Anti-GABA A Receptor alpha 1 antibody ab137436 Product datasheet 1 Image
... absence seizures (several per day) and bilateral, synchronous, symmetric 3-Hz spike waves on EEG. During adolescence, tonic-clonic and myoclonic seizures may develop. Absence seizures may either remit or persist into adulthood. Defects in GABRA1 are the cause of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy type 5 (E ...
... absence seizures (several per day) and bilateral, synchronous, symmetric 3-Hz spike waves on EEG. During adolescence, tonic-clonic and myoclonic seizures may develop. Absence seizures may either remit or persist into adulthood. Defects in GABRA1 are the cause of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy type 5 (E ...
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... Explain the role and describe the composition of the extracellular matrix in an animal cell. Compare the structure and function of adhesion, tight, and gap junctions in animals, and explain why a cell would be connected by a tight junction, rather than a gap junction or an adhesion junction. Explain ...
... Explain the role and describe the composition of the extracellular matrix in an animal cell. Compare the structure and function of adhesion, tight, and gap junctions in animals, and explain why a cell would be connected by a tight junction, rather than a gap junction or an adhesion junction. Explain ...
Exam 1 suggested answers (2010)
... 2.a. A synapse with Erev more negative than threshold is inhibitory. Even though it results in a depolarization when the neuron is at resting potential, this makes it harder for the neuron to depolarize to levels less negative than the E rev, thus making it harder to reach threshold. b. In this situ ...
... 2.a. A synapse with Erev more negative than threshold is inhibitory. Even though it results in a depolarization when the neuron is at resting potential, this makes it harder for the neuron to depolarize to levels less negative than the E rev, thus making it harder to reach threshold. b. In this situ ...
Unit-2-Status-Updates-2015
... For this activity you will focus on the most important details about each of the cell parts and contributors to the Cell Theory. First, think of one key word to associate with the topic; this should be some sort of mind-jogger. Then, using a bit of imagination, create a status update that could have ...
... For this activity you will focus on the most important details about each of the cell parts and contributors to the Cell Theory. First, think of one key word to associate with the topic; this should be some sort of mind-jogger. Then, using a bit of imagination, create a status update that could have ...
THE CELL – Chapter 3
... c. hypotonic-when solution has more water than the cell-water moves into cell and cell swells 2. Osmotic pressure is the difference in concentration of particles, and this pressure creates movement and water moves toward more particles D. Filtration-molecules are forced through membranes by hydrosta ...
... c. hypotonic-when solution has more water than the cell-water moves into cell and cell swells 2. Osmotic pressure is the difference in concentration of particles, and this pressure creates movement and water moves toward more particles D. Filtration-molecules are forced through membranes by hydrosta ...
1.2 Notes
... Protects cell by controlling what goes in and out of cell Directs cell’s activities Protects nucleus by controlling what goes in and out of nucleus Contains genetic material ...
... Protects cell by controlling what goes in and out of cell Directs cell’s activities Protects nucleus by controlling what goes in and out of nucleus Contains genetic material ...
Route of exposure, mode of action and modifying factors
... • The liver contains many non-specific enzymes that give it the ability to metabolize a broad spectrum of organic molecules • Two phases: – Phase I involves the addition of reactive polar groups through oxidation, reduction, or hydrolysis; sometimes this makes a non-toxic chemical more toxic – Phase ...
... • The liver contains many non-specific enzymes that give it the ability to metabolize a broad spectrum of organic molecules • Two phases: – Phase I involves the addition of reactive polar groups through oxidation, reduction, or hydrolysis; sometimes this makes a non-toxic chemical more toxic – Phase ...
Lysosomes
... • Autophagy may also lead to autophagic cell death, a form of programmed self-destruction, or autolysis, of the cell, which means that the cell is digesting itself. ...
... • Autophagy may also lead to autophagic cell death, a form of programmed self-destruction, or autolysis, of the cell, which means that the cell is digesting itself. ...
Topic: Parts of the Cell
... They work kinda like the organs in your body, each part does a different job. Eukaryotic cells are either plant or animal. Plant cells have a couple extra parts. ...
... They work kinda like the organs in your body, each part does a different job. Eukaryotic cells are either plant or animal. Plant cells have a couple extra parts. ...
Oncogenesis: abnormal developmental plasticity
... To generate the many different cell types one can encounter in a multicellular organism, some cells divide asymmetrically into two different daughter cells. To achieve this, protein determinants localize asymmetrically during mitosis and segregate into one of the two daughter cells making this cell ...
... To generate the many different cell types one can encounter in a multicellular organism, some cells divide asymmetrically into two different daughter cells. To achieve this, protein determinants localize asymmetrically during mitosis and segregate into one of the two daughter cells making this cell ...
The Organization of Cells Reading Assignments A. The Cell: The
... via vesicles that fuse with the cis region of the Golgi. • It adds signal molecules to proteins, directing them to various destinations. • Vesicles originating from the trans region of the Golgi contain proteins for different cellular locations. Some fuse with the plasma membrane and release their c ...
