Quantum Entanglement and the Geometry of Spacetime
... Quantum gravity in d + 1 dimensions with AdS boundary conditions = d dimensional ordinary quantum field theory (without gravity). QFT “lives on the boundary”. Map between the two theories is non-local. QFT has a large number of strongly interacting fields: ✓ ◆d 1 d 1 ...
... Quantum gravity in d + 1 dimensions with AdS boundary conditions = d dimensional ordinary quantum field theory (without gravity). QFT “lives on the boundary”. Map between the two theories is non-local. QFT has a large number of strongly interacting fields: ✓ ◆d 1 d 1 ...
A quantum-information-theoretic complement to a general
... Finally, it should be noted that we must reasonably expect that many of the issues we will encounter will only find a final resolution in a full quantum theory of gravity. In the absence of such a theory, however, let us proceed for now with the best available (classical) spacetime theory—GR. A mod ...
... Finally, it should be noted that we must reasonably expect that many of the issues we will encounter will only find a final resolution in a full quantum theory of gravity. In the absence of such a theory, however, let us proceed for now with the best available (classical) spacetime theory—GR. A mod ...
Mathematics
... Geometry and Measurement• name basic geometric figures • recognize intersecting lines, parallel lines, and skew lines • identify adjacent and vertical angles • relate angles formed by parallel lines • classify triangles and quadrilaterals • use “draw a diagram” as a problem solving strategy • identi ...
... Geometry and Measurement• name basic geometric figures • recognize intersecting lines, parallel lines, and skew lines • identify adjacent and vertical angles • relate angles formed by parallel lines • classify triangles and quadrilaterals • use “draw a diagram” as a problem solving strategy • identi ...
Homework
... What to Know in Chapter 16: Transformational Geometry To complete this chapter successfully student will: 1. Recognize (see and name) transformations including rigid and size transformations. 2. Define (both conceptually and abstractly) and use the four rigid motions: translation, rotation, reflecti ...
... What to Know in Chapter 16: Transformational Geometry To complete this chapter successfully student will: 1. Recognize (see and name) transformations including rigid and size transformations. 2. Define (both conceptually and abstractly) and use the four rigid motions: translation, rotation, reflecti ...
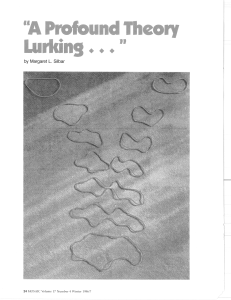
by Margaret L. Silbar
... as photons having both wave and particle properties. No one can yet make detailed predictions with superstring theory. Nor does anyone yet grasp an underlying principle that explains why strings make sense as nature's basic building blocks. For example, superstring theory is not yet based on a geome ...
... as photons having both wave and particle properties. No one can yet make detailed predictions with superstring theory. Nor does anyone yet grasp an underlying principle that explains why strings make sense as nature's basic building blocks. For example, superstring theory is not yet based on a geome ...
transformationunit
... What to Know in Chapter 16: Transformational Geometry To complete this chapter successfully student will: 1. Recognize (see and name) transformations including rigid and size transformations. 2. Define (both conceptually and abstractly) and use the four rigid motions: translation, rotation, reflecti ...
... What to Know in Chapter 16: Transformational Geometry To complete this chapter successfully student will: 1. Recognize (see and name) transformations including rigid and size transformations. 2. Define (both conceptually and abstractly) and use the four rigid motions: translation, rotation, reflecti ...
Goldstone Bosons and Chiral Symmetry Breaking in QCD
... uniquely fixed by the symmetry: L = fπ2 Tr(∂µ Σ† ∂ µ Σ). Expanding to second order in the pion fields gives ordinary kinetic terms; at higher orders we obtain derivative interactions. ...
... uniquely fixed by the symmetry: L = fπ2 Tr(∂µ Σ† ∂ µ Σ). Expanding to second order in the pion fields gives ordinary kinetic terms; at higher orders we obtain derivative interactions. ...
Unified rotational and permutational symmetry and selection rules in
... What can representation theory tell us? 1)U є U(2I+1) leaves ψ ψ invariant (U✝U=Id.) 2)P є SN describes permutation of particles ...
... What can representation theory tell us? 1)U є U(2I+1) leaves ψ ψ invariant (U✝U=Id.) 2)P є SN describes permutation of particles ...