Cole Research RCST 4029B Offic
... There are two types of nucleic acids: • Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) consists of a double helix of polymers made up of deoxyribose, phosphate, and four bases: A, G, C, and T. In the double helix, A pairs with T, and G pairs with C. • Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a single‐stranded polymer made up of ...
... There are two types of nucleic acids: • Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) consists of a double helix of polymers made up of deoxyribose, phosphate, and four bases: A, G, C, and T. In the double helix, A pairs with T, and G pairs with C. • Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a single‐stranded polymer made up of ...
chemical signaling
... • Second messengers are small, nonprotein, watersoluble molecules or ions • The extracellular signal molecule that binds to the membrane is a pathway’s “first messenger” • Second messengers can readily spread throughout cells by diffusion • Second messengers participate in pathways initiated by G-pr ...
... • Second messengers are small, nonprotein, watersoluble molecules or ions • The extracellular signal molecule that binds to the membrane is a pathway’s “first messenger” • Second messengers can readily spread throughout cells by diffusion • Second messengers participate in pathways initiated by G-pr ...
paracrine NO, neurotransmitters, … endocrine any hormone any
... Peptide signal molecules bind to cell surface receptors. Exosomes are membrane enclosed packets of protein or RNA that are released from cells. Nitric oxide (NO) is a paracrine signal molecule. Nitric oxide (NO) is synthesized in smooth muscle cells of arterioles. Active MPF is cyclin B bound to act ...
... Peptide signal molecules bind to cell surface receptors. Exosomes are membrane enclosed packets of protein or RNA that are released from cells. Nitric oxide (NO) is a paracrine signal molecule. Nitric oxide (NO) is synthesized in smooth muscle cells of arterioles. Active MPF is cyclin B bound to act ...
sgCh1Cell
... 1.______________basic units of structure and __________in living things. 2. Hooke observed _________________ 3. What did Leeuwenhoek observe? 4. The function of the cell wall is _____________________________________. 5. Organelles that control cells ______________________________. 6. What substance ...
... 1.______________basic units of structure and __________in living things. 2. Hooke observed _________________ 3. What did Leeuwenhoek observe? 4. The function of the cell wall is _____________________________________. 5. Organelles that control cells ______________________________. 6. What substance ...
Structure and Function of Membranes
... • More unsaturated FA, membrane stays fluid at lower temp (winter) • More saturated FA, membrane is more stable at high temperatures (summer) • Cholesterol embedded in animal membranes, keeps FA tails from twisting together ...
... • More unsaturated FA, membrane stays fluid at lower temp (winter) • More saturated FA, membrane is more stable at high temperatures (summer) • Cholesterol embedded in animal membranes, keeps FA tails from twisting together ...
Recitation 12 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... molecule binds to a receptor, conveys the message to the inside of the cell and then the cell changes its activity in response to the signal. These signals can be autocrine (chemicals act on cells that produce them), paracrine (diffuse to and out of a nearby cell) or endocrine (hormones that travel ...
... molecule binds to a receptor, conveys the message to the inside of the cell and then the cell changes its activity in response to the signal. These signals can be autocrine (chemicals act on cells that produce them), paracrine (diffuse to and out of a nearby cell) or endocrine (hormones that travel ...
END OF CHAPTER QUESTIONS
... of ATP. Centrioles are responsible for organizing microtubules that attach to chromosomes during cell division (mitosis). ...
... of ATP. Centrioles are responsible for organizing microtubules that attach to chromosomes during cell division (mitosis). ...
Ribosomes (20-30nm)
... Small organelles often attached to the ER but also found in the cytoplasm Large (protein) and small (rRNA) subunits form the functional ribosome o Subunits bind with mRNA in the cytoplasm o This starts translation of mRNA for protein synthesise (assembly of amino acids into proteins) Free ribo ...
... Small organelles often attached to the ER but also found in the cytoplasm Large (protein) and small (rRNA) subunits form the functional ribosome o Subunits bind with mRNA in the cytoplasm o This starts translation of mRNA for protein synthesise (assembly of amino acids into proteins) Free ribo ...
Review sheet exam 2
... Include ion channels, membrane pumps, ion movements, and membrane potentials. 2) Explain in detail how one neuron signals another across a synapse. Include ion channels, membrane pumps, ion movements, and membrane potentials. 3) Draw a diagram that illustrates the complete pathways used by a protein ...
... Include ion channels, membrane pumps, ion movements, and membrane potentials. 2) Explain in detail how one neuron signals another across a synapse. Include ion channels, membrane pumps, ion movements, and membrane potentials. 3) Draw a diagram that illustrates the complete pathways used by a protein ...
