Nervous System A basic overview What does it do? Allows us to
... Contains the nucleus and a nucleolus, mitchondria, gogli apparatus... those sorts of things Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes (Those things we just finished talking about) Has no centrioles (hence its amitotic nature – that means it can't divide to make new cells) Ha ...
... Contains the nucleus and a nucleolus, mitchondria, gogli apparatus... those sorts of things Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes (Those things we just finished talking about) Has no centrioles (hence its amitotic nature – that means it can't divide to make new cells) Ha ...
Photo Album
... Plant and Animal Cells Under the Microscope 1. What indicators were used to help view some organelles under the microscope? 2. What is the structural difference between cheek cells and frog’s blood? How does this affect the function? 3. What structure did plant cells have that animal cells did no ...
... Plant and Animal Cells Under the Microscope 1. What indicators were used to help view some organelles under the microscope? 2. What is the structural difference between cheek cells and frog’s blood? How does this affect the function? 3. What structure did plant cells have that animal cells did no ...
Berry Gray
... mitchondria, gogli apparatus... those sorts of things Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes (Those things we just finished talking about) Has no centrioles (hence its amitotic nature – that means it can't divide to make new cells) Has well-developed Nissl bodies (kind of like ro ...
... mitchondria, gogli apparatus... those sorts of things Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes (Those things we just finished talking about) Has no centrioles (hence its amitotic nature – that means it can't divide to make new cells) Has well-developed Nissl bodies (kind of like ro ...
Aim: What is a cell? Do Now: On your paper. Notes are in
... The algae Caulerpa looks like a multicellular plant- but is actually only a single cell- and it can grow to be a meter long (3 ¼ feet)! Thiomargarita namibiensis is the largest bacteria on Earth- it’s 0.75 mm in diameter- so big you can see it with only your eye!! ...
... The algae Caulerpa looks like a multicellular plant- but is actually only a single cell- and it can grow to be a meter long (3 ¼ feet)! Thiomargarita namibiensis is the largest bacteria on Earth- it’s 0.75 mm in diameter- so big you can see it with only your eye!! ...
The Science of Biology
... o Relationship between cell respiration and photosynthesis o Mitochondria o Yeast metabolism Cell Division (Chapter 10) o Surface area, volume, ratio of surface area to volume, % absorption o Cell cycle o Disadvantages of large cell size o Events that take place during interphase, mitosis and cytoki ...
... o Relationship between cell respiration and photosynthesis o Mitochondria o Yeast metabolism Cell Division (Chapter 10) o Surface area, volume, ratio of surface area to volume, % absorption o Cell cycle o Disadvantages of large cell size o Events that take place during interphase, mitosis and cytoki ...
Mock Exam 1 Chapters 1 – 7 Anthony Todd http
... d. Phospholipids contain a hydrophilic region, but triacylglycerols do not e. Phospholipids contain two phosphate groups, but triacylglycerols contain three ...
... d. Phospholipids contain a hydrophilic region, but triacylglycerols do not e. Phospholipids contain two phosphate groups, but triacylglycerols contain three ...
Cells and Their Environment - Coach Blair`s Biology Website
... • 1. Diffusion (simple) is the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. • Small molecules can pass through the cell membrane by diffusion • Diffusion across a membrane is a type of passive transport because it does not require energy. ...
... • 1. Diffusion (simple) is the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. • Small molecules can pass through the cell membrane by diffusion • Diffusion across a membrane is a type of passive transport because it does not require energy. ...
coloring packet cells and organelles
... The nucleus in the center of a cell is a spherical body containing the nucleolus that makes ribosomes. The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis). It also contains DNA assembled into chromosomes. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane. Color ...
... The nucleus in the center of a cell is a spherical body containing the nucleolus that makes ribosomes. The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis). It also contains DNA assembled into chromosomes. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane. Color ...
The nervous system - Mr T Pities the Fool
... neurone: 1. Sensory neurone – carry impulse from receptor to CNS 2. Relay – connects sensory to motor 3. Motor – connects CNS to effector which makes a response. (muscle, gland) ...
... neurone: 1. Sensory neurone – carry impulse from receptor to CNS 2. Relay – connects sensory to motor 3. Motor – connects CNS to effector which makes a response. (muscle, gland) ...
The Cell Theory
... • The Cell Theory is a widely accepted explanation of the relationship between cells and living things. – It refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure in every living thing. ...
... • The Cell Theory is a widely accepted explanation of the relationship between cells and living things. – It refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure in every living thing. ...
Transport across the cell membrane
... Hypotonic: The solution has a HIGHER concentration of water than the concentration of water inside the cell therefore water will GO INTO the cell and the cell increases in size. Isotonic: The solution has an EQUAL concentration compared to the inside of the cell therefore no water would move in or ...
... Hypotonic: The solution has a HIGHER concentration of water than the concentration of water inside the cell therefore water will GO INTO the cell and the cell increases in size. Isotonic: The solution has an EQUAL concentration compared to the inside of the cell therefore no water would move in or ...
