iowa Physics
... analyzer to measure the differential spectrum of the pulses, setting V = 0.4 volts and moving the baseline in 0.2 volt steps. Plot the results and identify the various features in the spectrum. C. Calibration of System with Radioactive Sources The size of the final pulse depends critically on the c ...
... analyzer to measure the differential spectrum of the pulses, setting V = 0.4 volts and moving the baseline in 0.2 volt steps. Plot the results and identify the various features in the spectrum. C. Calibration of System with Radioactive Sources The size of the final pulse depends critically on the c ...
Unusual Frequency Dividers
... flip-flop and the delay line back to the D input (see the schematic below). The flip-flop will trigger predictably if this delay is longer than the amount of time required for the flip-flop's internal circuitry to settle and the edge is not close to an input edge. Obviously, the circuit must divide ...
... flip-flop and the delay line back to the D input (see the schematic below). The flip-flop will trigger predictably if this delay is longer than the amount of time required for the flip-flop's internal circuitry to settle and the edge is not close to an input edge. Obviously, the circuit must divide ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reaction - An Introduction to Chemistry
... loses electrons, making it possible for another substance to gain electrons and be reduced. The oxidized substance is always the reducing agent. • An oxidizing agent is a substance that gains electrons, making it possible for another substance to lose electrons and be oxidized. The reduced substanc ...
... loses electrons, making it possible for another substance to gain electrons and be reduced. The oxidized substance is always the reducing agent. • An oxidizing agent is a substance that gains electrons, making it possible for another substance to lose electrons and be oxidized. The reduced substanc ...
arXiv:1206.0704v1 [physics.optics] 4 Jun 2012
... wavelength conversion process. The input (output) control laser is locked a mechanical frequency red-detuned from the first-order (secondorder) cavity mode at λ ≈ 1460 nm (λ ≈ 1545 nm). Both control beams can be amplitude modulated (a-m) to perform EIT-like spectroscopy of the cavity modes, or in th ...
... wavelength conversion process. The input (output) control laser is locked a mechanical frequency red-detuned from the first-order (secondorder) cavity mode at λ ≈ 1460 nm (λ ≈ 1545 nm). Both control beams can be amplitude modulated (a-m) to perform EIT-like spectroscopy of the cavity modes, or in th ...
Klystron

A klystron is a specialized linear-beam vacuum tube, invented in 1937 by American electrical engineers Russell and Sigurd Varian, which is used as an amplifier for high radio frequencies, from UHF up into the microwave range. Low-power klystrons are used as oscillators in terrestrial microwave relay communications links, while high-power klystrons are used as output tubes in UHF television transmitters, satellite communication, and radar transmitters, and to generate the drive power for modern particle accelerators.In the klystron, an electron beam interacts with the radio waves as it passes through resonant cavities, metal boxes along the length of the tube. The electron beam first passes through a cavity to which the input signal is applied. The energy of the electron beam amplifies the signal, and the amplified signal is taken from a cavity at the other end of the tube. The output signal can be coupled back into the input cavity to make an electronic oscillator to generate radio waves. The gain of klystrons can be high, 60 dB (one million) or more, with output power up to tens of megawatts, but the bandwidth is narrow, usually a few percent although it can be up to 10% in some devices.A reflex klystron is an obsolete type in which the electron beam was reflected back along its path by a high potential electrode, used as an oscillator.The name klystron comes from the stem form κλυσ- (klys) of a Greek verb referring to the action of waves breaking against a shore, and the suffix -τρον (""tron"") meaning the place where the action happens. The name ""klystron"" was suggested by Hermann Fränkel, a professor in the classics department at Stanford University when the klystron was under development.





















![arXiv:1206.0704v1 [physics.optics] 4 Jun 2012](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014484263_1-8848fbf71bdc502275cc8cd24bcdf657-300x300.png)