Vacuoles - SCHOOLinSITES
... Receives protein-filled vesicles that bud from the ER. Vesicles fuse with membrane of Golgi apparatus. ...
... Receives protein-filled vesicles that bud from the ER. Vesicles fuse with membrane of Golgi apparatus. ...
Cell Parts and Organelles Flash Cards
... Cell Parts and Organelles Flash Cards Directions: You will receive 21 notecards and a rubber band or paper clip. On the front of one notecard, write your name and class period and set that card aside. The other 20 notecards will be for your flash cards. Each flash card is worth 5 points and there ar ...
... Cell Parts and Organelles Flash Cards Directions: You will receive 21 notecards and a rubber band or paper clip. On the front of one notecard, write your name and class period and set that card aside. The other 20 notecards will be for your flash cards. Each flash card is worth 5 points and there ar ...
Directions: Use this information as a general reference tool to guide
... By the conclusion of this unit, you should know the following: _____1. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from where they are highly concentrated to where they are less concentrated. _____2. Osmosis (a special type of diffusion) is the movement of water from where it is highly concentrated to wh ...
... By the conclusion of this unit, you should know the following: _____1. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from where they are highly concentrated to where they are less concentrated. _____2. Osmosis (a special type of diffusion) is the movement of water from where it is highly concentrated to wh ...
Cell Parts and Organelles Flash Cards
... Cell Parts and Organelles Flash Cards Directions: You will receive 21 notecards and a rubber band or paper clip. On the front of one notecard, write your name and class period and set that card aside. The other 20 notecards will be for your flash cards. Each flash card is worth 5 points and there ar ...
... Cell Parts and Organelles Flash Cards Directions: You will receive 21 notecards and a rubber band or paper clip. On the front of one notecard, write your name and class period and set that card aside. The other 20 notecards will be for your flash cards. Each flash card is worth 5 points and there ar ...
The Chemical Senses and Transduction
... blood. When the concentration of either is too high or too low, the nervous system is notified and signals are sent out to the circulatory and respiratory systems to adjust the beating of the heart and the rate of breathing in the appropriate direction. Similarly, there are sensory endings in our mu ...
... blood. When the concentration of either is too high or too low, the nervous system is notified and signals are sent out to the circulatory and respiratory systems to adjust the beating of the heart and the rate of breathing in the appropriate direction. Similarly, there are sensory endings in our mu ...
FREE Sample Here
... important, its knock-out will result in lethality. On the other hand, if it's very important its function will be duplicated by another protein, and there will be no obvious phenotype for the knock-out." Please explain this statement in your own words. ...
... important, its knock-out will result in lethality. On the other hand, if it's very important its function will be duplicated by another protein, and there will be no obvious phenotype for the knock-out." Please explain this statement in your own words. ...
anatomy of the body
... Think of the “Cell Factory” Boss give orders to the rest of the factory (DNA in the nucleus surrounded by the nuclear membrane). The workers (ribosomes) on the assembly line are in the factory (cytosol) who receive orders for production from the boss’s messanger (mRNA). The raw materials are the am ...
... Think of the “Cell Factory” Boss give orders to the rest of the factory (DNA in the nucleus surrounded by the nuclear membrane). The workers (ribosomes) on the assembly line are in the factory (cytosol) who receive orders for production from the boss’s messanger (mRNA). The raw materials are the am ...
Overview of Cell Organelles
... • What are the 4 main structures/organelles that ALL living cells must have? • What are the primary structures (organelles), and their processes, for cells to function properly? • Differentiate between the structures and functions of plant and animal cell organelles (including cell membrane, cell wa ...
... • What are the 4 main structures/organelles that ALL living cells must have? • What are the primary structures (organelles), and their processes, for cells to function properly? • Differentiate between the structures and functions of plant and animal cell organelles (including cell membrane, cell wa ...
Page 1 of 1 DTU Systems Biology Mette Voldby Larsen, CBS
... KEY CONCEPTS 1. The cell is the basic unit of life. All cells come from preexisting cells and have certain processes, types of molecules, and structures in common. 2. Cells may have originated from “protocells”— cell-like structures thought to be similar to structures that can be produced in the lab ...
... KEY CONCEPTS 1. The cell is the basic unit of life. All cells come from preexisting cells and have certain processes, types of molecules, and structures in common. 2. Cells may have originated from “protocells”— cell-like structures thought to be similar to structures that can be produced in the lab ...
ces-1 (cG-17): sc-12177 - Santa Cruz Biotechnology
... Several proteins involved in regulating and executing programmed cell death have been identified in C. elegans. CED-2, which is similar to the human adaptor protein CrkII, as well as CED-5 and CED-7, which are orthologs of the mammalian DOCK180 and ABC transporter proteins, respectively, are involve ...
... Several proteins involved in regulating and executing programmed cell death have been identified in C. elegans. CED-2, which is similar to the human adaptor protein CrkII, as well as CED-5 and CED-7, which are orthologs of the mammalian DOCK180 and ABC transporter proteins, respectively, are involve ...
Final Exam KEY
... ______ There will be amplification but the fragment yield will be about half the amount. ___X___ There will be amplification but the fragment yield will be dramatically lower. ______ There will be amplification but the fragment size will be shorter than expected. ______ There will not be amplificati ...
