Enhanced cell lysis
... Enabling rapid intracellular component identification, quantification or isolation Background Prior to the investigation of intracellular proteins and organelles cells need to be disrupted or lysed to release these components for study. Sonication is one method commonly used by researchers to disrup ...
... Enabling rapid intracellular component identification, quantification or isolation Background Prior to the investigation of intracellular proteins and organelles cells need to be disrupted or lysed to release these components for study. Sonication is one method commonly used by researchers to disrup ...
Second exam study questions
... olfactory receptors are there? How is olfactory information carried to and within the brain? 5.What is the functional anatomy of a taste receptor cell? What are the types of taste receptors and what they respond to? How do taste cells stimulate sensory neurons and how is taste information carried to ...
... olfactory receptors are there? How is olfactory information carried to and within the brain? 5.What is the functional anatomy of a taste receptor cell? What are the types of taste receptors and what they respond to? How do taste cells stimulate sensory neurons and how is taste information carried to ...
Plasma Membrane
... with the plasma membrane. This is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve ...
... with the plasma membrane. This is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve ...
CH3
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Cell Transport
... • Most marine fish die if transferred to freshwater. • When a drop of blood is mixed with distilled water, the blood cells burst. • Living plant tissues that had lost water become firm when supplied with water. ...
... • Most marine fish die if transferred to freshwater. • When a drop of blood is mixed with distilled water, the blood cells burst. • Living plant tissues that had lost water become firm when supplied with water. ...
Cell Organelles
... -only found in the nucleus, except when the nuclear membrane disappears during cell division. -contains DNA and proteins (histones) densely coiled together -only visible near the time of cell division -contains all the genetic material for the cell / organism Mitochondria -site of cellular respirati ...
... -only found in the nucleus, except when the nuclear membrane disappears during cell division. -contains DNA and proteins (histones) densely coiled together -only visible near the time of cell division -contains all the genetic material for the cell / organism Mitochondria -site of cellular respirati ...
013368718X_CH04_047-066.indd
... Active Transport The movement of materials against a concentration difference is called active transport. Active transport requires energy. Transport proteins that act like pumps use energy to move small molecules and ions across cell membranes. The bulk transport of large molecules and clumps of ma ...
... Active Transport The movement of materials against a concentration difference is called active transport. Active transport requires energy. Transport proteins that act like pumps use energy to move small molecules and ions across cell membranes. The bulk transport of large molecules and clumps of ma ...
Transcript
... b. There a subtle differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes but they are very conserved molecules. Both types consist of a large and small subunit consisting of multiple proteins. c. A common pool of subunits made in the nucleolus and transported into cytosol where they assemble aroun ...
... b. There a subtle differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes but they are very conserved molecules. Both types consist of a large and small subunit consisting of multiple proteins. c. A common pool of subunits made in the nucleolus and transported into cytosol where they assemble aroun ...
Sensation2011
... from the senses to the thalamus , then to the various areas in the brain. Remember Ethan in Sky High. He changes his body to slime. Solid form to liquid form. Change from one form of energy to another. ...
... from the senses to the thalamus , then to the various areas in the brain. Remember Ethan in Sky High. He changes his body to slime. Solid form to liquid form. Change from one form of energy to another. ...
Cell Transport
... through a selectively permeable membrane. • Isotonic – The concentration of solutes is the same inside and outside the cell • Hypotonic – solution has a lower solute concentration than the cell. • Hypertonic – solution has a higher concentration of solute than the cell ...
... through a selectively permeable membrane. • Isotonic – The concentration of solutes is the same inside and outside the cell • Hypotonic – solution has a lower solute concentration than the cell. • Hypertonic – solution has a higher concentration of solute than the cell ...
Cells are organized into.
... 34 When a sea urchin egg is removed from the ocean and placed in freshwater, the egg swells and bursts. Which of these causes water to enter the egg? F Coagulation Means to clump together – Incorrect G Sodium pump Sodium is not being moved – ...
... 34 When a sea urchin egg is removed from the ocean and placed in freshwater, the egg swells and bursts. Which of these causes water to enter the egg? F Coagulation Means to clump together – Incorrect G Sodium pump Sodium is not being moved – ...
Chapter 6
... • Common to all cells • Selective permeability - regulates what enters and leaves • Made of lipid bilayer • Various molecules are attached to it ...
... • Common to all cells • Selective permeability - regulates what enters and leaves • Made of lipid bilayer • Various molecules are attached to it ...
Homeostasis Student
... molecules that can’t pass through the membrane Either too large or not lipid-soluble Proteins in the membrane help push them through From high to low concentration The proteins will change their shape and this pushes the molecules through ...
... molecules that can’t pass through the membrane Either too large or not lipid-soluble Proteins in the membrane help push them through From high to low concentration The proteins will change their shape and this pushes the molecules through ...
