Note Sheet 2-8
... June 30, 2013 Geometry 2-8 Proving Angle Relationships Postulate 2.10: Protractor Postulate: Given any angle, the measure can be assigned a value between 0 and 180. Postulate 2.11: Angle Addition Postulate: Point D is in the interior of ⦛ABC if and only if m⦛ABD + m ⦛DBC = m⦛ ABC. D ...
... June 30, 2013 Geometry 2-8 Proving Angle Relationships Postulate 2.10: Protractor Postulate: Given any angle, the measure can be assigned a value between 0 and 180. Postulate 2.11: Angle Addition Postulate: Point D is in the interior of ⦛ABC if and only if m⦛ABD + m ⦛DBC = m⦛ ABC. D ...
ExamView - Geometry 1st semester exam review.tst
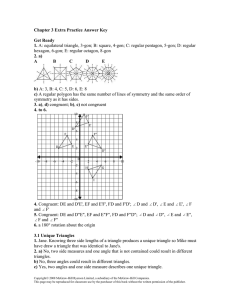
... Not drawn to scale a. m∠AEB = 60 b. ∠BEC and ∠CED are adjacent angles. c. m∠BEC = 120 d. ∠ AED and ∠BEC are adjacent angles. 64. ∠DFG and ∠JKL are complementary angles. m∠DFG = x + 5, and m∠JKL = x − 9. Find the measure of each angle. a. ∠DFG = 47, ∠JKL = 53 b. ∠DFG = 47, ∠JKL = 43 c. ∠DFG = 52, ∠JK ...
... Not drawn to scale a. m∠AEB = 60 b. ∠BEC and ∠CED are adjacent angles. c. m∠BEC = 120 d. ∠ AED and ∠BEC are adjacent angles. 64. ∠DFG and ∠JKL are complementary angles. m∠DFG = x + 5, and m∠JKL = x − 9. Find the measure of each angle. a. ∠DFG = 47, ∠JKL = 53 b. ∠DFG = 47, ∠JKL = 43 c. ∠DFG = 52, ∠JK ...
Math Geometry Honors - Morgan County School District Re-3
... Use the Segment Addition & Angle Addition Postulate Know the different types of angles Use postulates & theorems relating to points, lines and planes Use conditional statements & converses, as well as biconditionals. Use the properties from algebra to do algebraic proofs. Justify statements using po ...
... Use the Segment Addition & Angle Addition Postulate Know the different types of angles Use postulates & theorems relating to points, lines and planes Use conditional statements & converses, as well as biconditionals. Use the properties from algebra to do algebraic proofs. Justify statements using po ...
geometry - White Plains Public Schools
... Example 1: Naming Points, Lines, and Planes A. Name four coplanar points. ...
... Example 1: Naming Points, Lines, and Planes A. Name four coplanar points. ...
Proof. Consider the dilation with center C and scaling factor CA/CD
... This can now be proved in the traditional way, once you know SAS and ASA congruence. 11. (AA Similarity.) Assume that triangles ∆ABC and ∆XY Z are such that m6 A = m6 X, and m6 B = m6 Y . Prove that ∆ABC ∼ ∆XY Z. Proof. Consider a dilation (choose any center you like) with scaling factor XY /AB. App ...
... This can now be proved in the traditional way, once you know SAS and ASA congruence. 11. (AA Similarity.) Assume that triangles ∆ABC and ∆XY Z are such that m6 A = m6 X, and m6 B = m6 Y . Prove that ∆ABC ∼ ∆XY Z. Proof. Consider a dilation (choose any center you like) with scaling factor XY /AB. App ...