Supplementary Materials and Methods (doc 60K)
... database and be more than 30 for individual peptide ions when submitting peptide sequence spectra, assuming that the observed match is significant (P<0.05). PCR analysis. For PCR analysis, total RNA samples were isolated from control and celastrol-treated cells using the Total RNA isolation system ...
... database and be more than 30 for individual peptide ions when submitting peptide sequence spectra, assuming that the observed match is significant (P<0.05). PCR analysis. For PCR analysis, total RNA samples were isolated from control and celastrol-treated cells using the Total RNA isolation system ...
Synapse Formation
... • Synapse = the connection between neuron and target or two neurons • Axon grows to target – differentiates into the presynaptic terminal • Target cell also changes – into postsynaptic terminal • Both already carrying the components to form the synapse Æ contact is trigger ...
... • Synapse = the connection between neuron and target or two neurons • Axon grows to target – differentiates into the presynaptic terminal • Target cell also changes – into postsynaptic terminal • Both already carrying the components to form the synapse Æ contact is trigger ...
Nucleus
... • The nucleolus is also contained in the nucleus and makes ribosomes, organelles involved in the production of proteins. • The nuclear envelope is a two-membrane structure that surrounds the nucleus. ...
... • The nucleolus is also contained in the nucleus and makes ribosomes, organelles involved in the production of proteins. • The nuclear envelope is a two-membrane structure that surrounds the nucleus. ...
GCSE worksheet on cell structure and organelle function worksheet.
... therefore connected by a sea of water. Boats ferry items from building to building. There are many small power stations that ‘power’ the entire city by releasing energy from sugar. The sugar is grown by plants in giant greenhouses near to the power stations. The energy is used by buildings within th ...
... therefore connected by a sea of water. Boats ferry items from building to building. There are many small power stations that ‘power’ the entire city by releasing energy from sugar. The sugar is grown by plants in giant greenhouses near to the power stations. The energy is used by buildings within th ...
Chapter 6 A Tour of a Cell
... The Extracellular Matrix (ECM) of Animal Cells • Animal cells lack cell walls but are covered by an elaborate extracellular matrix (ECM) • The ECM is made up of glycoproteins such as collagen, proteoglycans, and fibronectin • ECM proteins bind to receptor proteins in the plasma membrane called inte ...
... The Extracellular Matrix (ECM) of Animal Cells • Animal cells lack cell walls but are covered by an elaborate extracellular matrix (ECM) • The ECM is made up of glycoproteins such as collagen, proteoglycans, and fibronectin • ECM proteins bind to receptor proteins in the plasma membrane called inte ...
Slide ()
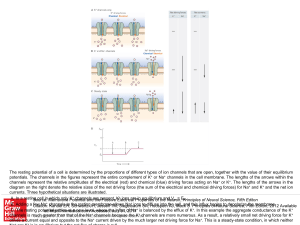
... Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available C. The resting potential settles at a new level, where the influx Na+ is balanced by the efflux of K+. In this example the aggregate conductance of the K+ at: http://mhm ...
... Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available C. The resting potential settles at a new level, where the influx Na+ is balanced by the efflux of K+. In this example the aggregate conductance of the K+ at: http://mhm ...
Structure, function and growth of prokaryote and eukaryote cells
... ‘Before the true nucleus’ •Comparison of DNA, presence or absence of nucleus and functions of organelles present, membranes and cytosol organisation Semi-fluid part of the cytoplasm that contains structures to support the cells organelles ...
... ‘Before the true nucleus’ •Comparison of DNA, presence or absence of nucleus and functions of organelles present, membranes and cytosol organisation Semi-fluid part of the cytoplasm that contains structures to support the cells organelles ...
Level The Cell and the City of Bling: using analogies to teach cell
... The energy is used by buildings within the city to make a variety of products. One such building is the Gucci clothes factory. This factory manufactures many different clothes that are all desig ...
... The energy is used by buildings within the city to make a variety of products. One such building is the Gucci clothes factory. This factory manufactures many different clothes that are all desig ...
5b Acquired Immunity I
... Haptens Can Become Antigenic Haptens are small molecules that cannot elicit an antibody response. They can combine with carrier molecules within the body (like proteins) and become antigenic. • Metals (e.g. nickel in jewelry), rubber, glue, preservatives, urushiol/quinone in poison ivy, halothane ( ...
... Haptens Can Become Antigenic Haptens are small molecules that cannot elicit an antibody response. They can combine with carrier molecules within the body (like proteins) and become antigenic. • Metals (e.g. nickel in jewelry), rubber, glue, preservatives, urushiol/quinone in poison ivy, halothane ( ...
CELL TRANSPORT
... This is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve cells communicate with each other. ...
... This is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve cells communicate with each other. ...
3D Cell Model Project
... cell model look like the pictures we have seen in class and are in your book. Use your book and other resources to help you design the cell organelles. You may choose either an animal cell or a plant cell, but do not do both. This project should not be expensive. You may use things you find around h ...
... cell model look like the pictures we have seen in class and are in your book. Use your book and other resources to help you design the cell organelles. You may choose either an animal cell or a plant cell, but do not do both. This project should not be expensive. You may use things you find around h ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.