Transport
... • One of the main jobs of the cell membrane is to separate the cytoplasm from the fluid outside the cell. • But the cell still needs an abundance of materials that comes from outside the cell. • Some substances that the cell needs can enter and leave the cell by diffusing across the cell membrane. • ...
... • One of the main jobs of the cell membrane is to separate the cytoplasm from the fluid outside the cell. • But the cell still needs an abundance of materials that comes from outside the cell. • Some substances that the cell needs can enter and leave the cell by diffusing across the cell membrane. • ...
F1 & F2- Microbes
... • Bacteria (formerly Eubacteria)More advanced • Eukarya- All life forms containing Eukaryotic cells (have a nucleus) ...
... • Bacteria (formerly Eubacteria)More advanced • Eukarya- All life forms containing Eukaryotic cells (have a nucleus) ...
The Guanine Nucleotide–Binding Switch in Three Dimensions
... unit and to describe the others as variations on this canonical structure (Fig. 1B). The G domains of the signal recognition particle SRP and its receptor SR show a divergent topology of the  sheet in addition to an extension and insertion, whereas tubulin and its bacterial homolog FtsZ are structu ...
... unit and to describe the others as variations on this canonical structure (Fig. 1B). The G domains of the signal recognition particle SRP and its receptor SR show a divergent topology of the  sheet in addition to an extension and insertion, whereas tubulin and its bacterial homolog FtsZ are structu ...
Cell- The Unit of Life
... with muscular structures that differ substantially from human technology (e.g. animals have no wheels), and must move with minimal energy usage, often over large distances and in variable environments. Organisms also employ passive regulation (i.e. movements are coordinated and regulated as a result ...
... with muscular structures that differ substantially from human technology (e.g. animals have no wheels), and must move with minimal energy usage, often over large distances and in variable environments. Organisms also employ passive regulation (i.e. movements are coordinated and regulated as a result ...
Syllabus for Medical Cell Biology
... The medical cell biology is a subject concerned with life activities, its mechanisms and principles, focusing on cells, but also applying modern physics, chemistry and test biology the experimental method. It deals with the structure and functions or the interaction of cell components by using diffe ...
... The medical cell biology is a subject concerned with life activities, its mechanisms and principles, focusing on cells, but also applying modern physics, chemistry and test biology the experimental method. It deals with the structure and functions or the interaction of cell components by using diffe ...
AP Biology
... Describe techniques used to study cell structure and function. Distinguish between magnification and resolving power. Describe the principles, advantages, and limitations of the light microscope, transmission electron microscope and the scanning light electron microscope. Describe cell fract ...
... Describe techniques used to study cell structure and function. Distinguish between magnification and resolving power. Describe the principles, advantages, and limitations of the light microscope, transmission electron microscope and the scanning light electron microscope. Describe cell fract ...
Ca 2+
... Quantal content was increased to 154%!! After a single injection of alphaBTX mEPPs were reduced in size by 60% but no increase in quantal content was observed! At timepoints between acute treatment and 6 weeks with alphaBTX quantal content increased, reaching a plateau Between 20 and 30 days. A mech ...
... Quantal content was increased to 154%!! After a single injection of alphaBTX mEPPs were reduced in size by 60% but no increase in quantal content was observed! At timepoints between acute treatment and 6 weeks with alphaBTX quantal content increased, reaching a plateau Between 20 and 30 days. A mech ...
Yeast are… - mvhs
... Yeast Mating • When the appropriate factors are released, a MATa and MAT a cell can mate • The binding of the pheromone to the receptor causes a signal transduction pathway to be activated. • Cells start to grow towards one another– they shmoo! ...
... Yeast Mating • When the appropriate factors are released, a MATa and MAT a cell can mate • The binding of the pheromone to the receptor causes a signal transduction pathway to be activated. • Cells start to grow towards one another– they shmoo! ...
Full Text - International Journal of Livestock Research
... fibrinogen, collagen, vitronectin, laminin, elastin, von Willebrand factor etc. Staphylococcal surface adhesion molecules like fibronectin, fibrinogen and collagen binding proteins have been shown to contribute to persistence of bacteria by adhering to sub epithelial tissue components after epitheli ...