THE NEuRoN - Big Picture
... The sheath is interrupted at regular intervals ( ‘nodes of Ranvier’), where the channels that generate the electrical signal are located. Myelin reduces leakage of electrical charge from the axon, resulting in a signal that rapidly jumps from one node of Ranvier to the next, speeding up the conducti ...
... The sheath is interrupted at regular intervals ( ‘nodes of Ranvier’), where the channels that generate the electrical signal are located. Myelin reduces leakage of electrical charge from the axon, resulting in a signal that rapidly jumps from one node of Ranvier to the next, speeding up the conducti ...
Big Picture
... much of the cell membrane. • Fats and Oils Fats and oils are lipids that store energy. When an organism has used up most of its carbohydrates, it can get energy from these lipids. ...
... much of the cell membrane. • Fats and Oils Fats and oils are lipids that store energy. When an organism has used up most of its carbohydrates, it can get energy from these lipids. ...
No Slide Title
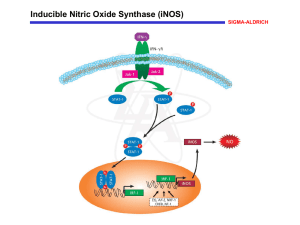
... the production of nitric oxide (NO) is central to this function. NO is generated by inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS, macNOS, Type II NOS) following exposure to certain cytokines, such as interferon- (IFN-). The IFN- receptor signals through the Janus kinase (JAK) family and signal transduce ...
... the production of nitric oxide (NO) is central to this function. NO is generated by inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS, macNOS, Type II NOS) following exposure to certain cytokines, such as interferon- (IFN-). The IFN- receptor signals through the Janus kinase (JAK) family and signal transduce ...
Physiology Lecture 1
... ● Target cells have receptors (proteins that bind specific signal molecules that cause the cell to respond). Each receptor binds to a specific hormone. • When a hormone binds to a receptor, binding triggers events that lead to changes within the cell. • Receptors can be found on the cell membrane, i ...
... ● Target cells have receptors (proteins that bind specific signal molecules that cause the cell to respond). Each receptor binds to a specific hormone. • When a hormone binds to a receptor, binding triggers events that lead to changes within the cell. • Receptors can be found on the cell membrane, i ...
Poor Primitive Prokaryotes
... Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus or any internal membrane-bound structures. Within these cells, membranes do not separate different areas from one another. Bacteria in the Kingdom Monera are prokaryotes. There are some universal structures that all bacteria have. Like every living organism, t ...
... Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus or any internal membrane-bound structures. Within these cells, membranes do not separate different areas from one another. Bacteria in the Kingdom Monera are prokaryotes. There are some universal structures that all bacteria have. Like every living organism, t ...
د. بشرى جبار Medical Biology Lecture 9 Round nucleus c
... cells that produce antibody molecules closely modeled after the receptors of the precursor B cell. Once released into the blood and lymph, these antibody molecules bind to the target antigen (foreign substance) and initiate its neutralization or destruction . ...
... cells that produce antibody molecules closely modeled after the receptors of the precursor B cell. Once released into the blood and lymph, these antibody molecules bind to the target antigen (foreign substance) and initiate its neutralization or destruction . ...
Reporting Category 1
... F. Water leaves the tubules of the kidney in response to the hypertonic fluid surrounding the tubules. G. During the process of digestion, digestive enzymes are excreted into the small intestine. H. White blood cells consume pathogens and cell debris at the site of an infection. J. Calcium is pumped ...
... F. Water leaves the tubules of the kidney in response to the hypertonic fluid surrounding the tubules. G. During the process of digestion, digestive enzymes are excreted into the small intestine. H. White blood cells consume pathogens and cell debris at the site of an infection. J. Calcium is pumped ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • All living things are made of cells. All cells have some structures in common, such as DNA. • Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. • Cells only come from already present cells (pre-existing). ...
... • All living things are made of cells. All cells have some structures in common, such as DNA. • Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. • Cells only come from already present cells (pre-existing). ...
Cell Biology Form and Function - This area is password protected
... consists of a liquid (called the cytosol that contains water, proteins and dissolved ions) and cell organelles. It is used to transport substances throughout the cell and create internal pressure and is where most chemical reactions occur. ...
... consists of a liquid (called the cytosol that contains water, proteins and dissolved ions) and cell organelles. It is used to transport substances throughout the cell and create internal pressure and is where most chemical reactions occur. ...
Cells (Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic)
... The nuclear membrane or sometimes called the nuclear envelope is a double-membrane structure.. Numerous pores occur in the envelope, allowing RNA and other chemicals to pass, but not DNA. ...
... The nuclear membrane or sometimes called the nuclear envelope is a double-membrane structure.. Numerous pores occur in the envelope, allowing RNA and other chemicals to pass, but not DNA. ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.