LectureSection3.3Trigonometry
... then you can find the missing sides and missing angles. This is where the trigonometry comes in. Recall in a previous table, we looked at some ratios. Remember, these ratios were driven by the angles in the triangle (and, of course, the sides). Trigonometry uses a shortcut method of referring ...
... then you can find the missing sides and missing angles. This is where the trigonometry comes in. Recall in a previous table, we looked at some ratios. Remember, these ratios were driven by the angles in the triangle (and, of course, the sides). Trigonometry uses a shortcut method of referring ...
Geometry - Concepts 9-12
... Theorem 4.4 – Converse of the Isosceles Triangle Theorem If two angles of a triangle are congruent, then the two sides opposite those angles are ___________________. ...
... Theorem 4.4 – Converse of the Isosceles Triangle Theorem If two angles of a triangle are congruent, then the two sides opposite those angles are ___________________. ...
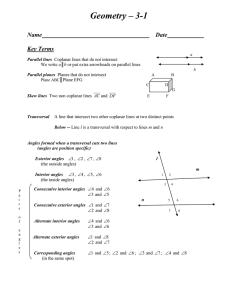
Geometry –3-1
... Exchanging the hypothesis (IF) and conclusion (THEN) of a conditional statement. Postulate 3.5 If given a line and a point not on the line, ...
... Exchanging the hypothesis (IF) and conclusion (THEN) of a conditional statement. Postulate 3.5 If given a line and a point not on the line, ...
Geometry Cornell Notes-Chapter 3
... Postulate 3.2 Two lines have the same slope if and only if they are parallel. Postulate 3.3 Two lines are perpendicular if and only if the product of their slopes is -1. Examples Determine whether AB and MN are parallel, perpendicular, or neither. 1. A(0,3), B(5,-7), M(-6,7), N(-2,-1) 2. A( -1, 4), ...
... Postulate 3.2 Two lines have the same slope if and only if they are parallel. Postulate 3.3 Two lines are perpendicular if and only if the product of their slopes is -1. Examples Determine whether AB and MN are parallel, perpendicular, or neither. 1. A(0,3), B(5,-7), M(-6,7), N(-2,-1) 2. A( -1, 4), ...
Glossary∗
... Divisor A factor of an integer. Example: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 are the positive divisors of 12. Domain The set of values that can be used as inputs for a given function. Edge The line segment where two faces of a three-dimensional shape intersect. Example: When a die is rolled, it never lands teeter ...
... Divisor A factor of an integer. Example: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 are the positive divisors of 12. Domain The set of values that can be used as inputs for a given function. Edge The line segment where two faces of a three-dimensional shape intersect. Example: When a die is rolled, it never lands teeter ...
Proving Triangles Similar AA ~ Postulate: If two angles of one
... If the measures of two sides of a triangles are proportional to the measures of two corresponding sides of another triangle and the included angles are congruent, then the triangles are similar. (SAS~) ...
... If the measures of two sides of a triangles are proportional to the measures of two corresponding sides of another triangle and the included angles are congruent, then the triangles are similar. (SAS~) ...