Name: Date: Period: ______ AP Biology: Unit 5, DBA #1 Review Ms
... ________________________K. A structure made of membrane with attached ribosomes that is used to create proteins that will exit the cell (aka secretory proteins). This structure also serves as a highway to move substances around the cell. ________________________L. A structure made of membranous tube ...
... ________________________K. A structure made of membrane with attached ribosomes that is used to create proteins that will exit the cell (aka secretory proteins). This structure also serves as a highway to move substances around the cell. ________________________L. A structure made of membranous tube ...
click - Uplift Education
... 19) Differentiate between continuous conduction and saltatory conduction. Where does each occur? Which is faster and why? ...
... 19) Differentiate between continuous conduction and saltatory conduction. Where does each occur? Which is faster and why? ...
Study Guide Cells Unit Test
... Read the following scenario and answer the questions that follow. Nick’s mother packed him sliced apples in his lunch everyday. Nick was disappointed when he would open his lunch and find brown, mushy apples. Nick decided that he would try to find a way to keep his sliced apples crisp and white. He ...
... Read the following scenario and answer the questions that follow. Nick’s mother packed him sliced apples in his lunch everyday. Nick was disappointed when he would open his lunch and find brown, mushy apples. Nick decided that he would try to find a way to keep his sliced apples crisp and white. He ...
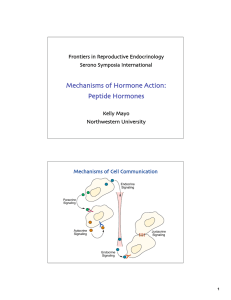
Mechanisms of Hormone Action: Peptide Hormones
... •Schlessinger (2000) Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 103:211. •Touw et al (2000) Signaling mechanisms of cytokine receptors and their perturbances in disease. ...
... •Schlessinger (2000) Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 103:211. •Touw et al (2000) Signaling mechanisms of cytokine receptors and their perturbances in disease. ...
Midterm Outline
... a) Lipids are not considered polymers. b) All lipids are nonpolar & hydrophobic molecules. c) Know the structures, chemical properties, & functions of fats, phospholipids, & steroids. 6) Proteins: a) Name end in -in b) Parts of an amino acid (amino & carboxyl groups). c) Peptide bonds (amino group t ...
... a) Lipids are not considered polymers. b) All lipids are nonpolar & hydrophobic molecules. c) Know the structures, chemical properties, & functions of fats, phospholipids, & steroids. 6) Proteins: a) Name end in -in b) Parts of an amino acid (amino & carboxyl groups). c) Peptide bonds (amino group t ...
Mouse LIFR / CD118 Protein (His Tag)
... transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) in a time-dependent manner. Further, blocking LIFR activation during preconditioning using a LIFR antagonist (LIF05) attenuated the induced STAT3 activation and also resulted in reduced preconditioning-induced protection of the retinal photorecepto ...
... transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) in a time-dependent manner. Further, blocking LIFR activation during preconditioning using a LIFR antagonist (LIF05) attenuated the induced STAT3 activation and also resulted in reduced preconditioning-induced protection of the retinal photorecepto ...
Use prefixes, suffixes, and roots to define the
... Learning Goals By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe the components of the cell membrane and their functions. Relate cellular transport to homeostasis. Differentiate between passive transport processes and active transport processes. ...
... Learning Goals By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe the components of the cell membrane and their functions. Relate cellular transport to homeostasis. Differentiate between passive transport processes and active transport processes. ...
Membranes around cells provide separation
... the diffusion gradient, they carry electrical charges, etc. In active transport, specific carrier proteins bind to these molecules and bring them inside the cell. This requires the use of energy. Endocytosis is a form of active transport where large molecules are transported across a membrane. 3 typ ...
... the diffusion gradient, they carry electrical charges, etc. In active transport, specific carrier proteins bind to these molecules and bring them inside the cell. This requires the use of energy. Endocytosis is a form of active transport where large molecules are transported across a membrane. 3 typ ...
Cell Organelles - keystonescience
... Found only inside eukaryotic cells All the stuff in between the organelles is cytosol Everything in a cell except the nucleus is cytoplasm ...
... Found only inside eukaryotic cells All the stuff in between the organelles is cytosol Everything in a cell except the nucleus is cytoplasm ...
doc
... determine the location for each organelle, and place a check mark in the column(s) of the types of cells in which the organelle can be found. ...
... determine the location for each organelle, and place a check mark in the column(s) of the types of cells in which the organelle can be found. ...
Chapter 5
... Passive Processes of Membrane Transport • Biological membranes are selectively permeable: allow some substances to pass, while others are restricted. • Some substances can move by Simple Diffusion: movement from high concentration to low concentration Facilitated Diffusion: passive movement of s ...
... Passive Processes of Membrane Transport • Biological membranes are selectively permeable: allow some substances to pass, while others are restricted. • Some substances can move by Simple Diffusion: movement from high concentration to low concentration Facilitated Diffusion: passive movement of s ...
Looking Inside Cells
... • Nucleus • Acts as the “brain” of the cell • The cell’s control center, directs cell’s activities • Nuclear envelope • Nucleus is surrounded by this membrane • Materials pass in and out of the nucleus through pores in this structure • Chromatin • Contains instructions that direct the functions of a ...
