Cell Organelle Table
... Protects the DNA from the rest of the cell’s contents - also made of a phospholipid bilayer with nuclear pores instead of proteins ...
... Protects the DNA from the rest of the cell’s contents - also made of a phospholipid bilayer with nuclear pores instead of proteins ...
Into and Out of the Cell
... Cells need to get nutrients and gases in through the cell membrane. ...
... Cells need to get nutrients and gases in through the cell membrane. ...
Practice Test MC and answers - Bremen High School District 228
... At puberty, an adolescent female body changes in both structure and function of several organ systems, primarily under the influence of changing concentrations of estrogens and other steroid hormones. How can one hormone, such as estrogen, mediate so many effects? a. Estrogen is produced in very lar ...
... At puberty, an adolescent female body changes in both structure and function of several organ systems, primarily under the influence of changing concentrations of estrogens and other steroid hormones. How can one hormone, such as estrogen, mediate so many effects? a. Estrogen is produced in very lar ...
Chemical Messengers
... • The target cells have specific receptors that bind to the neurotransmitter secreted by a neuron. • Although that neuron can potentially signal other cells, it is limited to the target cells in close proximity to that ...
... • The target cells have specific receptors that bind to the neurotransmitter secreted by a neuron. • Although that neuron can potentially signal other cells, it is limited to the target cells in close proximity to that ...
Document
... Usually attached to the outer surface These are different in each individual Cell recognition - “ID cards”, enable the body to ...
... Usually attached to the outer surface These are different in each individual Cell recognition - “ID cards”, enable the body to ...
SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS Student Version Outline
... in yeast trigger signaling pathways that lead to growth of cytoskeletal microfilaments in areas of the plasma membrane exposed to the highest concentration of mating ...
... in yeast trigger signaling pathways that lead to growth of cytoskeletal microfilaments in areas of the plasma membrane exposed to the highest concentration of mating ...
9/18 - MIT
... Structures of MAP kinase in its inactive, unphosphorylated form and active, phosphorylated form Phosphorylation of MAP kinase by MEK at tyrosine 185 (pY185) and threonine 183 ...
... Structures of MAP kinase in its inactive, unphosphorylated form and active, phosphorylated form Phosphorylation of MAP kinase by MEK at tyrosine 185 (pY185) and threonine 183 ...
Cell surface dynamics, and the role of endocytic machineries All
... machineries (coats) re-sculpture the plasma membrane into vesicular carriers that enclose molecules that are to be taken up into the cell. Besides the canonical clathrin coated endocytic machinery, it is becoming increasingly clear that additional membrane carriers such as caveolae and CLICs support ...
... machineries (coats) re-sculpture the plasma membrane into vesicular carriers that enclose molecules that are to be taken up into the cell. Besides the canonical clathrin coated endocytic machinery, it is becoming increasingly clear that additional membrane carriers such as caveolae and CLICs support ...
LEC 4
... These are involved in regulation of growth and response to metabolic signals The response time of enzyme initiated transduction is slow( minutes) eg. Insulin receptors platelate derived growth factors Activation of Tyrosine linked receptors results in autophophorylation of tryrosine residue le ...
... These are involved in regulation of growth and response to metabolic signals The response time of enzyme initiated transduction is slow( minutes) eg. Insulin receptors platelate derived growth factors Activation of Tyrosine linked receptors results in autophophorylation of tryrosine residue le ...
Chapter 4 Eukaryotic Cell
... DNA – packaged into nucleosomes Segments of DNA are wrapped around Histone proteins. ...
... DNA – packaged into nucleosomes Segments of DNA are wrapped around Histone proteins. ...
l2 biology: topics covered on the midterm exam and what to study
... Carbon: What makes it a unique element? What are the two types of chemical bonds? Look over basic chemistry notes from beginning of class. Enzymes Are a type of protein How do they function/are used in living organisms How do they work in a chemical reaction? Understand substrate, reactants, p ...
... Carbon: What makes it a unique element? What are the two types of chemical bonds? Look over basic chemistry notes from beginning of class. Enzymes Are a type of protein How do they function/are used in living organisms How do they work in a chemical reaction? Understand substrate, reactants, p ...
Quiz D - exam Q`s
... B. Found only in eukaryotic cells C. Found exclusively in the nucleus D. Formed during transcription of DNA 3. Lipids are A. Used as an energy source B. Involved in active transport C. Part of glycoproteins D. Transported by rough ER ...
... B. Found only in eukaryotic cells C. Found exclusively in the nucleus D. Formed during transcription of DNA 3. Lipids are A. Used as an energy source B. Involved in active transport C. Part of glycoproteins D. Transported by rough ER ...
“brains” of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains
... Rigid outermost layer in plant cells ...
... Rigid outermost layer in plant cells ...
Cell Communication
... the pore connects the extracellular fluid with the cytoplasm the pore is big enough for ions to pass through it ...
... the pore connects the extracellular fluid with the cytoplasm the pore is big enough for ions to pass through it ...
Basic Bio 3
... M. This is a tiny fluid-filled cavity in the cytoplasm. It can be used for storage of biochemicals. ...
