notes - UCSB College of Engineering
... These long polymers are the basis of information storage in living systems. Different sequences of the polymerized nucleotides encode different sets of information. Sequence contains information like a bar code. DNA is the source of genetic information; one DNA per cell. Called deoxyribonucleic acid ...
... These long polymers are the basis of information storage in living systems. Different sequences of the polymerized nucleotides encode different sets of information. Sequence contains information like a bar code. DNA is the source of genetic information; one DNA per cell. Called deoxyribonucleic acid ...
Chap 41 - Iowa State University
... 1. Nervous System is the response to changes in internal and external environments. What are the two categories the nervous system is broken into? Explain what each consists of. ...
... 1. Nervous System is the response to changes in internal and external environments. What are the two categories the nervous system is broken into? Explain what each consists of. ...
Bacteria are protected by a rigid cell wall composed of
... "nucleoid" refers to the region of the cytoplasm where chromosomal DNA is located, usually a singular, circularchromosome. Bacteria are usually singlecelled, except when they exist ...
... "nucleoid" refers to the region of the cytoplasm where chromosomal DNA is located, usually a singular, circularchromosome. Bacteria are usually singlecelled, except when they exist ...
Passive transport
... Channel proteins have a polar interior allowing polar molecules to pass through. Carrier proteins bind to a specific molecule to facilitate its passage. ...
... Channel proteins have a polar interior allowing polar molecules to pass through. Carrier proteins bind to a specific molecule to facilitate its passage. ...
10.4 Plant Cell Structure
... forms the boundary between cell walls. The cellulose molecules are found in microfibrils. ...
... forms the boundary between cell walls. The cellulose molecules are found in microfibrils. ...
Biology Chapter 4 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Shape shape is determined by its function Organization ...
... Shape shape is determined by its function Organization ...
CHAPTER 6 A TOUR OF THE CELL Learning objectives: A
... 1. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 2. Explain why there are both upper and lower limits to cell size. Be able to calculate the Surface Area to Volume ratio of a cube. 3. Explain the advantages of compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells. 4. Compare and contract plant and animal ...
... 1. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 2. Explain why there are both upper and lower limits to cell size. Be able to calculate the Surface Area to Volume ratio of a cube. 3. Explain the advantages of compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells. 4. Compare and contract plant and animal ...
1 Introduction to Neurobiology Rudolf Cardinal NST 1B
... is required to bring the neuron to threshold and fire an AP. However, if enough EPSPs arrive at the neuron and are close enough to each other in space and time (and overcome any inhibition from IPSPs) they may sum and trigger an AP. In this way the postsynaptic neuron can integrate information from ...
... is required to bring the neuron to threshold and fire an AP. However, if enough EPSPs arrive at the neuron and are close enough to each other in space and time (and overcome any inhibition from IPSPs) they may sum and trigger an AP. In this way the postsynaptic neuron can integrate information from ...
Dmca1A encodes voltage-gated calcium channels in
... Voltage-gated calcium channels are multimeric proteins containing pore forming -subunits that regulate the entry of calcium into excitable cells. There are three -subunit genes in Drosophila: Dmca1D, Dmca1A, and -1. Previous studies have demonstrated that Dmca1D forms functional calcium channel p ...
... Voltage-gated calcium channels are multimeric proteins containing pore forming -subunits that regulate the entry of calcium into excitable cells. There are three -subunit genes in Drosophila: Dmca1D, Dmca1A, and -1. Previous studies have demonstrated that Dmca1D forms functional calcium channel p ...
Complex carbohydrates
... from birch pollen, red areas show where surface structure has been conserved across the proteins. Given these two proteins' relative structural similarity to that of birch pollen, people allergic to birch pollen are more likely to also be allergic to apples than to celery. ...
... from birch pollen, red areas show where surface structure has been conserved across the proteins. Given these two proteins' relative structural similarity to that of birch pollen, people allergic to birch pollen are more likely to also be allergic to apples than to celery. ...
Cells
... • These organelles contain ___________ which is used in the “food making process”, or ________________, and give the plant a ________________color when exposed to light. Cell Membrane • The cell membrane is found in ...
... • These organelles contain ___________ which is used in the “food making process”, or ________________, and give the plant a ________________color when exposed to light. Cell Membrane • The cell membrane is found in ...
Name:___________________________ Date: ____________Period:_____
... carbohydrates to produce a small amount of ATP. 3. Factors that increase the rate of diffusion of molecules across a semi-permeable membrane are: ...
... carbohydrates to produce a small amount of ATP. 3. Factors that increase the rate of diffusion of molecules across a semi-permeable membrane are: ...
Slide ()
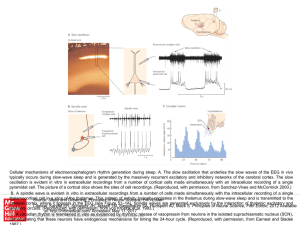
... oscillation is evident in vitro in extracellular recordings from a number of cortical cells made simultaneously with an intracellular recording of a single pyramidal cell. The picture of a cortical slice shows the sites of cell recordings. (Reproduced, with permission, from Sanchez-Vives and McCormi ...
... oscillation is evident in vitro in extracellular recordings from a number of cortical cells made simultaneously with an intracellular recording of a single pyramidal cell. The picture of a cortical slice shows the sites of cell recordings. (Reproduced, with permission, from Sanchez-Vives and McCormi ...
Cell Project
... and takes the players water when a time out is called and when the game is being played. ...
