Cells - Barbados SDA Secondary
... • To see even smaller things inside a cell, an electron microscope is used. • This uses a beam of electrons instead of light, and can magnify up to 500 000 times. This means that a lot more detail can be seen inside a cell, as shown in Next ...
... • To see even smaller things inside a cell, an electron microscope is used. • This uses a beam of electrons instead of light, and can magnify up to 500 000 times. This means that a lot more detail can be seen inside a cell, as shown in Next ...
Human Senses
... retina, located along the back wall of the eye. Light rays enter the eye through a curved, transparent structure called the cornea, and then pass through the pupil, an opening in the eyeball. The iris regulates the size of the pupil. Next, the lens focuses the light on the retina, which contains two ...
... retina, located along the back wall of the eye. Light rays enter the eye through a curved, transparent structure called the cornea, and then pass through the pupil, an opening in the eyeball. The iris regulates the size of the pupil. Next, the lens focuses the light on the retina, which contains two ...
Asset CSC unifying theme
... chromosomes. The information encoded within DNA can be subdivided into two types, structural and controlling elements. The structural elements, known as genes, encode information leading to the formation of essential molecules called proteins. Proteins vary dramatically in function, serving as struc ...
... chromosomes. The information encoded within DNA can be subdivided into two types, structural and controlling elements. The structural elements, known as genes, encode information leading to the formation of essential molecules called proteins. Proteins vary dramatically in function, serving as struc ...
Chapter 1
... Golgi apparatus- (UPS) packages, modifies, and distributes carbohydrates and lipids to proteins. Lysosomes- Enzymes that digest old and unused material within a cell. ...
... Golgi apparatus- (UPS) packages, modifies, and distributes carbohydrates and lipids to proteins. Lysosomes- Enzymes that digest old and unused material within a cell. ...
Chapter Eight - Danes. . .Back to Basics!!!
... Surrounded by a doublelayered membrane (nuclear enveloped) with large pores that allow materials to pass in and out of the nucleus. Contains chromatin – long tangles of DNA. ...
... Surrounded by a doublelayered membrane (nuclear enveloped) with large pores that allow materials to pass in and out of the nucleus. Contains chromatin – long tangles of DNA. ...
Notes on Unit 7A Cells
... might work together in an organ system, such as the digestive system. Organs are made up from special tissues. Tissues are made from cells, which do special things. We are multi-cellular because we are made from many, many cells. We use a microscope to look at cells. ...
... might work together in an organ system, such as the digestive system. Organs are made up from special tissues. Tissues are made from cells, which do special things. We are multi-cellular because we are made from many, many cells. We use a microscope to look at cells. ...
Organelle Sketch Function Cell Wall Cell Membrane Nucleus
... . What makes the surface of the “rough endoplasmic reticulum” rough? 10. Which organelle contains DNA and uses it to control the rest of the cell? 11. Why do plant cells need a cell wall? 12. What is meant by “selectively permeable”? ...
... . What makes the surface of the “rough endoplasmic reticulum” rough? 10. Which organelle contains DNA and uses it to control the rest of the cell? 11. Why do plant cells need a cell wall? 12. What is meant by “selectively permeable”? ...
Ch 4 Modern Bio Cell Biology Student copy The History of Cell
... II. Introduction to Cells a. Talk about the diversity of cells (intro) b. Cell Diversity i. Talk about the relationship of shape to function of cells. c. Cell size i. Describe the diversity of cell size ii. Why is surface area-to volume ratio important d. Basic Parts of a cell i. What is the plasma ...
... II. Introduction to Cells a. Talk about the diversity of cells (intro) b. Cell Diversity i. Talk about the relationship of shape to function of cells. c. Cell size i. Describe the diversity of cell size ii. Why is surface area-to volume ratio important d. Basic Parts of a cell i. What is the plasma ...
Cell Membrane Movement
... Because the cell is filled with salts, sugars, proteins, and other molecules, it will almost always be _________ to fresh _______. • If so, the osmotic pressure should produce a net _________ of water into the cell. As a result, the volume of the cell will _________ until the cell becomes swollen or ...
... Because the cell is filled with salts, sugars, proteins, and other molecules, it will almost always be _________ to fresh _______. • If so, the osmotic pressure should produce a net _________ of water into the cell. As a result, the volume of the cell will _________ until the cell becomes swollen or ...
Chapter 2 Cell Chemistry
... iii. Tertiary: “scribble” shape due to various bonds between R groups iv. Quaternary: two or more proteins, fibrous or globular D. Denaturation: breakage of bonds in protein, results in loss of function. High temperature and low pH (acidity) often denature proteins. ...
... iii. Tertiary: “scribble” shape due to various bonds between R groups iv. Quaternary: two or more proteins, fibrous or globular D. Denaturation: breakage of bonds in protein, results in loss of function. High temperature and low pH (acidity) often denature proteins. ...
Concepts IV Cell Structure and Function
... 1. Explain cell theory. 2. What is used to study cells? 3. Distinguish between eukaryotes and prokaryotes. 4. Describe the functions of the organelles: pages 175 – 181 Prentice Hall Biology or page 74 in HMH Biology Use notebook flashcards to do this. Include notebook page numbers here. 5. Identify ...
... 1. Explain cell theory. 2. What is used to study cells? 3. Distinguish between eukaryotes and prokaryotes. 4. Describe the functions of the organelles: pages 175 – 181 Prentice Hall Biology or page 74 in HMH Biology Use notebook flashcards to do this. Include notebook page numbers here. 5. Identify ...
