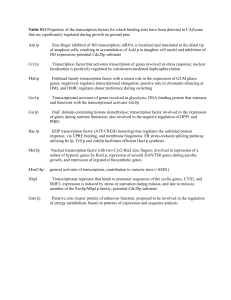
Table S11 Properties of the transcription factors for which binding
... Transcriptional repressor that binds to promoter sequences of the cyclin genes, CYS3, and SMF2; expression is induced by stress or starvation during mitosis, and late in meiosis; member of the Swi4p/Mbp1p family; potential Cdc28p substrate ...
... Transcriptional repressor that binds to promoter sequences of the cyclin genes, CYS3, and SMF2; expression is induced by stress or starvation during mitosis, and late in meiosis; member of the Swi4p/Mbp1p family; potential Cdc28p substrate ...
The AP BIOLOGY
... classes of macromolecules, and explain the biologically important functions of this group. Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry weight of most cells, and they are instrumental in almost everything organism do. Proteins are used for structure support, storage, transport of other substances, ...
... classes of macromolecules, and explain the biologically important functions of this group. Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry weight of most cells, and they are instrumental in almost everything organism do. Proteins are used for structure support, storage, transport of other substances, ...
Lecture 23 – SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION: G
... Starting with fructose-6-phosphate and proceeding to pyruvate what is the net yield of ATP? phosphofructokinase-1 = loss of 1ATP phosphoglycerate kinase = gain of 2ATP (fructose-1,6-bisphosphate splits to two molecules) pyruvate kinase = gain of 2ATP Net yield = gain of 3 ATP Describe how the intrac ...
... Starting with fructose-6-phosphate and proceeding to pyruvate what is the net yield of ATP? phosphofructokinase-1 = loss of 1ATP phosphoglycerate kinase = gain of 2ATP (fructose-1,6-bisphosphate splits to two molecules) pyruvate kinase = gain of 2ATP Net yield = gain of 3 ATP Describe how the intrac ...
COMPARISON OF PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS
... Cells vary widely in structure and function, even within the same organism. The human body, for example, has more than 200 different types of cells, each with a specialized organelles function. Each cell is made up of different ________________, each responsible for a different role to help the ...
... Cells vary widely in structure and function, even within the same organism. The human body, for example, has more than 200 different types of cells, each with a specialized organelles function. Each cell is made up of different ________________, each responsible for a different role to help the ...
BIOCHEMISTRY (CHEM 360)
... Valinomycin is an anti-bacterial that kills bacteria by surrounding K+ ions and shuttling them down their concentration gradient and across membranes. Which of the following might be the cause of cell death? (1) Disruption of secondary transport processes that depend on K+ ion concentration gradient ...
... Valinomycin is an anti-bacterial that kills bacteria by surrounding K+ ions and shuttling them down their concentration gradient and across membranes. Which of the following might be the cause of cell death? (1) Disruption of secondary transport processes that depend on K+ ion concentration gradient ...
Immunosuppressive drugs: the first 50 years and a glance forward
... During the past 50 years, many immunosuppressive drugs have been described. Often their mechanisms of action were established long after their discovery. Eventually these mechanisms were found to fall into five groups: (i) regulators of gene expression; (ii) alkylating agents; (iii) inhibitors of de ...
... During the past 50 years, many immunosuppressive drugs have been described. Often their mechanisms of action were established long after their discovery. Eventually these mechanisms were found to fall into five groups: (i) regulators of gene expression; (ii) alkylating agents; (iii) inhibitors of de ...
Vertebral Osteoporosis: Factors Affecting Urinary
... with CD.Suggesting that the HLA association is entirely due to the necessity to have these DQ alleles in orda to eapress CD, but that the main genet;c&kpcsitia~k atalmsotherthao theMHC. We hypouKsisedthat some of the insulin depeoacnt diabeta mllitus (lDDh4) susceptibility loci d d be common to CD s ...
... with CD.Suggesting that the HLA association is entirely due to the necessity to have these DQ alleles in orda to eapress CD, but that the main genet;c&kpcsitia~k atalmsotherthao theMHC. We hypouKsisedthat some of the insulin depeoacnt diabeta mllitus (lDDh4) susceptibility loci d d be common to CD s ...
An Introductory Overview of Cells, Chemical Bonds & Energy Part-I
... Found in the cytoplasm and on the ER. Their job is to make proteins. The nucleus makes the ribosomes. ...
... Found in the cytoplasm and on the ER. Their job is to make proteins. The nucleus makes the ribosomes. ...
Smell
... Receptor binding activates an effector Olfactory receptors between the olfactory receptor axons and known as the lateral olfactory tract Olfaction--sense of smell 1. Not the nose (water soluble) Circuit enzyme (either adenylate cyclase or phospho1.Only receptor discussed thus far that are mitral cel ...
... Receptor binding activates an effector Olfactory receptors between the olfactory receptor axons and known as the lateral olfactory tract Olfaction--sense of smell 1. Not the nose (water soluble) Circuit enzyme (either adenylate cyclase or phospho1.Only receptor discussed thus far that are mitral cel ...
