HS 03 Geometry Overview (Prentice Hall)
... Conditional Probability and the Rules of Probability; Using Probability to Make Decisions (6 weeks) ...
... Conditional Probability and the Rules of Probability; Using Probability to Make Decisions (6 weeks) ...
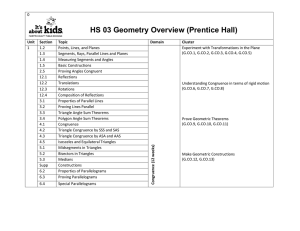
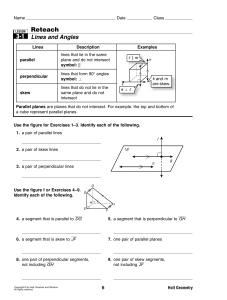
Geometry Learning Targets Section Section Title Learning Targets I
... I Can… 1. Identify, correctly label, and sketch the following geometric figures: point, line, plane, collinear points, coplanar points, segment, ray, opposite rays. 2. Use segment addition to calculate segment lengths. 3. Justify segment congruence on the coordinate plane. 4. Use the definitions of ...
... I Can… 1. Identify, correctly label, and sketch the following geometric figures: point, line, plane, collinear points, coplanar points, segment, ray, opposite rays. 2. Use segment addition to calculate segment lengths. 3. Justify segment congruence on the coordinate plane. 4. Use the definitions of ...
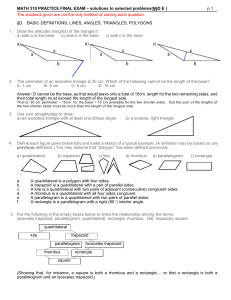
Geometry Practice Questions – Semester 1
... MAFS.912.G-GPE.2.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the ...
... MAFS.912.G-GPE.2.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the ...
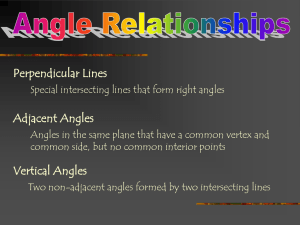
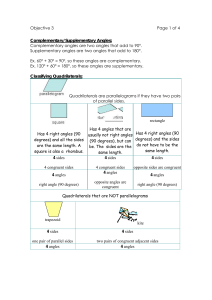
Objective 3 Page 1 of 4 Complementary/Supplementary Angles
... a solid that is enclosed by polygons (closed figures). Polygons that form polyhedrons. a polyhedron with two congruent bases that lie in parallel planes and whose other faces are rectangles. A prism is named by the shape of the base. ...
... a solid that is enclosed by polygons (closed figures). Polygons that form polyhedrons. a polyhedron with two congruent bases that lie in parallel planes and whose other faces are rectangles. A prism is named by the shape of the base. ...
Perspective (graphical)

Perspective (from Latin: perspicere to see through) in the graphic arts is an approximate representation, on a flat surface (such as paper), of an image as it is seen by the eye. The two most characteristic features of perspective are that objects are smaller as their distance from the observer increases; and that they are subject to foreshortening, meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight are shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight.Italian Renaissance painters including Paolo Uccello, Piero della Francesca and Luca Pacoima studied linear perspective, wrote treatises on it, and incorporated it into their artworks, thus contributing to the mathematics of art.