
Slide 1
... introns (bp sizes are in parentheses). Peptide sequences that correspond to translated TM regions are labeled with roman numerals (I– VII). An alternatively spliced region (orange box) is depicted between the stop sequences. Six isoforms of the receptor (labels are on the left) result from alternati ...
... introns (bp sizes are in parentheses). Peptide sequences that correspond to translated TM regions are labeled with roman numerals (I– VII). An alternatively spliced region (orange box) is depicted between the stop sequences. Six isoforms of the receptor (labels are on the left) result from alternati ...
Chitin is a component of ______ cell walls
... 2. Which of the following organisms do not have cell walls? a. plants b. fungi c. monerans d. animals. 3. Which of the following is NOT true of membranes? a. Folded membranes increase surface area for efficiency. b. Folded membranes do not form compartments in the cell. c. Endoplasmic reticulum is m ...
... 2. Which of the following organisms do not have cell walls? a. plants b. fungi c. monerans d. animals. 3. Which of the following is NOT true of membranes? a. Folded membranes increase surface area for efficiency. b. Folded membranes do not form compartments in the cell. c. Endoplasmic reticulum is m ...
cells and their organelles
... The cell is the basic unit of life. When cells group together they form tissues. For example, your body has muscle tissue which is a group of cells performing the same job. When a group of tissues combine to do the same job, they become organs. Your heart and lungs are great examples of organs. Some ...
... The cell is the basic unit of life. When cells group together they form tissues. For example, your body has muscle tissue which is a group of cells performing the same job. When a group of tissues combine to do the same job, they become organs. Your heart and lungs are great examples of organs. Some ...
Bio 30 Eukaryotic Cell Structure PP
... • Function - contains the cell structures (called organelles - parts of a cell are often called 'organelles' which means 'little organs') that are essential for the cell to function. • - Cytoplasm is contains a jelly-like material ...
... • Function - contains the cell structures (called organelles - parts of a cell are often called 'organelles' which means 'little organs') that are essential for the cell to function. • - Cytoplasm is contains a jelly-like material ...
Specification of cell fates
... Positional information: fields, boundaries, and gradients Development requires a dramatic increase in the amount of information contained within the organism. The "new" information is contained in the genome, and is gradually translated into cellular processes. The principal ways in which this happe ...
... Positional information: fields, boundaries, and gradients Development requires a dramatic increase in the amount of information contained within the organism. The "new" information is contained in the genome, and is gradually translated into cellular processes. The principal ways in which this happe ...
Eukaryotic Cell Organelles
... Small, round structure (vesicle) produced in the Golgi complex that are found floating in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells Common in animals, fungi, and protists Rare in plants Contain potent hydrolytic digestive and ...
... Small, round structure (vesicle) produced in the Golgi complex that are found floating in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells Common in animals, fungi, and protists Rare in plants Contain potent hydrolytic digestive and ...
Fluid Mosaic Model
... • Slime molds do not have cells as a basic unit. They have an unorganized cytoplasm and many nuclei, they also do not have a distinct cell shape ...
... • Slime molds do not have cells as a basic unit. They have an unorganized cytoplasm and many nuclei, they also do not have a distinct cell shape ...
THE CELL
... 1. All living things are made up of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function of all ...
... 1. All living things are made up of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function of all ...
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
... • Somatic cells (body cells) of a multicellular organism perform specialized functions to keep the organism functioning • Life cycle of a cell is called the Cell Cycle – Interphase – Mitosis ...
... • Somatic cells (body cells) of a multicellular organism perform specialized functions to keep the organism functioning • Life cycle of a cell is called the Cell Cycle – Interphase – Mitosis ...
Chapter 7 – Cell Structure and Function
... internal structures and membranes Generally contain many ____________________ structures act like specialized organs Many of the internal ___________________ _______ they are known as organelles Some live as single-celled organisms, many form large multicellular organisms (plants, animals, fungi, ...
... internal structures and membranes Generally contain many ____________________ structures act like specialized organs Many of the internal ___________________ _______ they are known as organelles Some live as single-celled organisms, many form large multicellular organisms (plants, animals, fungi, ...
Cells - NCSscience
... The process that most producer organisms use to change light energy into chemical energy (producer ...
... The process that most producer organisms use to change light energy into chemical energy (producer ...
Science Focus 10 Chapter 8 Review KEY
... 4. (a) A bacterial cell would be transported by endocytosis. It could be stored in a vacuole or transported in a vesicle. (b) Carbon dioxide is transported by diffusion. (c) Water is transported by osmosis. (d) Sodium ions are transported by active transport or facilitated diffusion. 5. The particle ...
... 4. (a) A bacterial cell would be transported by endocytosis. It could be stored in a vacuole or transported in a vesicle. (b) Carbon dioxide is transported by diffusion. (c) Water is transported by osmosis. (d) Sodium ions are transported by active transport or facilitated diffusion. 5. The particle ...
BIOCHEMISTRY WEBQUEST
... The four main classes of organic molecules that make up and are made by living cells are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. These are made up of different bonded combinations of CHONPS, with CARBON atoms forming the framework (or “backbone”) of each molecule. For this assignment, yo ...
... The four main classes of organic molecules that make up and are made by living cells are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. These are made up of different bonded combinations of CHONPS, with CARBON atoms forming the framework (or “backbone”) of each molecule. For this assignment, yo ...
Cytoskeleton 14
... Nine doublets of microtubules make a ring having two single microtubles in the center. Cross linking motor proteins along the length of flagellum and cilium connect the outer neighboring doublet. Centriole like basal body anchored the flagellum or cilium in the cell. Basal body of sperm in animals/h ...