... • Nucleus • Acts as the “brain” of the cell • The cell’s control center, directs cell’s activities • Nuclear envelope • Nucleus is surrounded by this membrane • Materials pass in and out of the nucleus through pores in this structure • Chromatin • Contains instructions that direct the functions of a ...
AP Biology Final Exam Study guide Fall 2013
... Enzymes: enzyme - substrate complex, active site, induced fit, cofactors, coenzymes, competitive vs. noncompetitive inhibition, allosteric regulation ...
... Enzymes: enzyme - substrate complex, active site, induced fit, cofactors, coenzymes, competitive vs. noncompetitive inhibition, allosteric regulation ...
vesicles - apbiostafford
... “optical sectioning” of fluorescently-stained specimens. Only a single plane of focus is illuminated; out-of-focus fluorescence above and below the plane is subtracted by a computer. A sharp image results, as seen in stained nervous tissue (top), where nerve cells are green, support cells are red, a ...
... “optical sectioning” of fluorescently-stained specimens. Only a single plane of focus is illuminated; out-of-focus fluorescence above and below the plane is subtracted by a computer. A sharp image results, as seen in stained nervous tissue (top), where nerve cells are green, support cells are red, a ...
Review Puzzle
... 22. List any 5 organelles on the back of this paper, and for EACH include: location in cell, function, and whether they are in animal or plant cells, or in both. ...
... 22. List any 5 organelles on the back of this paper, and for EACH include: location in cell, function, and whether they are in animal or plant cells, or in both. ...
PDF
... Here, Helen McNeill and colleagues study the genetic interactions between mammalian Fat genes and show that Fat proteins act both synergistically and antagonistically to regulate multiple aspects of tissue morphogenesis in mice (p. 1806). For example, the authors show that Fat1 and Fat4 synergise du ...
... Here, Helen McNeill and colleagues study the genetic interactions between mammalian Fat genes and show that Fat proteins act both synergistically and antagonistically to regulate multiple aspects of tissue morphogenesis in mice (p. 1806). For example, the authors show that Fat1 and Fat4 synergise du ...
PDF
... Here, Helen McNeill and colleagues study the genetic interactions between mammalian Fat genes and show that Fat proteins act both synergistically and antagonistically to regulate multiple aspects of tissue morphogenesis in mice (p. 1806). For example, the authors show that Fat1 and Fat4 synergise du ...
... Here, Helen McNeill and colleagues study the genetic interactions between mammalian Fat genes and show that Fat proteins act both synergistically and antagonistically to regulate multiple aspects of tissue morphogenesis in mice (p. 1806). For example, the authors show that Fat1 and Fat4 synergise du ...
Chapter 6 *The Cell*
... Wood, for ex., consists mainly of secondary walls. Plant cell walls are commonly perforated by channels between adjacent cells called plasmodesmata ...
... Wood, for ex., consists mainly of secondary walls. Plant cell walls are commonly perforated by channels between adjacent cells called plasmodesmata ...
Name
... 10. nerve endings which are sensitive and respond to light energy 11. stimulus strength strong enough to cause a response 12. when one pre-synaptic neuron affects a response in two post-synaptic neurons 13. ovoid glial cells that are phagocytic 14. not having the ability to reproduce 15. clusters of ...
... 10. nerve endings which are sensitive and respond to light energy 11. stimulus strength strong enough to cause a response 12. when one pre-synaptic neuron affects a response in two post-synaptic neurons 13. ovoid glial cells that are phagocytic 14. not having the ability to reproduce 15. clusters of ...
PDF
... Here, Helen McNeill and colleagues study the genetic interactions between mammalian Fat genes and show that Fat proteins act both synergistically and antagonistically to regulate multiple aspects of tissue morphogenesis in mice (p. 1806). For example, the authors show that Fat1 and Fat4 synergise du ...
... Here, Helen McNeill and colleagues study the genetic interactions between mammalian Fat genes and show that Fat proteins act both synergistically and antagonistically to regulate multiple aspects of tissue morphogenesis in mice (p. 1806). For example, the authors show that Fat1 and Fat4 synergise du ...
Cell Structure and Function Dr. Ehan Abdulhadi PhD in Microbology
... Derived form photosynthetic bacteria Solar energy capturing organelle ...
... Derived form photosynthetic bacteria Solar energy capturing organelle ...
Cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm
... molecule and associated proteins. • While bacteria do not have as many genes or DNA molecules as long as those in eukaryotes, their circular chromosome is still highly folded and coiled in the cell. ...
... molecule and associated proteins. • While bacteria do not have as many genes or DNA molecules as long as those in eukaryotes, their circular chromosome is still highly folded and coiled in the cell. ...
Biological membranes, cell compartments
... separating inner parts of the cell from the environment. • Plasma membrane is the surface of all cells and is selectively-permeable. This is the regulation part for the intake and excretion of the chemical substances. • Composed of lipids (phospholipids, glycolipids and cholesterol esters) and prote ...
... separating inner parts of the cell from the environment. • Plasma membrane is the surface of all cells and is selectively-permeable. This is the regulation part for the intake and excretion of the chemical substances. • Composed of lipids (phospholipids, glycolipids and cholesterol esters) and prote ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.