Cell Structure and Function
... All About Cells! Cells are the most basic unit of life. What are some ways that cells carry out life processes? ...
... All About Cells! Cells are the most basic unit of life. What are some ways that cells carry out life processes? ...
Unit 5 Anatomy and Physiology Cells
... Cells - the facts • The human body is made up of millions of tiny cells • These can only be seen under a microscope • They appear in many different shapes and sizes and have different functions • Each cell has a nucleus which contains the genetic coding called DNA • Cells cannot function by themsel ...
... Cells - the facts • The human body is made up of millions of tiny cells • These can only be seen under a microscope • They appear in many different shapes and sizes and have different functions • Each cell has a nucleus which contains the genetic coding called DNA • Cells cannot function by themsel ...
cell_structure_tt
... A structure consisting of protein fibres found in eukaryotic cells during cell division. Chromosomes become attached to the spindle at their centromeres, and spindle fibres guide the movement of chromosomes to opposite end of the cell at telophase ...
... A structure consisting of protein fibres found in eukaryotic cells during cell division. Chromosomes become attached to the spindle at their centromeres, and spindle fibres guide the movement of chromosomes to opposite end of the cell at telophase ...
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
... 4. There is compelling evidence that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once primitive bacterial cells. This evidence is described in the endosymbiotic theory. Symbiosis occurs when two different species benefit from living and working together. When one organism actually lives inside the other it's ...
... 4. There is compelling evidence that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once primitive bacterial cells. This evidence is described in the endosymbiotic theory. Symbiosis occurs when two different species benefit from living and working together. When one organism actually lives inside the other it's ...
UNIT 2 CELLS AND SYSTEMS
... DIFFUSION- the movement of particles in liquids and gases from an area of higher concentration to and area of lower concentration (spreading out process) OSMOSIS- the diffusion of a solvent through a selectively permeable membrane VASCULAR TISSUES- tissues found in plants that connect the roots to t ...
... DIFFUSION- the movement of particles in liquids and gases from an area of higher concentration to and area of lower concentration (spreading out process) OSMOSIS- the diffusion of a solvent through a selectively permeable membrane VASCULAR TISSUES- tissues found in plants that connect the roots to t ...
ACHAEAN- One of two prokaryote domains that includes organisms
... ACHAEAN- One of two prokaryote domains that includes organisms with different plasma membranes and ribosomes than bacteria BACTERIA- One of two prokaryote domains that includes organisms with different plasma membranes and ribosomes than archaeans BIOLOGY- the study of life, living things, and the c ...
... ACHAEAN- One of two prokaryote domains that includes organisms with different plasma membranes and ribosomes than bacteria BACTERIA- One of two prokaryote domains that includes organisms with different plasma membranes and ribosomes than archaeans BIOLOGY- the study of life, living things, and the c ...
Cellular Organization and Cell Theory Notes
... necessary material for life. Unicellular – organisms that are composed of only one cell Multi-cellular – organisms that are composed of more than one cell ...
... necessary material for life. Unicellular – organisms that are composed of only one cell Multi-cellular – organisms that are composed of more than one cell ...
Mitosis - Spanish Point Biology
... • how the cytoplasm divides in animal cells • how the cytoplasm divides in plant cells • the function of mitosis in single celled ...
... • how the cytoplasm divides in animal cells • how the cytoplasm divides in plant cells • the function of mitosis in single celled ...
Animal Cell
... Forms a boundary that separates the cell from its environment. It controls what comes in and out of the cell. In both plant and animal cells ...
... Forms a boundary that separates the cell from its environment. It controls what comes in and out of the cell. In both plant and animal cells ...
Inside the Cell - Riverdale Middle School
... When specialized cells work together to perform a specific function, it is called a tissue. Muscle cells work together to form muscle tissue. When groups of tissues work together to perform a specific function, it is called an organ. Muscle tissue and other types of tissue work together to form an ...
... When specialized cells work together to perform a specific function, it is called a tissue. Muscle cells work together to form muscle tissue. When groups of tissues work together to perform a specific function, it is called an organ. Muscle tissue and other types of tissue work together to form an ...
Life Science Semester Review Part 2 NAME
... 36. Which of the following correctly matches an organelle with its “Cell City” function? a. Golgi Apparatus to Post office b. Cell wall to Mayer c. Mitochondria to solar panel 37. How are plant cells different from animal cells? a. Plant cells have cell walls. b. Animal cells have cell membranes. c. ...
... 36. Which of the following correctly matches an organelle with its “Cell City” function? a. Golgi Apparatus to Post office b. Cell wall to Mayer c. Mitochondria to solar panel 37. How are plant cells different from animal cells? a. Plant cells have cell walls. b. Animal cells have cell membranes. c. ...
Mitosis - Mahopac Voyagers!
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
Exporter la page en pdf
... Asymmetric cell division generates cell fate diversity during development and adult life. Recent findings have demonstrated that during stem cell divisions, the movement of centrosomes is asymmetric in prophase and that such asymmetry participates in mitotic spindle orientation and cell polarization. ...