... Nine doublets of microtubules make a ring having two single microtubles in the center. Cross linking motor proteins along the length of flagellum and cilium connect the outer neighboring doublet. Centriole like basal body anchored the flagellum or cilium in the cell. Basal body of sperm in animals/h ...
Bioenergetics Structures and Functions of Cells
... 6. contain oxidases and catalases 7. provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to another 8. sites of protein synthesis 9. plastids containing pigments other than chlorophyll 10.allow bacteria to exchange DNA during conjugation ...
... 6. contain oxidases and catalases 7. provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to another 8. sites of protein synthesis 9. plastids containing pigments other than chlorophyll 10.allow bacteria to exchange DNA during conjugation ...
What is the Golgi Apparatus?
... What is the function of the Golgi Apparatus? A. Produce proteins B. Process and sort proteins for transportation C. Provide the energy for a cell D. Non of the Above Which part of the cell does the Cis Face, face? A. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum ...
... What is the function of the Golgi Apparatus? A. Produce proteins B. Process and sort proteins for transportation C. Provide the energy for a cell D. Non of the Above Which part of the cell does the Cis Face, face? A. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum ...
cells - Plain Local Schools
... I. Chloroplasts A. Chloroplasts are the photosynthetic organelles found in some cells of plants and algae B. Photosynthesis is a complex, multi-step process and the chloroplasts provides the necessary organization for the process to take place C. Inside the chloroplasts are disks that act as the “p ...
... I. Chloroplasts A. Chloroplasts are the photosynthetic organelles found in some cells of plants and algae B. Photosynthesis is a complex, multi-step process and the chloroplasts provides the necessary organization for the process to take place C. Inside the chloroplasts are disks that act as the “p ...
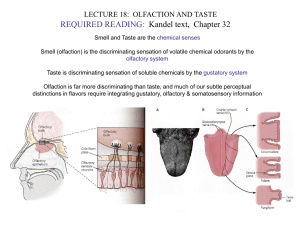
LECTURE18.Olfaction&Taste
... Taste perception is also shaped by parallel olfactory input; the somatosensory stimulus “fools” us to perceive the olfaction as part of the taste. ...
... Taste perception is also shaped by parallel olfactory input; the somatosensory stimulus “fools” us to perceive the olfaction as part of the taste. ...
1
... A network of protein fibers, collectively called the CYTOSKELETON, extending throughout the cytoplasm of the cell. These fibers function like a skeleton in providing for both structural support and cell motility. These movements generally require the interaction of the cytoskeleton with proteins ca ...
... A network of protein fibers, collectively called the CYTOSKELETON, extending throughout the cytoplasm of the cell. These fibers function like a skeleton in providing for both structural support and cell motility. These movements generally require the interaction of the cytoskeleton with proteins ca ...
the cell context influences rainbow trout gonadotropin receptors
... BACKGROUND: The presence of two distinct gonadotropin receptors (GtHRs) in a single fish species was confirmed by the molecular cloning of two different cDNAs in several fish species including trout. In mammals, GtHRs show little cross-activation (0.01–0.1%). In contrast, the bioactivity of fish gon ...
... BACKGROUND: The presence of two distinct gonadotropin receptors (GtHRs) in a single fish species was confirmed by the molecular cloning of two different cDNAs in several fish species including trout. In mammals, GtHRs show little cross-activation (0.01–0.1%). In contrast, the bioactivity of fish gon ...
Chapter 3
... h. Proteins protruding into the cell anchor supportive rods and tubules. i. Still other proteins have carbohydrates attached; these complexes are used in cell identification. Membrane proteins called cellular adhesion molecules (CAMs) help determine one cell’s interactions with others. ...
... h. Proteins protruding into the cell anchor supportive rods and tubules. i. Still other proteins have carbohydrates attached; these complexes are used in cell identification. Membrane proteins called cellular adhesion molecules (CAMs) help determine one cell’s interactions with others. ...
supplementary methods
... To quantify Western blot protein levels phosphatase-conjugated secondary antibodies were used (Jackson ImmunoResearch) and visualised with the ECF reagent (Amersham Biosciences). Quantification of CDK11 fluorescence signal on the nitrocellulose membrane was performed using the Storm840 apparatus (Mo ...
... To quantify Western blot protein levels phosphatase-conjugated secondary antibodies were used (Jackson ImmunoResearch) and visualised with the ECF reagent (Amersham Biosciences). Quantification of CDK11 fluorescence signal on the nitrocellulose membrane was performed using the Storm840 apparatus (Mo ...
Protista
... Member of Protista Kingdom. Unicellular microscopic organism found at the bottom of freshwater ponds or muddy soil. ...
... Member of Protista Kingdom. Unicellular microscopic organism found at the bottom of freshwater ponds or muddy soil. ...
Chapter_3_Cells[1]
... Osmotic pressure ( Additional information on osmotic pressure ) A solution with the same osmotic pressure as body fluids is called isotonic; one with higher osmotic pressure than body fluids is hypertonic; one with lower osmotic pressure is hypotonic. ...
... Osmotic pressure ( Additional information on osmotic pressure ) A solution with the same osmotic pressure as body fluids is called isotonic; one with higher osmotic pressure than body fluids is hypertonic; one with lower osmotic pressure is hypotonic. ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.






















![Chapter_3_Cells[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008099623_1-12c4980db7f2ebad1f4d82b4b14122ae-300x300.png)