Reading Guide
... 2. Define concentration gradient. Draw a membrane with a concentration gradient where the molecules would move from the inside of the cell to the outside of the cell. ...
... 2. Define concentration gradient. Draw a membrane with a concentration gradient where the molecules would move from the inside of the cell to the outside of the cell. ...
Organic Macromolecule Notes
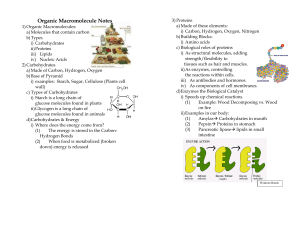
... a) Made of these elements: i) Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen b) Building Blocks: i) Amino acids c) Biological roles of proteins i) As structural molecules, adding strength/flexibility to tissues such as hair and muscles. ii) As enzymes, controlling the reactions within cells. iii) As antibodies ...
... a) Made of these elements: i) Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen b) Building Blocks: i) Amino acids c) Biological roles of proteins i) As structural molecules, adding strength/flexibility to tissues such as hair and muscles. ii) As enzymes, controlling the reactions within cells. iii) As antibodies ...
7.2 Cell Structure 196-207
... 8. How are contractile vacuoles different from other types of vacuoles? ...
... 8. How are contractile vacuoles different from other types of vacuoles? ...
Cell Structure and Function
... 2. This is combined in a special way to form glucose. 3. Bodies which pinch off vesicles at end. 4. Site of protein manufacture. 5. Keeps cell contents separate from external environment. 6. Strong substance that makes up cell walls. 7. Spaces between cells are called ____________ cellular spaces. 8 ...
... 2. This is combined in a special way to form glucose. 3. Bodies which pinch off vesicles at end. 4. Site of protein manufacture. 5. Keeps cell contents separate from external environment. 6. Strong substance that makes up cell walls. 7. Spaces between cells are called ____________ cellular spaces. 8 ...
3.2 Powerpoint
... • You are now going to make a study tool using paper plates. • Follow along while I show you how to fold the plate, use the directions as a guide. • Pass out plates ...
... • You are now going to make a study tool using paper plates. • Follow along while I show you how to fold the plate, use the directions as a guide. • Pass out plates ...
Topic: “Flow cytometric measurement of intracellular proteins”
... cells and B cells), monocytes, NK cells and granulocytes. 2. The presentation of antigen to T lymphocytes –MHC class I restriction; MHC class II restriction, characteristic of superantigens 3. Markers of the cell activation Basic literature: Janeway’s Immunobiology. available online at http://www.nc ...
... cells and B cells), monocytes, NK cells and granulocytes. 2. The presentation of antigen to T lymphocytes –MHC class I restriction; MHC class II restriction, characteristic of superantigens 3. Markers of the cell activation Basic literature: Janeway’s Immunobiology. available online at http://www.nc ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide
... _____ 9.One of the major differences in the cell division of prokaryotic cells compared to eukaryotic cell is that: a. cytokinesis does not occur in prokaryotic cells. b. genes are not replicated on chromosomes in prokaryotic cells. c. the duplicated chromosomes are attached to the nuclear membrane ...
... _____ 9.One of the major differences in the cell division of prokaryotic cells compared to eukaryotic cell is that: a. cytokinesis does not occur in prokaryotic cells. b. genes are not replicated on chromosomes in prokaryotic cells. c. the duplicated chromosomes are attached to the nuclear membrane ...
here - STAO
... Stimulants increase the activity of the nervous system, while depressants have the opposite effect. Cocaine and amphetamines are similar in structure to norepinephrine, and therefore have similar effects. Caffeine is also a stimulant, but its actions are a little different from the previous two exam ...
... Stimulants increase the activity of the nervous system, while depressants have the opposite effect. Cocaine and amphetamines are similar in structure to norepinephrine, and therefore have similar effects. Caffeine is also a stimulant, but its actions are a little different from the previous two exam ...
B1: Cell Structure
... 3. What is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? – Prokaryotes lack a nucleus as well as membrane enclosed structures (e.g. bacteria); – whereas eukaryotes have a nucleus and possess membrane enclosed structures ...
... 3. What is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? – Prokaryotes lack a nucleus as well as membrane enclosed structures (e.g. bacteria); – whereas eukaryotes have a nucleus and possess membrane enclosed structures ...
Document
... fibers of collagen or microtubules (~25nm in diameter, microns long) Proteins also can act as enzymes, “catalyzing” chemical reactions that break and reform covalent bonds ...
... fibers of collagen or microtubules (~25nm in diameter, microns long) Proteins also can act as enzymes, “catalyzing” chemical reactions that break and reform covalent bonds ...
cell organelles keynote ppt - Concordia Shanghai Teacher Websites
... responsible for storage of food, enzymes and wastes it is a sac-like structure in which digestion of nutrients occurs in animal cells they are small ...
... responsible for storage of food, enzymes and wastes it is a sac-like structure in which digestion of nutrients occurs in animal cells they are small ...
Muscle Study Questions
... Each bundle is enclosed in a sheath of fibrous connective tissue called fascia Each fascicle contains 12 to 1000s of individual muscle cells – called muscle fibers The outer surface of the whole muscle is covered with several more layers of fascia – at the ends all come together forming tendons ...
... Each bundle is enclosed in a sheath of fibrous connective tissue called fascia Each fascicle contains 12 to 1000s of individual muscle cells – called muscle fibers The outer surface of the whole muscle is covered with several more layers of fascia – at the ends all come together forming tendons ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.