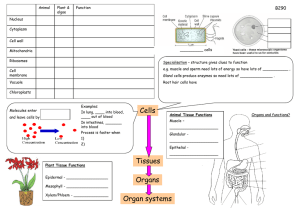
Cells
... Cells Tissues • Cells (basic units) – Organisms either unicellular or multi-cellular ...
... Cells Tissues • Cells (basic units) – Organisms either unicellular or multi-cellular ...
Aim: How do the organelles work together to maintain homeostasis?
... 1.The cell membrane forms a boundary that separates the cellular contents from the outside environment. 2. The cell membrane forms a barrier that keeps all substances that might harm the cell from entering the cell. 3. The cell membrane is capable of receiving and recognizing chemical signals. 4. Th ...
... 1.The cell membrane forms a boundary that separates the cellular contents from the outside environment. 2. The cell membrane forms a barrier that keeps all substances that might harm the cell from entering the cell. 3. The cell membrane is capable of receiving and recognizing chemical signals. 4. Th ...
Are All Cells Alike?
... Parts of the cell membrane are assembled and some proteins are changed (modified) Rough ER –in charge of protein synthesis (Called rough because of ribosomes) Smooth ER – no ribosomes present Contains enzymes that perform specialized tasks such as lipid synthesis ...
... Parts of the cell membrane are assembled and some proteins are changed (modified) Rough ER –in charge of protein synthesis (Called rough because of ribosomes) Smooth ER – no ribosomes present Contains enzymes that perform specialized tasks such as lipid synthesis ...
to Study Guide for Test 1-Stephen Grant
... 4. Electrons: atomic number; negatively charged particle Protons: atomic number; positively charged particle Neutrons: atomic mass-atomic number; neirtral charge Atomic number - equal to the number of proton and electrons for that atom Atomic mass - how much anatamweighs Atomic model structure ...
... 4. Electrons: atomic number; negatively charged particle Protons: atomic number; positively charged particle Neutrons: atomic mass-atomic number; neirtral charge Atomic number - equal to the number of proton and electrons for that atom Atomic mass - how much anatamweighs Atomic model structure ...
Reproduction
... Structure of DNA Structure of DNA • DNA looks like a twisted ladder - two strands wrap around each other in a spiral shape. • The sides of the DNA ladder are made of sugar and phosphate. • The steps of the ladder are made of four ...
... Structure of DNA Structure of DNA • DNA looks like a twisted ladder - two strands wrap around each other in a spiral shape. • The sides of the DNA ladder are made of sugar and phosphate. • The steps of the ladder are made of four ...
posterexample2
... initiated in the chloroplasts and completed in the peroxisomes. JA is then exported to the cytoplasm where it is conjugated to isoleucine to form JA-Ile, which binds to its receptor and induce the signal that turns on array of defense genes , including plant defensin, PDF1.2. Enzymes that function i ...
... initiated in the chloroplasts and completed in the peroxisomes. JA is then exported to the cytoplasm where it is conjugated to isoleucine to form JA-Ile, which binds to its receptor and induce the signal that turns on array of defense genes , including plant defensin, PDF1.2. Enzymes that function i ...
MICROSCOPE cell LEARNING TARGETS `16
... compound light microscope and accurately draw the object to scale based on my field of view. MS 03. I can use a compound light microscope to observe and draw objects at different magnifications. Vocabulary: eyepiece, base, arm, stage, tube, revolving nosepiece, low powered objective, medium powered ...
... compound light microscope and accurately draw the object to scale based on my field of view. MS 03. I can use a compound light microscope to observe and draw objects at different magnifications. Vocabulary: eyepiece, base, arm, stage, tube, revolving nosepiece, low powered objective, medium powered ...
Cell power point
... • Controls movement of materials into and out of cell • Helps cell to maintain homeostasis (balance) ...
... • Controls movement of materials into and out of cell • Helps cell to maintain homeostasis (balance) ...
Basic Structure of a Cell
... 2. The cell or __________ membrane is made of a double layer of _________________ and _____________. The cell membrane surrounds _____ cells and controls what _______ or ________ the _________. A phospholipid contains ________ and ________. The ________ is hydrophilic and the _________ are hydrophob ...
... 2. The cell or __________ membrane is made of a double layer of _________________ and _____________. The cell membrane surrounds _____ cells and controls what _______ or ________ the _________. A phospholipid contains ________ and ________. The ________ is hydrophilic and the _________ are hydrophob ...
Chapter 5
... repels polar molecules but not nonpolar molecules – Nonpolar molecules will move until the concentration is equal on both sides – Limited permeability to small polar molecules – Very limited permeability to larger polar molecules and ions ...
... repels polar molecules but not nonpolar molecules – Nonpolar molecules will move until the concentration is equal on both sides – Limited permeability to small polar molecules – Very limited permeability to larger polar molecules and ions ...
government - Humble ISD
... B 4A CH 7-1 Identify the differences between plant, animal, and bacterial cells. (S) A Vocabulary: prokaryote, eukaryote, plasma membrane, lipid, bi-layer, cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, nucleolus, chromosomes, nuclear membrane, mitochondria, chloroplast, ribosomes, lysosomes, vacuole, rough endopla ...
