CPSD MATHEMATICS PACING GUIDE Geometry
... Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on the c ...
... Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on the c ...
1 Definition 2 Ordering of Angles
... the source of two rays ba and bc. We write a = [∠abc]. It is easy to see that given a point p and a ray ρ emanating from p, we can find, in each free angle, a representative whose one side is ρ. In other words, for any free angle a, it is possible to write a = [∠αpρ] for some ray α. Now we are ready ...
... the source of two rays ba and bc. We write a = [∠abc]. It is easy to see that given a point p and a ray ρ emanating from p, we can find, in each free angle, a representative whose one side is ρ. In other words, for any free angle a, it is possible to write a = [∠αpρ] for some ray α. Now we are ready ...
INDUCTIVE REASONING
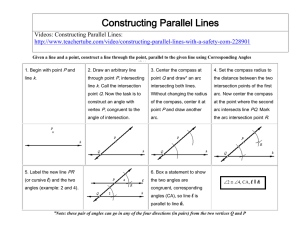
... If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then corresponding angles are ______________________, alternate interior angles are __________________________, and alternate exterior angles are ________________________ Complete each statement. 1. If two angles are vertical angles, then they are ____ ...
... If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then corresponding angles are ______________________, alternate interior angles are __________________________, and alternate exterior angles are ________________________ Complete each statement. 1. If two angles are vertical angles, then they are ____ ...