CHAPTER - 8 CELL – STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS
... were separated from each other by a wall or partition. He named each box as a Cell. The cells which Hooke observed were actually dead cells of plants. ...
... were separated from each other by a wall or partition. He named each box as a Cell. The cells which Hooke observed were actually dead cells of plants. ...
Students Mitosis 2011.ppt
... the original fertilized egg has to divide… and divide… and divide… and divide… ...
... the original fertilized egg has to divide… and divide… and divide… and divide… ...
Cellular Injury and Responses to stress
... • Hyperplasia can be a fertile soil for development of neoplasia ...
... • Hyperplasia can be a fertile soil for development of neoplasia ...
The Cell- Powerpoint
... membrane. Cut the outer membrane to get a better look inside. With the outer membrane removed it is much easier to see the contents of the chloroplast. The stacks of disk-like structures are called the GRANA. The membranes connecting them are the THYLAKOID MEMBRANES. ...
... membrane. Cut the outer membrane to get a better look inside. With the outer membrane removed it is much easier to see the contents of the chloroplast. The stacks of disk-like structures are called the GRANA. The membranes connecting them are the THYLAKOID MEMBRANES. ...
Development - s3.amazonaws.com
... • Form of cellular signaling during development • Ability of one group of embryonic cells to influence the development of another. ...
... • Form of cellular signaling during development • Ability of one group of embryonic cells to influence the development of another. ...
Lecture Notes
... d. Structural support, movement, and communication between cells are functions of the ...
... d. Structural support, movement, and communication between cells are functions of the ...
name date ______ period
... A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving D. Cell membranes surround all animal, plant, and bacterial cells. E. It i ...
... A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving D. Cell membranes surround all animal, plant, and bacterial cells. E. It i ...
Prokaryotes
... Smaller .5 to 2um (~1/1000th mm) ANALOGY No Nucleus -DNA in nucleoid region Prokarytic cell wall (peptidoglycan) -rigid, maintain shape of cell -protection - surrounds plasma membrane Capsule – found around some prokaryotes over cell wall - sticky polysaccharide covering - protection - found on many ...
... Smaller .5 to 2um (~1/1000th mm) ANALOGY No Nucleus -DNA in nucleoid region Prokarytic cell wall (peptidoglycan) -rigid, maintain shape of cell -protection - surrounds plasma membrane Capsule – found around some prokaryotes over cell wall - sticky polysaccharide covering - protection - found on many ...
Chapter 2
... Lipids: Three kinds: What 3 elements do they all contain? _________________ supply energy, are built from glycerol and three fatty acids. Fatty acids with hydrogen at every position along the carbon chain are saturated; those with one or more double bonds are called ______________ fats. ____________ ...
... Lipids: Three kinds: What 3 elements do they all contain? _________________ supply energy, are built from glycerol and three fatty acids. Fatty acids with hydrogen at every position along the carbon chain are saturated; those with one or more double bonds are called ______________ fats. ____________ ...
To: parties interested in the live
... Unlike animals with a heartbeat, establishing the live-dead status in plants and especially in unicellular microscopic plankton, is difficult. Theoretically the only method that unequivocally establishes microscopic cell death is the complete disintegration of cellular compounds: nucleus, plastids a ...
... Unlike animals with a heartbeat, establishing the live-dead status in plants and especially in unicellular microscopic plankton, is difficult. Theoretically the only method that unequivocally establishes microscopic cell death is the complete disintegration of cellular compounds: nucleus, plastids a ...
Cells
... Cytoplasm is the material between the cell’s nucleus and the cell membrane. It fills the entire cell. It contains a large variety of organelles and nutrients. The cytoplasm consists of an outer ectoplasm and an inner endoplasm. ...
... Cytoplasm is the material between the cell’s nucleus and the cell membrane. It fills the entire cell. It contains a large variety of organelles and nutrients. The cytoplasm consists of an outer ectoplasm and an inner endoplasm. ...
Cell Parts Quiz Review 2011
... 1.History: Be familiar with how the following scientists contributed towards understanding cells: Hooke, Leeuwenhoek, Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow 2.Structures and Function of Cells- Know the function of each and be able to apply an analogy (Like your cell factory). Also be able to label a cell pictu ...
... 1.History: Be familiar with how the following scientists contributed towards understanding cells: Hooke, Leeuwenhoek, Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow 2.Structures and Function of Cells- Know the function of each and be able to apply an analogy (Like your cell factory). Also be able to label a cell pictu ...
Unit 2 test - Lemon Bay High School
... chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use? ...
... chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use? ...
Unit 3( Celluar Transport)
... Score 2: The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes that support the learning goal(s). A2, Given a diagram, I can label the parts of the cell membrane. B2. Given an example, I can identify a process as active or passive transport. C2. I can desc ...
... Score 2: The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes that support the learning goal(s). A2, Given a diagram, I can label the parts of the cell membrane. B2. Given an example, I can identify a process as active or passive transport. C2. I can desc ...
Apple Anatomy - Agriculture in the Classroom
... when looking through their microscope. The cell membrane forms a barrier between the inside of the apple and the outside. The cell membrane allows waste to exit the cell. The cell wall is used to provide structural support and control the amount of water entering the cell. The golgi body stores and ...
... when looking through their microscope. The cell membrane forms a barrier between the inside of the apple and the outside. The cell membrane allows waste to exit the cell. The cell wall is used to provide structural support and control the amount of water entering the cell. The golgi body stores and ...
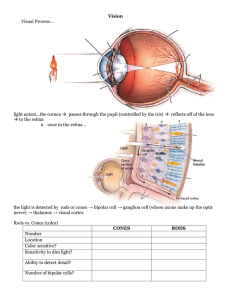
Vision Lecture Notes
... ● Frequency theory: the basilar membrane vibrates at the same rate as incoming sound waves, triggering neural impulses at the same rate ● explains low-pitched sounds ● Place theory: different frequencies cause vibrations at different locations (hair cells) along the basilar membrane, triggering the ...
... ● Frequency theory: the basilar membrane vibrates at the same rate as incoming sound waves, triggering neural impulses at the same rate ● explains low-pitched sounds ● Place theory: different frequencies cause vibrations at different locations (hair cells) along the basilar membrane, triggering the ...
Biology Monday, October 16
... – with the concentration gradient (from high concentration to low concentration) – This does not require energy – Particles that are too large to fit between lipids: such as glucose http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_facilitated_di ffusion_works.htm ...
... – with the concentration gradient (from high concentration to low concentration) – This does not require energy – Particles that are too large to fit between lipids: such as glucose http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_facilitated_di ffusion_works.htm ...
Lecture 3a - Membs and Transport
... 4. Receptors - signaling (ligand) 5. Transport Carriers - transport things in/out Channels – pore allowing ions in/out ...
... 4. Receptors - signaling (ligand) 5. Transport Carriers - transport things in/out Channels – pore allowing ions in/out ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.