... and takes the players water when a time out is called and when the game is being played. ...
Video
... 1 Compound Light Microscope- Uses light and more than one lens to look at living cells (Can magnify up to 1500 times) 2 Scanning Electron Microscope- (SEM) sweeps a beam of electrons over the surface of the specimen causing electrons to be emitted from the specimen (3-D realistic pictures with magn ...
... 1 Compound Light Microscope- Uses light and more than one lens to look at living cells (Can magnify up to 1500 times) 2 Scanning Electron Microscope- (SEM) sweeps a beam of electrons over the surface of the specimen causing electrons to be emitted from the specimen (3-D realistic pictures with magn ...
A plant cell consists of many organelles. Each one of them plays its
... cytoplasm. It has enzymes which take molecules and break them down. This then allows individual organelles to use them when they need to. Plasma Membrane- a plasma membrane is found in all living cells. They regulate the passage of molecules in and out of cells. Plastids- the main function for a pla ...
... cytoplasm. It has enzymes which take molecules and break them down. This then allows individual organelles to use them when they need to. Plasma Membrane- a plasma membrane is found in all living cells. They regulate the passage of molecules in and out of cells. Plastids- the main function for a pla ...
VE-cadherin (C-19): sc-6458
... structure and morphogenesis. Cadherins each contain a large extracellular domain at the amino terminus, which is characterized by a series of five homologous repeats, the most distal of which is thought to be responsible for binding specificity. The relatively short carboxy terminal, intracellular d ...
... structure and morphogenesis. Cadherins each contain a large extracellular domain at the amino terminus, which is characterized by a series of five homologous repeats, the most distal of which is thought to be responsible for binding specificity. The relatively short carboxy terminal, intracellular d ...
Cell nucleus File
... as emerin and nesprin, bind to the cytoskeleton to provide structural support. Lamins are also found inside the nucleoplasm where they form another regular structure, known as the nucleoplasmic veil,[14] that is visible using fluorescence microscopy. The actual function of the veil is not clear, alt ...
... as emerin and nesprin, bind to the cytoskeleton to provide structural support. Lamins are also found inside the nucleoplasm where they form another regular structure, known as the nucleoplasmic veil,[14] that is visible using fluorescence microscopy. The actual function of the veil is not clear, alt ...
Recitation Worksheet 11
... 1. The gustatory system uses a labeled line model whereby each taste cell detects only one type of taste – for example, sweet is detected by taste cells that respond only to sweet, and each sweet taste cell is innervated only by neurons that carry sweet information. The olfactory system, however, us ...
... 1. The gustatory system uses a labeled line model whereby each taste cell detects only one type of taste – for example, sweet is detected by taste cells that respond only to sweet, and each sweet taste cell is innervated only by neurons that carry sweet information. The olfactory system, however, us ...
Chapter 7
... • Cells containing membrane-bound structures • Mostly multicellular with some exceptions such as algae and yeast • Ex: plants and animals ...
... • Cells containing membrane-bound structures • Mostly multicellular with some exceptions such as algae and yeast • Ex: plants and animals ...
Learning Guide: Origins of Life
... o Explain using an example how variations in the cell membrane lipid compositions can be an evolutionary adaptation o Membrane proteins are the mosaic part of the model. Describe each of the two main categories: integral proteins and peripheral proteins. o Membrane carbohydrates are important in cel ...
... o Explain using an example how variations in the cell membrane lipid compositions can be an evolutionary adaptation o Membrane proteins are the mosaic part of the model. Describe each of the two main categories: integral proteins and peripheral proteins. o Membrane carbohydrates are important in cel ...
Programmed Cell Death(Apoptosis)
... potentially harmful mutations, including cells with mutations that might lead to the development of cancer. During development, programmed cell death plays a key role by eliminating unwanted cells from a variety of tissues. Apoptosis is responsible for the elimination of larval tissues during amphib ...
... potentially harmful mutations, including cells with mutations that might lead to the development of cancer. During development, programmed cell death plays a key role by eliminating unwanted cells from a variety of tissues. Apoptosis is responsible for the elimination of larval tissues during amphib ...
Biology 3B-1 - secondary
... 2. Compare and contrast optimal point, optimal range, range of tolerance, and limit of tolerance Optimal point- the point where organisms function ...
... 2. Compare and contrast optimal point, optimal range, range of tolerance, and limit of tolerance Optimal point- the point where organisms function ...
File
... 6. Can plants (such as African violets) complete cytokinesis by using a cleavage furrow? Explain. 7. Is mitosis the same thing as Cytokinesis? Explain. 8. Imagine another cell mutation. This one allows the cell to ignore anchorage dependency. Discuss what might be the results of this mutation? 10. W ...
... 6. Can plants (such as African violets) complete cytokinesis by using a cleavage furrow? Explain. 7. Is mitosis the same thing as Cytokinesis? Explain. 8. Imagine another cell mutation. This one allows the cell to ignore anchorage dependency. Discuss what might be the results of this mutation? 10. W ...
P systems–based Modelling of Cellular Signalling Pathways
... reasonable in some circumstances but not in many cases due to internal structure and low numbers and non–uniform distributions of certain key molecules in the cell. While differential equations models may produce useful results under certain conditions, they provide a rather incomplete view of what ...
... reasonable in some circumstances but not in many cases due to internal structure and low numbers and non–uniform distributions of certain key molecules in the cell. While differential equations models may produce useful results under certain conditions, they provide a rather incomplete view of what ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.