... B 4A CH 7-1 Identify the differences between plant, animal, and bacterial cells. (S) A Vocabulary: prokaryote, eukaryote, plasma membrane, lipid, bi-layer, cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, nucleolus, chromosomes, nuclear membrane, mitochondria, chloroplast, ribosomes, lysosomes, vacuole, rough endopla ...
Slides
... Instructive: a signal from the inducing cell is necessary for initiating new gene expression in the responding cell - e.g. optic vesicle placed under a new region of head ectoderm - without inducing cell, the responding cell is not capable of differentiating (in that particular way). - tend to restr ...
... Instructive: a signal from the inducing cell is necessary for initiating new gene expression in the responding cell - e.g. optic vesicle placed under a new region of head ectoderm - without inducing cell, the responding cell is not capable of differentiating (in that particular way). - tend to restr ...
Phospholipid bilayer
... Transporters- Involved in the movement of substances. Enzymes- Allow chemical reactions on the interior of membrane Cell surface receptors- Detect chemical messages Cell surface identity markers- different cell types have unique markers Cell adhesion proteins- cause cells to stick to one another Att ...
... Transporters- Involved in the movement of substances. Enzymes- Allow chemical reactions on the interior of membrane Cell surface receptors- Detect chemical messages Cell surface identity markers- different cell types have unique markers Cell adhesion proteins- cause cells to stick to one another Att ...
3-3 Cell Organelles
... Scattered on the surface are many small channels called _____________ _________, Substances made in the nucleus, such as ribosomal proteins and _______, move through these into the ______________. Ribosomes are partially assembled in the ______________. The _______________ information of a eukaryoti ...
... Scattered on the surface are many small channels called _____________ _________, Substances made in the nucleus, such as ribosomal proteins and _______, move through these into the ______________. Ribosomes are partially assembled in the ______________. The _______________ information of a eukaryoti ...
Study Guide Chapter 10 in Fox
... Understand the difference between “sensory receptors” and “ligand receptors” Most sensory receptors are either ______________ or _______________ These receptors receive some form of ___________ and convert it into action potentials. Because they convert energy from one form to another, receptors are ...
... Understand the difference between “sensory receptors” and “ligand receptors” Most sensory receptors are either ______________ or _______________ These receptors receive some form of ___________ and convert it into action potentials. Because they convert energy from one form to another, receptors are ...
Chapter 7 Exam Review Sheet
... What is the basic unit of life? Who was the first person to look at a cork cell and give it the name “cell”? What are the 3 statements made in the cell theory? What is the difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? What is the function or job of the mitochondria? What is the function of t ...
... What is the basic unit of life? Who was the first person to look at a cork cell and give it the name “cell”? What are the 3 statements made in the cell theory? What is the difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? What is the function or job of the mitochondria? What is the function of t ...
Exam 4
... -Describe the locations and functions of receptors for tactile, thermal, and pain sensations, and for proprioception (Describe the location and function of the somatic sensory receptors for tactile, thermal, and pain sensations). -Identify the receptors for proprioception and describe their function ...
... -Describe the locations and functions of receptors for tactile, thermal, and pain sensations, and for proprioception (Describe the location and function of the somatic sensory receptors for tactile, thermal, and pain sensations). -Identify the receptors for proprioception and describe their function ...
Life of a Protein #1 This outline describes the job of a specialized
... Determine 1) the cells location in the human body and 2) its job description from these clues. Epithelial cells release proteins, which communicate to our cell through the PLASMA MEMBRANE. The NUCLEUS gets the signal. Genes in the NUCLEUS that code for specialized proteins are activated. Messanger R ...
... Determine 1) the cells location in the human body and 2) its job description from these clues. Epithelial cells release proteins, which communicate to our cell through the PLASMA MEMBRANE. The NUCLEUS gets the signal. Genes in the NUCLEUS that code for specialized proteins are activated. Messanger R ...
Basic Cell Structure
... is a tough rigid outer covering that protects the plant cell and helps it maintain its shape. It is composed mostly of cellulose. Fungi, algae, and bacteria also have cell walls. • **Animal cells DO NOT have cell walls. ...
... is a tough rigid outer covering that protects the plant cell and helps it maintain its shape. It is composed mostly of cellulose. Fungi, algae, and bacteria also have cell walls. • **Animal cells DO NOT have cell walls. ...
Shrink Tours, Inc.
... Overview of Tour: On the next few pages you will find: An overview of the various organelles encountered during the tour The function of each organelle A photograph or drawing of each organelle* A joke about each organelle *Not all organelles have a picture (some are camera-shy) (the lyso ...
... Overview of Tour: On the next few pages you will find: An overview of the various organelles encountered during the tour The function of each organelle A photograph or drawing of each organelle* A joke about each organelle *Not all organelles have a picture (some are camera-shy) (the lyso ...
chapter 12.rtf - HCC Learning Web
... 8) For a chemotherapeutic drug to be useful for treating cancer cells, which of the following is most desirable? A) It does not alter metabolically active cells. B) It is safe enough to limit all apoptosis. C) It interferes with cells entering G0. D) It only attacks cells that are density dependent. ...
... 8) For a chemotherapeutic drug to be useful for treating cancer cells, which of the following is most desirable? A) It does not alter metabolically active cells. B) It is safe enough to limit all apoptosis. C) It interferes with cells entering G0. D) It only attacks cells that are density dependent. ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.