Anti-Phospho-Ser181 TAO2 Antibody
... Product Description: Affinity purified rabbit polyclonal antibody. Biological Significance: In vitro, TAO (thousand and one amino acid) protein kinase 2 (TAO2) activates MAP/ERK kinases (MEKs) 3, 4, and 6 toward their substrates p38 MAP kinase JNK/SAPK (Chen et al., 1999; Chen and Cobb, 2001). This ...
... Product Description: Affinity purified rabbit polyclonal antibody. Biological Significance: In vitro, TAO (thousand and one amino acid) protein kinase 2 (TAO2) activates MAP/ERK kinases (MEKs) 3, 4, and 6 toward their substrates p38 MAP kinase JNK/SAPK (Chen et al., 1999; Chen and Cobb, 2001). This ...
Make protein for the cell.
... between cell and within cell. Breaks down some medicines. Makes lipids (fat). Packages proteins for release from the cell. Rough E.R. has ribosomes on it. Smooth E.R. does not have ribosomes on it. **Provides a system of transport from the nucleus to the cell.** ...
... between cell and within cell. Breaks down some medicines. Makes lipids (fat). Packages proteins for release from the cell. Rough E.R. has ribosomes on it. Smooth E.R. does not have ribosomes on it. **Provides a system of transport from the nucleus to the cell.** ...
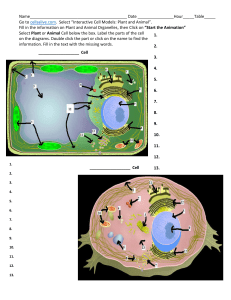
Biochemistry_and_Digestion_2010[1]
... Organisms that can not manufacture the organic molecules they require ...
... Organisms that can not manufacture the organic molecules they require ...
Worksheet - Moore Public Schools
... Cytosol: The cytosol is the "soup" within which all the other cell organelles reside and where most of the cellular metabolism occurs. Though mostly water, the cytosol is full of proteins that control cell 9. ____________________________ including signal transduction pathways, glycolysis, intracellu ...
... Cytosol: The cytosol is the "soup" within which all the other cell organelles reside and where most of the cellular metabolism occurs. Though mostly water, the cytosol is full of proteins that control cell 9. ____________________________ including signal transduction pathways, glycolysis, intracellu ...
Document
... Read pages 184-189 Answer the following questions: 1. What are some of the functions of the cell membrane? 2. What is diffusion? Does it move from a high to low concentration, or a low to high concentration? 3. What is osmosis? 4. What does it mean to be selectively permeable? 5. Describe the basic ...
... Read pages 184-189 Answer the following questions: 1. What are some of the functions of the cell membrane? 2. What is diffusion? Does it move from a high to low concentration, or a low to high concentration? 3. What is osmosis? 4. What does it mean to be selectively permeable? 5. Describe the basic ...
Ch 11 Part 2 - Groch Biology
... HAP: CHAPTER 11- 2nd part 1. Matching. a. ganglion b. neuroglia c. neurotransmitters d. nerve e. nodes of Ranvier f. nucleus g. synapse h. stimuli i. tract 1. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 2. Chemicals released by neurons that stimulate other neurons, muscles, or glands. ...
... HAP: CHAPTER 11- 2nd part 1. Matching. a. ganglion b. neuroglia c. neurotransmitters d. nerve e. nodes of Ranvier f. nucleus g. synapse h. stimuli i. tract 1. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 2. Chemicals released by neurons that stimulate other neurons, muscles, or glands. ...
Tutorial 3: Cells and Organelles
... lipids) can move through 3. Certain molecules, such as hydrophilic molecules or ions, move slowly through or cannot pass at all. How do they get through? ...
... lipids) can move through 3. Certain molecules, such as hydrophilic molecules or ions, move slowly through or cannot pass at all. How do they get through? ...
Biology 11th Class 2015-16
... and function; urine formation, osmoregulation; regulation of kidney function - renin angiotensin, atrial natriuretic factor, ADH and diabetes insipidus; role of other organs in excretion; disorders - uraemia, renal failure, renal calculi, nephritis; dialysis and artificial kidney. Chapter-20: Locomo ...
... and function; urine formation, osmoregulation; regulation of kidney function - renin angiotensin, atrial natriuretic factor, ADH and diabetes insipidus; role of other organs in excretion; disorders - uraemia, renal failure, renal calculi, nephritis; dialysis and artificial kidney. Chapter-20: Locomo ...
Lecture 5 – Cell Structure and Function
... In 1839, Schleiden and Schwann proposed the basic concepts of the modern cell theory • All organisms consists of one or more cells • A cell is the smallest unit with the properties of life • Each new cell arises from division of another, preexisting cell • Each cell passes its hereditary material ...
... In 1839, Schleiden and Schwann proposed the basic concepts of the modern cell theory • All organisms consists of one or more cells • A cell is the smallest unit with the properties of life • Each new cell arises from division of another, preexisting cell • Each cell passes its hereditary material ...
Lecture 1 Cell Biology
... quantities of specific substances, even though those substances may not be very concentrated in the extracellular fluid. Embedded in the membrane are proteins with specific receptors sites exposed to the extracellular fluid. The receptors proteins are clustered in regions of the membrane called ...
... quantities of specific substances, even though those substances may not be very concentrated in the extracellular fluid. Embedded in the membrane are proteins with specific receptors sites exposed to the extracellular fluid. The receptors proteins are clustered in regions of the membrane called ...