... ______ There will be amplification but the fragment yield will be about half the amount. ___X___ There will be amplification but the fragment yield will be dramatically lower. ______ There will be amplification but the fragment size will be shorter than expected. ______ There will not be amplificati ...
asdfs
... When you mix iodine starch with ____________ you will see a black/purple color change. ...
... When you mix iodine starch with ____________ you will see a black/purple color change. ...
Methods of Movement in the Cell
... Materials Important? • All living things have certain requirements they must satisfy in order to remain alive. – Exchanging gases (usually CO2 and O2), – Taking in water, minerals, and food – Eliminating wastes ...
... Materials Important? • All living things have certain requirements they must satisfy in order to remain alive. – Exchanging gases (usually CO2 and O2), – Taking in water, minerals, and food – Eliminating wastes ...
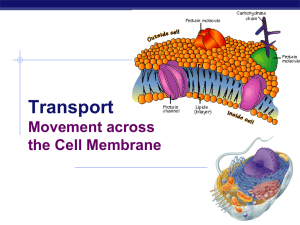
3 - Cell Structure and Function
... • Fluid mosaic model – it’s made up of many separate components that can freely flow and change position while maintaining the integrity of the membrane; the components include – Lipids • Bilayer of phospholipids – separates cytoplasm from extracellular fluid (ECF) – Polar/hydrophilic heads interact ...
... • Fluid mosaic model – it’s made up of many separate components that can freely flow and change position while maintaining the integrity of the membrane; the components include – Lipids • Bilayer of phospholipids – separates cytoplasm from extracellular fluid (ECF) – Polar/hydrophilic heads interact ...
Cell Growth
... 1. cells go or stay in G1, S, and G2 because of the presence or accumulation of "trigger proteins" 2. this control keeps organisms and their cells in homeostasis 3. regulation of the cell cycle is ESSENTIAL B. Uncontrolled division of cells 1. cancer is (**the uncontrolled ‘growth’ or division of ce ...
... 1. cells go or stay in G1, S, and G2 because of the presence or accumulation of "trigger proteins" 2. this control keeps organisms and their cells in homeostasis 3. regulation of the cell cycle is ESSENTIAL B. Uncontrolled division of cells 1. cancer is (**the uncontrolled ‘growth’ or division of ce ...
Original
... air, and in a process called photosynthesis, they convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars In addition to containing almost all of the types of organelles that animal cells contain, plant cells contain three unique features. Those features are the cell wall, the central vacuole, and plastids, ...
... air, and in a process called photosynthesis, they convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars In addition to containing almost all of the types of organelles that animal cells contain, plant cells contain three unique features. Those features are the cell wall, the central vacuole, and plastids, ...
Cells - Organelles and Cell Cycle
... from the time the cell is formed until the time it goes through cell division • Includes Interphase, Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) and cytokinesis ...
... from the time the cell is formed until the time it goes through cell division • Includes Interphase, Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) and cytokinesis ...
Bio background
... Assigning Function to Proteins While 25000 genes have been identified in the human genome, relatively few have known functional annotation. Determining the function of the protein can be done in several ways. ...
... Assigning Function to Proteins While 25000 genes have been identified in the human genome, relatively few have known functional annotation. Determining the function of the protein can be done in several ways. ...
Unicellular Multicellular Prokaryotic Organelles cell membrane
... Is a type of vesical organelle containing enzymes that digest food particles, viruses, bacteria, worn out cell part, and sometimes the cell itself. ...
... Is a type of vesical organelle containing enzymes that digest food particles, viruses, bacteria, worn out cell part, and sometimes the cell itself. ...
Unit 2 Practice Questions
... made and refined in the ER and Golgi apparatus. The new membrane then forms transport vesicles that travel to the cell surface. On which side of the vesicle membrane are the carbohydrates? 4. What happens to a cell placed in a hypertonic solution? Describe the free water concentration inside and out ...
... made and refined in the ER and Golgi apparatus. The new membrane then forms transport vesicles that travel to the cell surface. On which side of the vesicle membrane are the carbohydrates? 4. What happens to a cell placed in a hypertonic solution? Describe the free water concentration inside and out ...
Ask the Doctor - Lyme Disease Association of Australia
... to function. These membrane proteins are responsible for many specialized functions; some act as receptors that allow the cell to respond to external signals, some are responsible for the selective transport of molecules across the membrane and others, participate in electron transport and oxidative ...
... to function. These membrane proteins are responsible for many specialized functions; some act as receptors that allow the cell to respond to external signals, some are responsible for the selective transport of molecules across the membrane and others, participate in electron transport and oxidative ...
03 Movement in and out of cells
... Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from an area of high water potential to an area of low water potential (concentration) across a partially permeable membrane. ...
... Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from an area of high water potential to an area of low water potential (concentration) across a partially permeable membrane. ...
Name - wwphs
... The sputum (fluid coughed up from the lungs) of many smokers contains cells with mutations (errors) in the genes for p53. The smoking induced mutations appear to be an early signal showing that cancer of the lungs will follow. What is the likely relationship between early p53 mutation and the develo ...
... The sputum (fluid coughed up from the lungs) of many smokers contains cells with mutations (errors) in the genes for p53. The smoking induced mutations appear to be an early signal showing that cancer of the lungs will follow. What is the likely relationship between early p53 mutation and the develo ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.