... fibrinogen, collagen, vitronectin, laminin, elastin, von Willebrand factor etc. Staphylococcal surface adhesion molecules like fibronectin, fibrinogen and collagen binding proteins have been shown to contribute to persistence of bacteria by adhering to sub epithelial tissue components after epitheli ...
04_Instructor_Guide - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... 1. ATP functions in cells much like money functions in modern societies. Each holds value that can be generated in one place and “spent” in another. This analogy has been very helpful for many students. 2.Mitochondria and chloroplasts are each wrapped by multiple membranes. In both organelles, the i ...
... 1. ATP functions in cells much like money functions in modern societies. Each holds value that can be generated in one place and “spent” in another. This analogy has been very helpful for many students. 2.Mitochondria and chloroplasts are each wrapped by multiple membranes. In both organelles, the i ...
5. CH 5 PPT The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... The Molecules of Life • Within cells, small organic molecules are joined together to form larger molecules • Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands of covalently connected atoms ...
... The Molecules of Life • Within cells, small organic molecules are joined together to form larger molecules • Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands of covalently connected atoms ...
Grade 7 Science-Unit 2: Formative Pre
... determine the best types of treatment for their diseases. Who will have access to this technology in the near future? A. most everyone because DNA analysis is such a powerful technology B. people in industrialized countries because the procedures will be expensive at first C. all people worldwide wh ...
... determine the best types of treatment for their diseases. Who will have access to this technology in the near future? A. most everyone because DNA analysis is such a powerful technology B. people in industrialized countries because the procedures will be expensive at first C. all people worldwide wh ...
Homeostasis and Interacting Behavior What is hom
... Conditions inside living things must remain within tolerable limits or else the cells/organisms will not be able to function properly. What are some examples of things that need to be kept within a certain range in our bodies? • Body temperature • Blood pressure • Blood pH level • Glucose levels in ...
... Conditions inside living things must remain within tolerable limits or else the cells/organisms will not be able to function properly. What are some examples of things that need to be kept within a certain range in our bodies? • Body temperature • Blood pressure • Blood pH level • Glucose levels in ...
Action Potentials
... • After the action potential, it is impossible to stimulate the cell membrane to reach another action potential. • Potassium channels are slow to close so too many K+ ions diffuse out of the neurone. • This makes the cell more negative than -70mV, which is the resting potential. • This is called the ...
... • After the action potential, it is impossible to stimulate the cell membrane to reach another action potential. • Potassium channels are slow to close so too many K+ ions diffuse out of the neurone. • This makes the cell more negative than -70mV, which is the resting potential. • This is called the ...
siop lesson plan for
... SLIDE: Organelles: In cell biology, an organelle /ɔrɡəˈnɛl/ is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function, and it is usually separately enclosed within its own lipid bilayer. The name organelle comes from the idea that these structures are to cells what an organis to the body ...
... SLIDE: Organelles: In cell biology, an organelle /ɔrɡəˈnɛl/ is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function, and it is usually separately enclosed within its own lipid bilayer. The name organelle comes from the idea that these structures are to cells what an organis to the body ...
Relations in Open Biological Ontologies
... this would return all metabolites, genes, gene products that generally influence the activity of alcohol dehydrogenasis. however, this will not work using GO: alcohol-dehydrogenasis is or would be defined as a class, not as an instance... in effect this means since most instances are influenced by d ...
... this would return all metabolites, genes, gene products that generally influence the activity of alcohol dehydrogenasis. however, this will not work using GO: alcohol-dehydrogenasis is or would be defined as a class, not as an instance... in effect this means since most instances are influenced by d ...
Does intracrine amplification provide a unifying principle for the
... sought; their interruption would be therapeutically beneficial in disease modification. These networks, usually weak and indolent, can, as is likely in some cases of CTE and AD, be more robust. They are likely mediated by misfolded proteindriven regulation of transition metal transport. Fourth, PrPc ...