File
... 21. The raw materials for respiration are __________ oxygen and ____________ 22. The products of respiration are ______________, carbon dioxide Energy water and ____________. ________ Diffusion 23. __________ is the process by which molecules spread out. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a 2 ...
... 21. The raw materials for respiration are __________ oxygen and ____________ 22. The products of respiration are ______________, carbon dioxide Energy water and ____________. ________ Diffusion 23. __________ is the process by which molecules spread out. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a 2 ...
Chapter 3 Chemistry of Life Modern Biology Textbook Holt
... protein’s shape and function. There are 20 different types identified by their R group. • Dipeptides: Two amino acids are joined by peptide bonds to form a dipeptide. • Polypeptides: A long chain of amino acids is called a polypeptide. ...
... protein’s shape and function. There are 20 different types identified by their R group. • Dipeptides: Two amino acids are joined by peptide bonds to form a dipeptide. • Polypeptides: A long chain of amino acids is called a polypeptide. ...
PowerPoint - Biological Sciences
... • Difficult to get crystal structure for more than one or two carbohydrate residues ...
... • Difficult to get crystal structure for more than one or two carbohydrate residues ...
The Cell Membrane
... Transport of materials across the plasma membrane that does not require energy from the cell but does use transport proteins is called ...
... Transport of materials across the plasma membrane that does not require energy from the cell but does use transport proteins is called ...
CH 7 CELL TEST
... Which of the following is a function of the cytoskeleton? a. helps a cell keep its shape c. surrounds the cell b. contains DNA d. helps make proteins Which structures carry out cell movement? a. cytoplasm and ribosomes c. microtubules and microfilaments b. nucleolus and nucleus d. chromosomes The ma ...
... Which of the following is a function of the cytoskeleton? a. helps a cell keep its shape c. surrounds the cell b. contains DNA d. helps make proteins Which structures carry out cell movement? a. cytoplasm and ribosomes c. microtubules and microfilaments b. nucleolus and nucleus d. chromosomes The ma ...
Year 7 Information Evening Presentation
... 2. Learn the names of at least one specialised plant cell and one specialised animal cell. Explain how they are adapted to carry out their function (job). ...
... 2. Learn the names of at least one specialised plant cell and one specialised animal cell. Explain how they are adapted to carry out their function (job). ...
Biochemistry cont`d
... - located in the center of the cell - controls all functions of organelles - cell reproduction/division takes place - DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is housed - blueprint of heredity - as cell divides the DNA coil tightly, called chromatin, to form chromosomes (46) - bound by nuclear envelope: double l ...
... - located in the center of the cell - controls all functions of organelles - cell reproduction/division takes place - DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is housed - blueprint of heredity - as cell divides the DNA coil tightly, called chromatin, to form chromosomes (46) - bound by nuclear envelope: double l ...
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell
... embedded in proteoglycans (protein with many carbohydrates attached) ...
... embedded in proteoglycans (protein with many carbohydrates attached) ...
Review for Cell Theory and Cell Organelle Exam
... Mitochondrial DNA • Mitochondria has its own DNA • A long time ago mitochondria was a bacteria cell on its own • Then a eukaryotic cell saw that it could be useful to have and a symbiotic relationship followed ...
... Mitochondrial DNA • Mitochondria has its own DNA • A long time ago mitochondria was a bacteria cell on its own • Then a eukaryotic cell saw that it could be useful to have and a symbiotic relationship followed ...
travel_bro. student instructions
... Objective: In the study of plant and animal cells, students will make comparisons to show relationships and associations between cell organelle functions and a roadside attraction or “city”. Students will develop a unique travel brochure demonstrating the ability to accurately describe and explain t ...
... Objective: In the study of plant and animal cells, students will make comparisons to show relationships and associations between cell organelle functions and a roadside attraction or “city”. Students will develop a unique travel brochure demonstrating the ability to accurately describe and explain t ...
Cells notes
... body functioning to stay alive. Cells also have “organs”, but we call them organelles. What are organelles? Specialized structures found in the cell that perform a distinct process within the cell. Examples: Nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondria, chloroplast, and etc. ...
... body functioning to stay alive. Cells also have “organs”, but we call them organelles. What are organelles? Specialized structures found in the cell that perform a distinct process within the cell. Examples: Nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondria, chloroplast, and etc. ...
Cells Study Guide
... Make protein? (Yes/No) Have DNA? (Yes/No) Have cell membrane? (Yes/No) DNA contained in nucleus? (Yes/No) Have membrane-bound organelles? (Yes/No) Multicellular or unicellular? ...
... Make protein? (Yes/No) Have DNA? (Yes/No) Have cell membrane? (Yes/No) DNA contained in nucleus? (Yes/No) Have membrane-bound organelles? (Yes/No) Multicellular or unicellular? ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.