... via vesicles that fuse with the cis region of the Golgi. • It adds signal molecules to proteins, directing them to various destinations. • Vesicles originating from the trans region of the Golgi contain proteins for different cellular locations. Some fuse with the plasma membrane and release their c ...
Prokaryotic_cells
... Structure and function of bacterial cell organelles: Cytoplasm. Contains all the enzymes needed for all metabolic reactions, since there are no organelles Ribosomes. The smaller (70 S) type. Nucleoid (or Nuclear Zone). The region of the cytoplasm that contains DNA. It is not surrounded by a nuclear ...
... Structure and function of bacterial cell organelles: Cytoplasm. Contains all the enzymes needed for all metabolic reactions, since there are no organelles Ribosomes. The smaller (70 S) type. Nucleoid (or Nuclear Zone). The region of the cytoplasm that contains DNA. It is not surrounded by a nuclear ...
Plasma Membrane
... means predicting how a cell will react in a solution (hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic) ...
... means predicting how a cell will react in a solution (hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic) ...
Surface Display
... Ribosome display The DNA library constructs contain all the signals required for cell-free in vitro transcription and translation. The absence of a stop codon at the end of the coding sequence prevents the release of the mRNA and the nascent polypeptide from the ribosomes. Low temperatures and an e ...
... Ribosome display The DNA library constructs contain all the signals required for cell-free in vitro transcription and translation. The absence of a stop codon at the end of the coding sequence prevents the release of the mRNA and the nascent polypeptide from the ribosomes. Low temperatures and an e ...
Claudia G. Almeida, Group leader CG Almeida graduated in
... the University of Lisbon. During her master she found that the neuromodulator adenosine protects neurons from oxidative stress, results published in Neuroscience Letters. In 2002, she joined the laboratory of Dr. Gouras at Cornell Medical College in New York. She discovered that the initial cellular ...
... the University of Lisbon. During her master she found that the neuromodulator adenosine protects neurons from oxidative stress, results published in Neuroscience Letters. In 2002, she joined the laboratory of Dr. Gouras at Cornell Medical College in New York. She discovered that the initial cellular ...
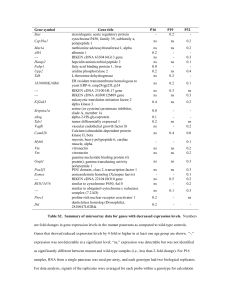
Table S2. Summary of microarray data for genes with decreased
... “Present” in at least one array out of a total of 4 arrays were selected for further analyses, and those with ratios ≤ 0.5 or ≥ 2.0 were considered as differentially expressed genes at a significant level. For P19 and P32 experiments, cDNA sample was similarly generated from total pancreatic RNA (10 ...
... “Present” in at least one array out of a total of 4 arrays were selected for further analyses, and those with ratios ≤ 0.5 or ≥ 2.0 were considered as differentially expressed genes at a significant level. For P19 and P32 experiments, cDNA sample was similarly generated from total pancreatic RNA (10 ...
o Cells are the
... Regulates what ___________________________________ the cell ________________________________ has proteins and carbohydrates embedded in it Think of it as a ____________________! Made up of phospholipids which have _________________________________________ _________________________________ ...
... Regulates what ___________________________________ the cell ________________________________ has proteins and carbohydrates embedded in it Think of it as a ____________________! Made up of phospholipids which have _________________________________________ _________________________________ ...
Wolfram Stacklies Force Distribution in Macromolecules Abstract All
... W olfram Stacklies Force Distribution in M acromolecules Abstract All living organisms utilize thousands of molecular building blocks to perform mechanical tasks. These building blocks are mostly proteins, and their mechanical properties define the way they can be utilized by the cell. The spectrum ...
... W olfram Stacklies Force Distribution in M acromolecules Abstract All living organisms utilize thousands of molecular building blocks to perform mechanical tasks. These building blocks are mostly proteins, and their mechanical properties define the way they can be utilized by the cell. The spectrum ...
7-2 - Kleins
... frame work of a cell that is made of protein filaments and helps maintain shape and cell ...
... frame work of a cell that is made of protein filaments and helps maintain shape and cell ...
Chapter 7 Notes - Cloudfront.net
... work like miniature organs, carrying out specific functions in the cell (suspended in the cytosol) 2. Function a. Biological reactions take place in the cytosol b. Organelles each have specific jobs within the cell ...
... work like miniature organs, carrying out specific functions in the cell (suspended in the cytosol) 2. Function a. Biological reactions take place in the cytosol b. Organelles each have specific jobs within the cell ...
Proteins
... 2. Carboxyl group –COOH 3. R group -different for every AA -determines the properties of AA Joined together by peptide bonds ...
... 2. Carboxyl group –COOH 3. R group -different for every AA -determines the properties of AA Joined together by peptide bonds ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.