Lecture 7 – Synaptic Transmission II -
... pore forming loop connecting M1 and M3 that dips into and out of the membrane, like P loop of voltage-gated channels – except loop is on intracellular surface of membrane. C terminus is intracellular. 7. Metabotropic receptor actions. Slower than ligand-gated channel (ionotropic receptor) actions. O ...
... pore forming loop connecting M1 and M3 that dips into and out of the membrane, like P loop of voltage-gated channels – except loop is on intracellular surface of membrane. C terminus is intracellular. 7. Metabotropic receptor actions. Slower than ligand-gated channel (ionotropic receptor) actions. O ...
Cell Communication
... – Ex: Steroid hormones, Thyroid hormones. – Ex: Testosterone • Binds to intracellular receptors and enter nucleus to turn on genes that control male sex characteristics. Figure 11.6 ...
... – Ex: Steroid hormones, Thyroid hormones. – Ex: Testosterone • Binds to intracellular receptors and enter nucleus to turn on genes that control male sex characteristics. Figure 11.6 ...
Structure of Eukaryotic Cells
... • Innermost surface has DNA attachment sites • Pores span bilayer ...
... • Innermost surface has DNA attachment sites • Pores span bilayer ...
UNIVERSITY OF MALTA
... differences, inducibility and regulation. It is now routine at an early stage in drug discovery to determine the human CYP isoform(s) responsible for the major oxidative pathways in the metabolism of a new chemical entity (NCE). The pregnane X receptor (PXR) and the constitutive androstane receptor ...
... differences, inducibility and regulation. It is now routine at an early stage in drug discovery to determine the human CYP isoform(s) responsible for the major oxidative pathways in the metabolism of a new chemical entity (NCE). The pregnane X receptor (PXR) and the constitutive androstane receptor ...
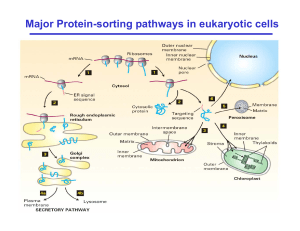
Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells
... Major topological classes of integral membrane proteins synthesized on the rough ER ...
... Major topological classes of integral membrane proteins synthesized on the rough ER ...
endocrine system - Solon City Schools
... ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Act by means of hormones, synthesized in glands and secreted in blood • Hormones- chemical signals that act on target cells; work on specific targets! ...
... ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Act by means of hormones, synthesized in glands and secreted in blood • Hormones- chemical signals that act on target cells; work on specific targets! ...
Matching Cell Parts WS File
... ____3. Also called the plasma membrane ____4. Bags of enzymes used to digest particles/bacteria; “garbage men” of the cell; work with vacuoles. ____5. Control center of the cell; contains nucleolus and DNA ____6. External surface is studded with ribosomes ____7. Formed from a piece of cell membrane ...
... ____3. Also called the plasma membrane ____4. Bags of enzymes used to digest particles/bacteria; “garbage men” of the cell; work with vacuoles. ____5. Control center of the cell; contains nucleolus and DNA ____6. External surface is studded with ribosomes ____7. Formed from a piece of cell membrane ...
Game 1
... These reactions use light energy to split H2O and release O2 into the atmosphere, and also regengerate ATP & NADPH ...
... These reactions use light energy to split H2O and release O2 into the atmosphere, and also regengerate ATP & NADPH ...
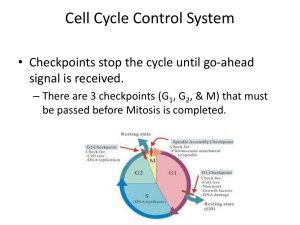
Cell Cycle Control System - Santa Susana High School
... • Cdks - cyclin-dependent kinase (remember that a kinase is an enzyme that activate or inactivate by phosphorylating) – cyclin is always present in the cell and is activated when phosphorylated – synthesized during the S-phase ...
... • Cdks - cyclin-dependent kinase (remember that a kinase is an enzyme that activate or inactivate by phosphorylating) – cyclin is always present in the cell and is activated when phosphorylated – synthesized during the S-phase ...
SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS Outline
... Hormone-Receptor complex enters nucleus and serves as a transcription factor. Transcription Factors determine which genes on a chromosome should be transcribed into a protein. The steroid receptor carries out the signal transduction. Other receptors (example: the thyroid receptor) are already in nuc ...
... Hormone-Receptor complex enters nucleus and serves as a transcription factor. Transcription Factors determine which genes on a chromosome should be transcribed into a protein. The steroid receptor carries out the signal transduction. Other receptors (example: the thyroid receptor) are already in nuc ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.