... Asymmetric cell division generates cell fate diversity during development and adult life. Recent findings have demonstrated that during stem cell divisions, the movement of centrosomes is asymmetric in prophase and that such asymmetry participates in mitotic spindle orientation and cell polarization. ...
Due to Weather Revised Oct 10-14
... Standard H.B.2: The student will demonstrate the understanding that the essential functions of life take place within cells or systems of cells. H.B.2A. Conceptual Understanding: The essential functions of a cell involve chemical reactions that take place between many different types of molecules (i ...
... Standard H.B.2: The student will demonstrate the understanding that the essential functions of life take place within cells or systems of cells. H.B.2A. Conceptual Understanding: The essential functions of a cell involve chemical reactions that take place between many different types of molecules (i ...
First Six Weeks Test Corrections The cell membrane controls what
... 8. Carbon is considered to be an element and carbon dioxide is considered a compound. Carbon dioxide has two different elements. 9. Organic means made from living material. 10. Carbon is found in all organic compounds. 11. Na, Fe, K and C are elements ...
... 8. Carbon is considered to be an element and carbon dioxide is considered a compound. Carbon dioxide has two different elements. 9. Organic means made from living material. 10. Carbon is found in all organic compounds. 11. Na, Fe, K and C are elements ...
caenorhabditis elegans
... Caenorhabditis elegans - Gastulation Gastrulation in C. elegans is not as overtly dramatic as in many other animal embryos, since cells move only small distances, generally single cell diameters, and the blastocoel space is small. Despite this, gastrulation plays an essential role in development, in ...
... Caenorhabditis elegans - Gastulation Gastrulation in C. elegans is not as overtly dramatic as in many other animal embryos, since cells move only small distances, generally single cell diameters, and the blastocoel space is small. Despite this, gastrulation plays an essential role in development, in ...
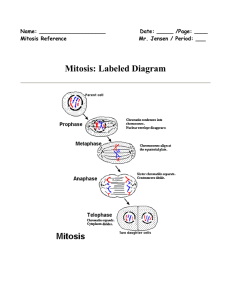
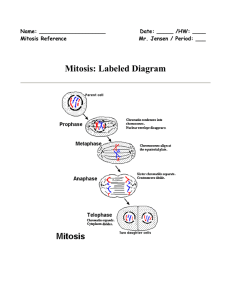
Mitosis: Labeled Diagram
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
ANATOMI
... Consists of newly formed cells, small sized, with thin cell wall and dense protoplasm, box shaped and having six surfaces, a large nucleus and small vacuoles Cells are always actively dividing When mature, the cell shape differs according to the cell function, while the vacuoles increase in size ...
... Consists of newly formed cells, small sized, with thin cell wall and dense protoplasm, box shaped and having six surfaces, a large nucleus and small vacuoles Cells are always actively dividing When mature, the cell shape differs according to the cell function, while the vacuoles increase in size ...
The Cell
... 1. In 1665, Robert Hooke used a simple microscope to view thin slices of cork from plants. This was one of the first viewings of the cell. 2. Cells are the basic unit of life. 3. Anton van Leeuwenhoek was one of the first people to identify and observe that there were life forms found in water. 4. T ...
... 1. In 1665, Robert Hooke used a simple microscope to view thin slices of cork from plants. This was one of the first viewings of the cell. 2. Cells are the basic unit of life. 3. Anton van Leeuwenhoek was one of the first people to identify and observe that there were life forms found in water. 4. T ...
Ch 7 Cell Overview and Theory
... *pili are usually longer and fewer than fimbriae, both function for attachment and recognition of host cells (or (sexual reproduction) ...
... *pili are usually longer and fewer than fimbriae, both function for attachment and recognition of host cells (or (sexual reproduction) ...
ANATOMI
... Consists of newly formed cells, small sized, with thin cell wall and dense protoplasm, box shaped and having six surfaces, a large nucleus and small vacuoles Cells are always actively dividing When mature, the cell shape differs according to the cell function, while the vacuoles increase in size ...
... Consists of newly formed cells, small sized, with thin cell wall and dense protoplasm, box shaped and having six surfaces, a large nucleus and small vacuoles Cells are always actively dividing When mature, the cell shape differs according to the cell function, while the vacuoles increase in size ...
Archaea
... heterotrophic procaryotes autotrophic procaryotes eucaryotic cells colonial cells multicellular organisms ...
... heterotrophic procaryotes autotrophic procaryotes eucaryotic cells colonial cells multicellular organisms ...
Tissue engineering

Tissue engineering is the use of a combination of cells, engineering and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to improve or replace biological functions. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field in its own right.While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e., bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. The term has also been applied to efforts to perform specific biochemical functions using cells within an artificially-created support system (e.g. an artificial pancreas, or a bio artificial liver). The term regenerative medicine is often used synonymously with tissue engineering, although those involved in regenerative medicine place more emphasis on the use of stem cells or progenitor cells to produce tissues.