cell structures - Learn District 196
... FOUND ONLY IN PLANT CELLS GREEN PIGMENTED STRUCTURES THAT CONTAIN CHLOROPHYLL THAT IS NEEDED TO MAKE FOOD FOR THE CELL ...
... FOUND ONLY IN PLANT CELLS GREEN PIGMENTED STRUCTURES THAT CONTAIN CHLOROPHYLL THAT IS NEEDED TO MAKE FOOD FOR THE CELL ...
Role of mechanical tensile forces in cell fate acquisition Institute of
... controlled by the differential activation of Notch. Notch is activated by the ligand Delta present on the surface of adjacent cells. It has been suggested that the regulation of receptor Notch and ligand Delta sorting along the apical-basal axis of epithelial cells during cytokinesis is a mechanism ...
... controlled by the differential activation of Notch. Notch is activated by the ligand Delta present on the surface of adjacent cells. It has been suggested that the regulation of receptor Notch and ligand Delta sorting along the apical-basal axis of epithelial cells during cytokinesis is a mechanism ...
Cell Wall
... protects and supports the cells of plants, algae, fungi, and most bacteria. Composed of cellulose protective layer around all cellsmaintains chemical balance within the cell, semi permeable Gelatin-like substance inside cell membrane that contains the organelles Directs the cells activities; include ...
... protects and supports the cells of plants, algae, fungi, and most bacteria. Composed of cellulose protective layer around all cellsmaintains chemical balance within the cell, semi permeable Gelatin-like substance inside cell membrane that contains the organelles Directs the cells activities; include ...
Organelle Membrane Bound Description/Function Plant/ Animal
... Description/Function Surrounded by nuclear envelope; Directs the cells activities; stores DNA Located inside the nucleus, it the site of ribosome manufacturing Small organelle consisting of RNA and proteins; They Produces Proteins Double Membranes; It converts food into usable energy for cells Doubl ...
... Description/Function Surrounded by nuclear envelope; Directs the cells activities; stores DNA Located inside the nucleus, it the site of ribosome manufacturing Small organelle consisting of RNA and proteins; They Produces Proteins Double Membranes; It converts food into usable energy for cells Doubl ...
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use – Enclosed by two membranes • Inner membrane is highly folded – Called cristae ...
... food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use – Enclosed by two membranes • Inner membrane is highly folded – Called cristae ...
cell review
... 13. The voltage across the cell membrane due to charge separation is referred to as ….. 14. What is responsible for the polarity difference extracellularly and intracellularly in a cell. 15. What tends to keep intracellular K+ ion concentration high? List as many as possible. 16. Which event follows ...
... 13. The voltage across the cell membrane due to charge separation is referred to as ….. 14. What is responsible for the polarity difference extracellularly and intracellularly in a cell. 15. What tends to keep intracellular K+ ion concentration high? List as many as possible. 16. Which event follows ...
L1 - Seattle Central College
... microvilli – increases surface area of the cell membrane enhancing its ability to transport material across by both active processes and passive processes of transport cilia/flagellum – moves either materials along the surface of the cell or moves the whole cell B. Organelles in the cytoplasm mitoch ...
... microvilli – increases surface area of the cell membrane enhancing its ability to transport material across by both active processes and passive processes of transport cilia/flagellum – moves either materials along the surface of the cell or moves the whole cell B. Organelles in the cytoplasm mitoch ...
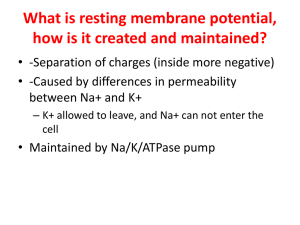
What is resting membrane potential, how is it created and maintained?
... describe different parts of process • --Conduction of electric current • 1. If above threshold, voltage gated channels open = rapid depolarization • 2. Action potential ends; K+ channels open leading to hyperpolarization ...
... describe different parts of process • --Conduction of electric current • 1. If above threshold, voltage gated channels open = rapid depolarization • 2. Action potential ends; K+ channels open leading to hyperpolarization ...
Document
... Golgi bodies are very small particles composed of membrane aggregates and are responsible for the secretion of certain proteins. Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles of low density and are responsible for food digestion, osmotic regulation, and wasteproduct storage. Chloroplasts are relatively lar ...
... Golgi bodies are very small particles composed of membrane aggregates and are responsible for the secretion of certain proteins. Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles of low density and are responsible for food digestion, osmotic regulation, and wasteproduct storage. Chloroplasts are relatively lar ...