... sought; their interruption would be therapeutically beneficial in disease modification. These networks, usually weak and indolent, can, as is likely in some cases of CTE and AD, be more robust. They are likely mediated by misfolded proteindriven regulation of transition metal transport. Fourth, PrPc ...
Document
... - essential to keep matured chloroplast active under fluctuating environmental conditions (day/night, light stress, temperature ..) ...
... - essential to keep matured chloroplast active under fluctuating environmental conditions (day/night, light stress, temperature ..) ...
499 Med Chem Chap 1 problems
... b. Water and ions are unable to cross the bilayer due to the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid molecules. c. There are charged groups at the inner and outer surfaces of the cell membrane. d. The molecules in the bilayer are fluid and so the cell membrane is porous allowing the passage of ions an ...
... b. Water and ions are unable to cross the bilayer due to the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid molecules. c. There are charged groups at the inner and outer surfaces of the cell membrane. d. The molecules in the bilayer are fluid and so the cell membrane is porous allowing the passage of ions an ...
PDF
... ubiquitous transgene expression throughout development, equivalent to the Rosa26 locus used in mouse genetics. But no longer, for in one of Development’s inaugural Technical papers (p. 169), Leonard Zon and co-workers report that the zebrafish ubiquitin (ubi) promoter can drive constitutive transgen ...
... ubiquitous transgene expression throughout development, equivalent to the Rosa26 locus used in mouse genetics. But no longer, for in one of Development’s inaugural Technical papers (p. 169), Leonard Zon and co-workers report that the zebrafish ubiquitin (ubi) promoter can drive constitutive transgen ...
53 XIX BLY 122 Lecture Notes (O`Brien)
... 3. The influx of Na+ causes positive charges to spread away from Na+ channels. 4. Positive feedback occurs, which causes more Na+ channels to open. 5. The action potential does not propagate back up the axon. Fig 45.11 6. Speed of propagation is enhanced by either large axon size or myelination. Fig ...
... 3. The influx of Na+ causes positive charges to spread away from Na+ channels. 4. Positive feedback occurs, which causes more Na+ channels to open. 5. The action potential does not propagate back up the axon. Fig 45.11 6. Speed of propagation is enhanced by either large axon size or myelination. Fig ...
PDF
... ubiquitous transgene expression throughout development, equivalent to the Rosa26 locus used in mouse genetics. But no longer, for in one of Development’s inaugural Technical papers (p. 169), Leonard Zon and co-workers report that the zebrafish ubiquitin (ubi) promoter can drive constitutive transgen ...
... ubiquitous transgene expression throughout development, equivalent to the Rosa26 locus used in mouse genetics. But no longer, for in one of Development’s inaugural Technical papers (p. 169), Leonard Zon and co-workers report that the zebrafish ubiquitin (ubi) promoter can drive constitutive transgen ...
PDF
... ubiquitous transgene expression throughout development, equivalent to the Rosa26 locus used in mouse genetics. But no longer, for in one of Development’s inaugural Technical papers (p. 169), Leonard Zon and co-workers report that the zebrafish ubiquitin (ubi) promoter can drive constitutive transgen ...
... ubiquitous transgene expression throughout development, equivalent to the Rosa26 locus used in mouse genetics. But no longer, for in one of Development’s inaugural Technical papers (p. 169), Leonard Zon and co-workers report that the zebrafish ubiquitin (ubi) promoter can drive constitutive transgen ...
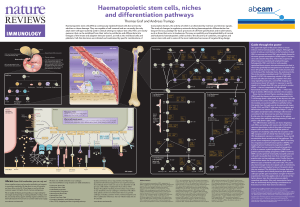
Haematopoietic stem cells, niches and differentiation
... which they gradually become quiescent. As shown in the lower left panel, dormant HSCs are mostly located close to the lining of the trabecular bone, the endosteal niche. This niche contains osteoblasts and CXC-chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12)-expressing reticular (CAR) cells. Several cell adhesion molec ...
... which they gradually become quiescent. As shown in the lower left panel, dormant HSCs are mostly located close to the lining of the trabecular bone, the endosteal niche. This niche contains osteoblasts and CXC-chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12)-expressing reticular (CAR) cells. Several cell adhesion molec ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.