... M. This is a tiny fluid-filled cavity in the cytoplasm. It can be used for storage of biochemicals. ...
THE CELL MEMBRANE Composition The cell membrane is a
... ● One the signal is inside the cell, the signal is carried by a second messenger. ○ The most common second messenger is cyclic AMP (cAMP). ● Notice that the ligand, the first messenger, never enters the cell. ● Three examples of cell surface receptors are ion channels receptors, Gproteincouple ...
... ● One the signal is inside the cell, the signal is carried by a second messenger. ○ The most common second messenger is cyclic AMP (cAMP). ● Notice that the ligand, the first messenger, never enters the cell. ● Three examples of cell surface receptors are ion channels receptors, Gproteincouple ...
Introduction
... •Because cytosolic Ca2+ is so low, small changes in the absolute numbers of ions causes a relatively large percentage change in Ca2+ concentration. •Signal-transduction pathways trigger the release of Ca2+ from the cell’ s ER. •The pathways leading to release involve still other second messengers, d ...
... •Because cytosolic Ca2+ is so low, small changes in the absolute numbers of ions causes a relatively large percentage change in Ca2+ concentration. •Signal-transduction pathways trigger the release of Ca2+ from the cell’ s ER. •The pathways leading to release involve still other second messengers, d ...
Lecture 4
... bind GDP and GTP with high affinity, but adopt different structure depending on the bound nucleotide. GTP-bound complex has high affinity for other proteins (“acceptor’), affecting their enzymatic activity possess intrinsic GTPase activity that is usually activated by interaction with regulatory pro ...
... bind GDP and GTP with high affinity, but adopt different structure depending on the bound nucleotide. GTP-bound complex has high affinity for other proteins (“acceptor’), affecting their enzymatic activity possess intrinsic GTPase activity that is usually activated by interaction with regulatory pro ...
No Slide Title
... bind GDP and GTP with high affinity, but adopt different structure depending on the bound nucleotide. GTP-bound complex has high affinity for other proteins (“acceptor’), affecting their enzymatic activity possess intrinsic GTPase activity that is usually activated by interaction with regulatory pro ...
... bind GDP and GTP with high affinity, but adopt different structure depending on the bound nucleotide. GTP-bound complex has high affinity for other proteins (“acceptor’), affecting their enzymatic activity possess intrinsic GTPase activity that is usually activated by interaction with regulatory pro ...
Anatomy Chapter 3 section 3 Active Transport Diffusion or facilitated
... exposed on its outer surface. Proteins are receptors to which specific molecules from the fluids surrd cell can bind and selectively enter cell, while other types of molecules are left behind. Molecules that bind specifically to receptors are called – Ligands. EX: ...
... exposed on its outer surface. Proteins are receptors to which specific molecules from the fluids surrd cell can bind and selectively enter cell, while other types of molecules are left behind. Molecules that bind specifically to receptors are called – Ligands. EX: ...
Cell Organelle Table
... Machines that makes proteins according to the directions of the DNA – not bound by membrane Modify and sorts proteins from RER, Loads them into vesicles and sends them to destinations Transport proteins (enzymes), lipids (steroids) and carbohydrates to specific locations Single membrane bound struct ...
... Machines that makes proteins according to the directions of the DNA – not bound by membrane Modify and sorts proteins from RER, Loads them into vesicles and sends them to destinations Transport proteins (enzymes), lipids (steroids) and carbohydrates to specific locations Single membrane bound struct ...
Activities
... ________ 1. organism that has cells containing a nucleus and other organelles ________ 2. an organelle inside eukaryotic cells where the DNA is located ________ 3. a structure within the cytoplasm of a cell that is enclosed within a membrane and performs a specific job ________ 4. the material insid ...
... ________ 1. organism that has cells containing a nucleus and other organelles ________ 2. an organelle inside eukaryotic cells where the DNA is located ________ 3. a structure within the cytoplasm of a cell that is enclosed within a membrane and performs a specific job ________ 4. the material insid ...
Intro to Cells and Biochemistry Molecule General Molecular Shape
... Intro to Cells and Biochemistry 1. List the things that biologically define life. 2. Choose a sports game you like to play or watch. Explain how life is like that game. 5 sentences minimum. Use actual examples from both sport and life to illustrate. 3. What is the cell considered the basic unit of l ...
... Intro to Cells and Biochemistry 1. List the things that biologically define life. 2. Choose a sports game you like to play or watch. Explain how life is like that game. 5 sentences minimum. Use actual examples from both sport and life to illustrate. 3. What is the cell considered the basic unit of l ...
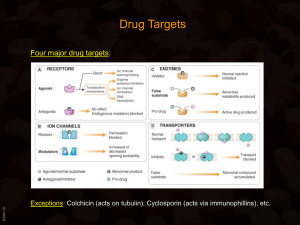
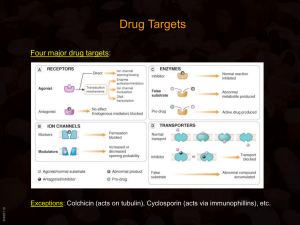
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.