Cellular Activities - Berks Catholic High School
... shaped like the substrate and competes for the enzyme Feedback inhibition – an accumulation of products inactivates the first enzyme in a series Precursor activation - the presence of the first substrate activates all enzymes in the series. Animation of enzyme action http://programs.northlandc ...
... shaped like the substrate and competes for the enzyme Feedback inhibition – an accumulation of products inactivates the first enzyme in a series Precursor activation - the presence of the first substrate activates all enzymes in the series. Animation of enzyme action http://programs.northlandc ...
The Cell PPT File
... the type of protein a cell can make and the chemical reactions that occur in the cell (controls the cell activity) • When DNA is not duplicating, it is found as chromatin. In a dividing cell it found as chromosomes. ...
... the type of protein a cell can make and the chemical reactions that occur in the cell (controls the cell activity) • When DNA is not duplicating, it is found as chromatin. In a dividing cell it found as chromosomes. ...
Cellular Activities
... lHow enzymes provide activation energy: • Increase the number of collisions between atoms and molecules; therefore bonds can be broken and new bonds formed. ...
... lHow enzymes provide activation energy: • Increase the number of collisions between atoms and molecules; therefore bonds can be broken and new bonds formed. ...
Biology I Cells
... protein channels – Cell uses no energy, substances move from high to low concentration (still diffusion) – Used when molecules are polar, charged, or too big ...
... protein channels – Cell uses no energy, substances move from high to low concentration (still diffusion) – Used when molecules are polar, charged, or too big ...
MBBT 12513
... (ii) describe the functional relationships among different cellular compartments and ...
... (ii) describe the functional relationships among different cellular compartments and ...
RED &WHITE BLOOD CELLS
... formed by the tissue metabolism. Is composed of a membrane surrounding the hemoglobin. Hb forms about 95% of the intracellular protein of the red cell. ...
... formed by the tissue metabolism. Is composed of a membrane surrounding the hemoglobin. Hb forms about 95% of the intracellular protein of the red cell. ...
Receptors and Neurotransmitters
... . This neurotransmitter is involved in the control of skeletal muscle action in the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), stimulating skeletal muscle contraction at neuromuscular junctions. It can excite or inhibit ANS synapses. Most of the postganglionic fibers of th ...
... . This neurotransmitter is involved in the control of skeletal muscle action in the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), stimulating skeletal muscle contraction at neuromuscular junctions. It can excite or inhibit ANS synapses. Most of the postganglionic fibers of th ...
Unit 4: Cells and Transport Short Answer Five of
... Five of the following will be chosen for the Short Answer portion of the exam. 1. What do all cells have in common? 2. How can you tell the difference between a plant and an animal cell? List at least 3 differences. ...
... Five of the following will be chosen for the Short Answer portion of the exam. 1. What do all cells have in common? 2. How can you tell the difference between a plant and an animal cell? List at least 3 differences. ...
CELL TYPES EPITHELIA CONNECTIVE TISSUE NERVOUS TISSUE
... together by cell junctions that give the sheet mechanical strength and also make it impermeable to small molecules. The sheet rests on a basal lamina. ...
... together by cell junctions that give the sheet mechanical strength and also make it impermeable to small molecules. The sheet rests on a basal lamina. ...
PPT
... Paracrine signaling. The signaling molecules released by one cell act on neighboring target cells (neurotransmitters). Autocrine signaling. Cells respond to signaling molecules that they themselves produce (response of the immune system to foreign antigens and cancer cells). ...
... Paracrine signaling. The signaling molecules released by one cell act on neighboring target cells (neurotransmitters). Autocrine signaling. Cells respond to signaling molecules that they themselves produce (response of the immune system to foreign antigens and cancer cells). ...
Protein
... very close proximity The outward propagation of the signal is limited by -cellular uptake, -extracellular degradation -& binding ...
... very close proximity The outward propagation of the signal is limited by -cellular uptake, -extracellular degradation -& binding ...
Exam 2
... 7. If a cell has 12 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each of its daughter cells have after mitosis? a. 4 b. 6 c. 12 d. 24 8. Which is NOT a job of the proteins in the cell membrane? a. Cell Surface Receptors b. Transport of Ions c. Surface Antigens d. Transport of Antigens 9. Bacterial Cells u ...
... 7. If a cell has 12 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each of its daughter cells have after mitosis? a. 4 b. 6 c. 12 d. 24 8. Which is NOT a job of the proteins in the cell membrane? a. Cell Surface Receptors b. Transport of Ions c. Surface Antigens d. Transport of Antigens 9. Bacterial Cells u ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.