Senses - HumanAandP
... Science formally acknowledges that human have at least 11 senses and some list 19 or more. • Input receptor which provides information to the brain. • 12 pairs of cranial nerves branching out from the brain assist in this. • Dependent on 6 senses, all which directly have direct connections to the b ...
... Science formally acknowledges that human have at least 11 senses and some list 19 or more. • Input receptor which provides information to the brain. • 12 pairs of cranial nerves branching out from the brain assist in this. • Dependent on 6 senses, all which directly have direct connections to the b ...
Martin R. Larsen Rio..
... Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a group of disorders characterized by chronic hyperglycemia with disturbances of carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action or both. T1D: Absolute insulin deficiency due to an autoimmune associated destruction of the ...
... Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a group of disorders characterized by chronic hyperglycemia with disturbances of carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action or both. T1D: Absolute insulin deficiency due to an autoimmune associated destruction of the ...
Document
... All the polypeptides have the same charge per unit length All are subject to the same electromotive force in the electric field Separation based on the sieving effect of the polyacrylamide gel Separation is by molecular weight only SDS does not break covalent bonds (i.e., disulfides) (but can treat ...
... All the polypeptides have the same charge per unit length All are subject to the same electromotive force in the electric field Separation based on the sieving effect of the polyacrylamide gel Separation is by molecular weight only SDS does not break covalent bonds (i.e., disulfides) (but can treat ...
Cellular Neuroscience
... • The “F0/F1” ratio is often used to distinguish simple (approximately linear) V1 neurons from complex (nonlinear) ones. • Responses are recorded to sinusoidal contrast gratings. If the cell is linear, the output should contain only the input frequency F0. • Fourier analysis is performed on the post ...
... • The “F0/F1” ratio is often used to distinguish simple (approximately linear) V1 neurons from complex (nonlinear) ones. • Responses are recorded to sinusoidal contrast gratings. If the cell is linear, the output should contain only the input frequency F0. • Fourier analysis is performed on the post ...
Unit 1 Lesson 2
... • Organisms use nutrients for energy and as building materials. • A lipid is a fat molecule or a molecule that has similar properties. Lipids have many jobs in cells, such as storing energy. • Your cells get lipids from foods such as olive oil and fish. ...
... • Organisms use nutrients for energy and as building materials. • A lipid is a fat molecule or a molecule that has similar properties. Lipids have many jobs in cells, such as storing energy. • Your cells get lipids from foods such as olive oil and fish. ...
Lecture 10
... Assess whether nutrients and growth factors are available for growth Rb (retinoblastoma) protein and its metabolic state is involved in decision o Acts like a molecular switch to decide whether the cell proceeds through the cell cycle. o If Rb has a phosphate group added to it, the cell cycle ca ...
... Assess whether nutrients and growth factors are available for growth Rb (retinoblastoma) protein and its metabolic state is involved in decision o Acts like a molecular switch to decide whether the cell proceeds through the cell cycle. o If Rb has a phosphate group added to it, the cell cycle ca ...
Concentration gradient
... Passive transport is the passage of particles/molecules across the plasma membrane without the use of energy. This is movement with the concentration gradient from high to low. Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis are the 3 types of passive ...
... Passive transport is the passage of particles/molecules across the plasma membrane without the use of energy. This is movement with the concentration gradient from high to low. Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis are the 3 types of passive ...
DW#4 CellsAlive Websearch
... Cytosol: The cytosol is the "soup" within which all the other cell organelles reside and where most of the cellular metabolism occurs. Though mostly water, the cytosol is full of proteins that control cell 9. ____________________________ including signal transduction pathways, glycolysis, intracellu ...
... Cytosol: The cytosol is the "soup" within which all the other cell organelles reside and where most of the cellular metabolism occurs. Though mostly water, the cytosol is full of proteins that control cell 9. ____________________________ including signal transduction pathways, glycolysis, intracellu ...
Slide 1
... Breathing motions in myoglobin opens up pathways for oxygen atoms to enter its binding site or diffuse out ...
... Breathing motions in myoglobin opens up pathways for oxygen atoms to enter its binding site or diffuse out ...
Life on Earth ch 12
... •General characteristics –Composed of one or more amino acids –There are 20 different amino acids which join by dehydration synthesis to form a molecular chain –Various functions – either a hormone, an enzyme or a structural protein –3 dimensional shape which gives proteins their function: primary, ...
... •General characteristics –Composed of one or more amino acids –There are 20 different amino acids which join by dehydration synthesis to form a molecular chain –Various functions – either a hormone, an enzyme or a structural protein –3 dimensional shape which gives proteins their function: primary, ...
Cell Division
... • Found throughout interphase • This form of DNA is being used to make proteins ...
... • Found throughout interphase • This form of DNA is being used to make proteins ...
`synapse`.
... Impulse from the action potential opens ion channels for Ca++ The increased Ca++ concentration in the axon terminal initiates the release of the neurotransmitter (NT) NT is released from its vesicle and crosses the “gap” or synaptic cleft and attaches to a protein receptor on the dendrite ...
... Impulse from the action potential opens ion channels for Ca++ The increased Ca++ concentration in the axon terminal initiates the release of the neurotransmitter (NT) NT is released from its vesicle and crosses the “gap” or synaptic cleft and attaches to a protein receptor on the dendrite ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.

![Biochemistry_and_Digestion_2010[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008289894_1-a2dae968af20e40d29d6bcd9c3fab727-300x300.png)